This 3-page publication provides a brief overview of resistance to gastrointestinal nematode infections in Florida Native sheep. Written by Zaira M. Estrada Reyes, Owen Rae, Carol Postley, and Raluca G. Mateescu, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences, August 2020.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an361
Category: Agriculture
Use of Recycled Potting Medium for Containerized Production of Squash
Vegetable growers are keen on cost-cutting measures to increase profitability. Containerized vegetable production can be done in a shade-house or garden, and it often requires commercial potting media. Although expensive, potting media are lightweight and provide high water- and nutrient-holding capacities, and thus they are widely used by growers. Growers often discard or compost the potting media after a single season due to issues such as diseases, pests, and weeds. However, old potting media could be reused for containerized production if appropriately sterilized and amended with fertilizer salts. The current study was conducted to determine the feasibility of using sterilized recycled potting medium amended with fertilizer salts for containerized production of squash. This new 4-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department was written by Marie Dorval, Riphine Mainviel, Vincent Michael, Yuqing Fu, Bala Rathinasabapathi, and Geoffrey Meru.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1404
Transitioning from Conventional to Organic Farming Using Conservation Tillage
Organic farming is one of the fastest-growing segments of the agricultural industry in the United States and in Florida. Conservation tillage is often employed to reduce soil erosion, improve physical and biological properties of soil, and increase water use efficiency. This 5-page article aims to provide recommendations to row crop farmers who wish to implement conservation tillage practices during their transition to a certified organic system. Written by D. L. Wright, J. Moyer, D. Treadwell, I. M. Small, and S. George, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, revised November 2020.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag246
How Are Our Future Agriculture and Natural Resources Projected under Varying Climate?
This 8-page article explains how agriculture and natural resources may respond to projected future climate and how climate projections can be useful in developing management plans for the improved sustainability of Florida's agriculture and natural resources. It also aims to help increase the public awareness of climate change impacts on Florida and improve understanding of the connections among climate, agriculture, and natural resources. Written by Young Gu Her, Ashley Smyth, Zachary Brym, and Elias Bassil, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, September 2020.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae545
Planning for a Successful Commercial Subtropical/Tropical Fruit Grove
Planning is the key to successful grove establishment, maintenance, and production. Developing a detailed infrastructure description and plan, cultural program, and financial and marketing plan for a new or existing grove with a new fruit crop will save you time and money and help minimize mistakes. Prospective growers should compile and analyze information needed to select a grove site, establish the needed infrastructure, and develop maintenance plans for the plants and how the production will be marketed. This new 15-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department presents an outline of the type of information growers need when establishing a tropical fruit grove or contemplating management or modification of an existing grove. Written by Jonathan Crane, Yuncong Li, Edward Evans, Fredy Ballen, and Jeff Wasielewski.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1387
Bagasse: A Potential Organic Soil Amendment Used in Sugarcane Production
Bagasse is an agricultural by-product derived from the sugarcane milling process. It is a dry and fibrous residue left after the extraction of sugar juice from sugarcane. This 5-page document is a preliminary investigation into the possible effects of using bagasse as a soil amendment. Written by Jehangir H. Bhadha, Nan Xu, Raju Khatiwada, Stewart Swanson, and Chris LaBorde, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences, August 2020.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss690
Implementation of Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation in Florida Tomato Production
Anaerobic soil disinfestation (ASD) is a relatively new technique that appears to be a promising tool for soilborne pest management and crop production improvement. This new 5-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department is intended to introduce ASD for Florida vegetable growers. Written by Bodh R. Paudel, Francesco Di Gioia, Qiang Zhu, Xin Zhao, Monica Ozores-Hampton, Marilyn E. Swisher, Kaylene Sattanno, Jason C. Hong, and Erin N. Rosskopf.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1345
Bok Choy, an Asian Leafy Green Vegetable Emerging in Florida
Asian vegetable crops are rapidly expanding in Florida in the last decade due to their health benefits combined with their high profitability. These crops can help increase vegetable growers’ income and diversify Florida’s crop production, and they are new to most Floridians. This new 5-page article provides a general overview of bok choy for vegetable growers, crop consultants, certified crop advisors, Extension agents, and graduate students. Written by Hai Liu and Guodong Liu and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1337
Ecosystem Services Provided by Grass-Legume Pastures
Grasslands produce far more than beef and milk. They provide ecosystem services that benefit people and the environment. This new 3-page document discusses how integrating forage legumes into grasslands enhances their capacity to provide ecosystem services, such as C sequestration, habitat for wildlife and pollinators, water catchment and purification, and nutrient cycling. Written by Jose Dubeux, Jr., Lynn Sollenberger, Mark Mauldin, and Liza Garcia, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, October 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag423
Improving, Restoring, and Managing Natural Resources on Rural Properties in Florida: Sources of Financial Assistance
Interested in conserving natural resources, such as wildlife habitat, or protecting the agricultural heritage of your land? Both federal and state governments have technical and financial assistance programs to help rural landowners achieve natural resource goals. These challenges are addressed through land rentals, technical assistance, cost-shares, and incentive payments and include both time-limited and permanent land-use options.
This 8-page fact sheet written by Chris Demers, Martin B. Main and Mark E. Hostetler and published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation informs landowners about government programs available to help conserve natural resources.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr156
Implementing the Four Rs (4Rs) in Nutrient Stewardship for Tomato Production
 Fertilization plays a critical role in tomato production across the state of Florida. However, appropriate fertilization management depends on four major components (4Rs): right source, right rate, right placement, and right timing. Farming practices that follow the 4Rs can provide nutrients for optimal tomato productivity while minimizing the risk of nutrient losses and adverse environmental effects, both of which are important to the development of agricultural sustainability. This 6-page fact sheet discusses the 4Rs as well as conventional dry source fertilizers, controlled-release or slow-release source fertilizers, and liquid source fertilizers. Written by Qingren Wang, Guodong Liu, Kelly Morgan, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2015.
Fertilization plays a critical role in tomato production across the state of Florida. However, appropriate fertilization management depends on four major components (4Rs): right source, right rate, right placement, and right timing. Farming practices that follow the 4Rs can provide nutrients for optimal tomato productivity while minimizing the risk of nutrient losses and adverse environmental effects, both of which are important to the development of agricultural sustainability. This 6-page fact sheet discusses the 4Rs as well as conventional dry source fertilizers, controlled-release or slow-release source fertilizers, and liquid source fertilizers. Written by Qingren Wang, Guodong Liu, Kelly Morgan, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1269
What Else Can Surface Water Buffer Systems Do?: Exploring Multiple Ecosystem Services
 As society confronts the consequences of global warming, deteriorating water quality, and impoverished biodiversity, there is a growing urgency to develop and expand water buffers' multifunctional ecosystem services. However, limited information is available on other potential co-benefits associated with the use of buffers, particularly VFSs. This 5-page fact sheet provides information on buffers' multiple ecosystem benefits, such as niche products production, carbon sequestration, and flood risk mitigation, as well as recommendations on future research needs necessary to enhance multiple ecosystem services and benefits of buffers. Written by Lei Wu, Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2015.
As society confronts the consequences of global warming, deteriorating water quality, and impoverished biodiversity, there is a growing urgency to develop and expand water buffers' multifunctional ecosystem services. However, limited information is available on other potential co-benefits associated with the use of buffers, particularly VFSs. This 5-page fact sheet provides information on buffers' multiple ecosystem benefits, such as niche products production, carbon sequestration, and flood risk mitigation, as well as recommendations on future research needs necessary to enhance multiple ecosystem services and benefits of buffers. Written by Lei Wu, Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss647
A Practical Guide for Aquaponics as an Alternative Enterprise
 Aquaponics is an intensive sustainable agricultural production system that connects hydroponic and aquaculture systems to produce multiple cash crops with reduced water and fertilizer inputs. It is highly suited for small farm producers targeting local markets and agritourism opportunities. This 10-page fact sheet was written by Richard Tyson and Eric Simonne, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, September 2014.
Aquaponics is an intensive sustainable agricultural production system that connects hydroponic and aquaculture systems to produce multiple cash crops with reduced water and fertilizer inputs. It is highly suited for small farm producers targeting local markets and agritourism opportunities. This 10-page fact sheet was written by Richard Tyson and Eric Simonne, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1252
Introduction to Organic Crop Production
 Organic farming can generally be described as a method of production that utilizes non-synthetic inputs and emphasizes biological and ecological process to improve soil quality, manage soil fertility, and optimize pest management. This 16-page fact sheet is written for commercial producers who are transitioning to or beginning organic production. Written by D.D. Treadwell, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2014.
Organic farming can generally be described as a method of production that utilizes non-synthetic inputs and emphasizes biological and ecological process to improve soil quality, manage soil fertility, and optimize pest management. This 16-page fact sheet is written for commercial producers who are transitioning to or beginning organic production. Written by D.D. Treadwell, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/cv118
Opciones de gestion agronomica para la variabilidad y para el cambio climatico: El riego localizado (HS1212)
 Esta publicación se enfoca en el uso del riego localizado para mejorar los sistemas de producción. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Lincoln Zotarelli, Clyde Fraisse, and Daniel Dourte, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, January 2013.
Esta publicación se enfoca en el uso del riego localizado para mejorar los sistemas de producción. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Lincoln Zotarelli, Clyde Fraisse, and Daniel Dourte, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1212
Pretreatment of Ligno-cellulosic Biomass for Biofuels and Bioproducts (AE495)
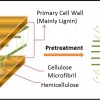 This 4-page fact sheet discusses bioethanol as a renewable form of energy, explaining the importance of using ligno-cellulosic biomass to produce biofuels. It describes the pretreatment step in producing biofuels and the need for more research into this step so that ligno-cellulosic biofuels can be produced cheaply and efficiently at a commercial scale. Written by Zhaohui Tong, Nusheng Cheng, and Pratap Pullammanappallil, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, January 2013.
This 4-page fact sheet discusses bioethanol as a renewable form of energy, explaining the importance of using ligno-cellulosic biomass to produce biofuels. It describes the pretreatment step in producing biofuels and the need for more research into this step so that ligno-cellulosic biofuels can be produced cheaply and efficiently at a commercial scale. Written by Zhaohui Tong, Nusheng Cheng, and Pratap Pullammanappallil, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae495
Cultivos en asocio, diversidad de cultivos y manejo integrado de plagas (ENY862S/IN932)
 El cultivo en asocio (o cultivo intercalado) es una práctica en donde se siembran diversos cultivos en un mismo campo. Adicionalmente plantas que no son cultivos, tales como las malezas, cultivos rastreros o de cobertura, así como plantas del hábitat, se pueden combinar en el espacio y tiempo para influir en el número de plagas o artrópodos benéficos en un cultivo principal. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Hugh Smith y Oscar Liburd. Traducido por Ana Lucrecia MacVean, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, June 2012.
El cultivo en asocio (o cultivo intercalado) es una práctica en donde se siembran diversos cultivos en un mismo campo. Adicionalmente plantas que no son cultivos, tales como las malezas, cultivos rastreros o de cobertura, así como plantas del hábitat, se pueden combinar en el espacio y tiempo para influir en el número de plagas o artrópodos benéficos en un cultivo principal. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Hugh Smith y Oscar Liburd. Traducido por Ana Lucrecia MacVean, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, June 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in932
Agricultural Management Options for Climate Variability and Change: Sensor-Based, Variable-Rate Nitrogen Management (AE487)
 Nitrogen fertilizer cost represents about 10%–15% of total farm costs for corn, cotton, and wheat in the Southeastern United States. The efficiency of nitrogen use can be highly variable for producers, so a sensor-based, variable-rate nitrogen application (SVNA) system has been developed for irrigated and dryland row crops to reduce production costs. Using sensor-based N application, there is a minimum 20% reduction in N usage. If that rate reduction were applied to all the cotton, corn, and wheat grown in the United States, CO2 emissions from N fertilizer production would be decreased by 2.7 million tons.
Nitrogen fertilizer cost represents about 10%–15% of total farm costs for corn, cotton, and wheat in the Southeastern United States. The efficiency of nitrogen use can be highly variable for producers, so a sensor-based, variable-rate nitrogen application (SVNA) system has been developed for irrigated and dryland row crops to reduce production costs. Using sensor-based N application, there is a minimum 20% reduction in N usage. If that rate reduction were applied to all the cotton, corn, and wheat grown in the United States, CO2 emissions from N fertilizer production would be decreased by 2.7 million tons.
This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wesley Porter, Ahmad Khalilian, Daniel Dourte, and Clyde Fraisse, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, July 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae487
Agricultural Management Options for Climate Variability and Change: Conservation Tillage (AE486)
 This 4-page fact sheet focuses on the use of conservation tillage in crop production systems as a strategy to minimize the risks associated with climate variability and change and to improve resource-use efficiency. Written by Kip Balkcom, Leah Duzy, Daniel Dourte, and Clyde Fraisse, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, June 2012.
This 4-page fact sheet focuses on the use of conservation tillage in crop production systems as a strategy to minimize the risks associated with climate variability and change and to improve resource-use efficiency. Written by Kip Balkcom, Leah Duzy, Daniel Dourte, and Clyde Fraisse, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, June 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae486
Intercropping, Crop Diversity and Pest Management (ENY862/IN922)
Growing different crops in the same field and/or planting different crops on the same plot during different times of the year can reduce insect pest populations, increasing beneficial insects, and suppress weeds. In addition, non-crop plants such as weeds, cover crops, and habitat plantings can be combined in space and time to influence numbers of pest and beneficial arthropods on the main crop. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Hugh A. Smith and Oscar E. Liburd, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, February 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in922









