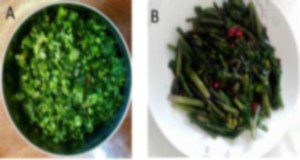
Vegetable amaranth is a beautiful and nutritious vegetable in the family Amaranthaceae. This vegetable has been cultivated in China for more than 400 years and has been introduced to several US states, such as Mississippi and Missouri. Florida’s mild climate combined with amaranth’s exceptional taste, nutrients, and colorful foliage suggest amaranth is a potential crop for commercial production for Florida. This new 7-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department is intended to provide Florida growers with a production guide for vegetable amaranth to enhance its competitiveness and boost the economy by introducing this potential cash crop to growers. Written by Yuheng Qiu and Guodong Liu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1407
Tag: Guodong Liu
Chinese Mustard Cultivation Guide for Florida
Chinese mustard is a nutritious leafy vegetable in the family Brassicaceae. Chinese mustard also goes by many common names, such as brown mustard, mustard greens, leaf mustard, Indian mustard, Oriental mustard, and vegetable mustard. Although it is considered a weed in a few states, such as Michigan, this species is not listed as invasive in Florida and has been cultivated in several counties, including Levy, Palm Beach, and Miami-Dade. This new 8-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department provides a short cultivation guide as well as information on the uses and marketability of Chinese mustard. Written by Yuheng Qiu, Mary Dixon, and Guodong Liu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1402
Tomato Production in Florida Using Fertigation Technology
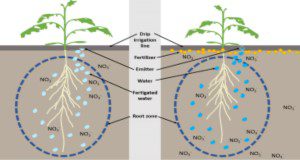
Tomato is in high demand because of its taste and health benefits. In Florida, tomato is the number one vegetable crop in terms of both acreage and value. Because of its high value and wide acreage, it is important for tomato production to be efficient in its water and nutrient use, which may be improved through fertigation practices. Therefore, the objective of this new 7-page article is to disseminate research-based methods of tomato production utilizing fertigation to enhance yield and nutrient use efficiency. Written by Mary Dixon and Guodong Liu, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1392
Goji Berry: a Novel Nutraceutical “Superfruit” for Florida Master Gardeners
Goji berries have been used in both fresh and processed forms for food and medicine for more than 4,000 years in China. The goji berry fruit is known as a “superfruit” thanks to its high levels of vitamins and minerals, as well as other medicinal benefits recognized in many countries around the world. Most of Florida’s climate is favorable for goji berry, and a few Florida growers have cultivated it for years. This species can tolerate infertile and unfavorable growth conditions, and the prominent health benefits of this crop may be highly profitable for Florida growers. The objective of this new 7-page article is to provide a general overview of how the goji berry can be grown in Florida. Written by Yujie Jiao and Guodong Liu, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1391
Leek Cultivation Guide for Florida
Leek (Allium porrum L.) is a member of Amaryllidaceae, a family with ornamental crops, like amaryllis, and with vegetable crops, like onion. Leek is a highly demanded vegetable because of its flavor and nutrient content. Although there is great potential for leek to be grown commercially in Florida due to demand and appropriate climatic conditions, the United States does not currently produce a significant quantity of leek compared to countries such as Indonesia, Turkey, and China. This new 7-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, written by Mary Dixon and Guodong Liu, provides a basic guide to cultivation of leek in Florida, as well as information on its agricultural, culinary, and medicinal uses.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1388
Implementing the Five Rs of Nutrient Stewardship for Fertigation in Florida’s Vegetable Production
The five Rs of nutrient stewardship is a mnemonic device used to emphasize accuracy and precision for nutrient management so as to apply the (1) right source of fertilizer at the (2) right rate at the (3) right time in the (4) right place with the (5) right irrigation. Because the majority of Florida’s soils are sandy, this fifth R is imperative for sustainable nutrient management for commercial crop production. These main points of nutrient management (source, rate, time, place, irrigation) may help enhance sustainability by reducing pollution by eutrophication, nitrogen loss through ammonia volatilization, and climate change from soil greenhouse gas emission. This new 8-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department was written by Mary Dixon and Guodong Liu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1386
Production Guide for Choy Sum: An Emerging Asian Vegetable in Florida
Choy sum, also known as Chinese flowering cabbage, is a leafy vegetable that has been widely cultivated in southern China for more than 1,000 years, and is currently cultivated and consumed by a growing population in the western world. This new 5-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, written by Yanlin Wang and Guodong Liu, provides a brief overview of choy sum and its cultivation, as well as some suggestions for how to include it in a meal.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1380
Daikon Radish Cultivation Guide for Florida
Daikon radish is a versatile vegetable crop in the mustard family. It produces a large, white, cylindrical fleshy root weighing up to 4-7 lb. Daikon radish is an especially common vegetable in Asia, particularly Japan, and it tends to be less spicy than other garden types of radish. This new 7-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department provides a primer on cultivation of daikon in Florida, including sections on propagation, growing conditions, pests and diseases, and agricultural, culinary, and medicinal uses. Written by Mary Dixon and Guodong Liu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1370
Florida Cultivation Guide for Malabar Spinach
Malabar spinach (Basella spp.) is a nutritious vegetable in the family Basellaceae. Malabar spinach goes by many names, including Indian spinach, Ceylon spinach, vine spinach, and climbing spinach. Malabar spinach has long been established in cultivation in China and India. This spinach is a novel crop to Florida and is currently grown only for niche markets. However, Florida’s suitable climate coupled with Malabar spinach’s great taste and nutritional quality suggest that this crop has great potential for commercial cultivation. This new 8-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department describes in brief how to grow Malabar spinach, manage pests, harvest, and market it. Written by Yuheng Qiu and Guodong Liu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1371
Fertigation via Center Pivot Irrigation for Commercial Potato Production in Florida
Potatoes are an important crop in the United States, and Florida is ranked the 7th producer nationwide for potato production. In Florida, potatoes are mainly planted on sandy soils with low nutrient- and water-holding capacities. Nitrogen is the most limiting nutrient in these soils. Adopting efficient fertilization methods such as fertigation is imperative for minimizing leaching and improving use efficiency of nitrogen. This new 12-page article provides step-by-step guidelines for fertigation practices for commercial potato production. Written by Xiangju Fu, Guodong Liu, Lincoln Zotarelli, Steven Sargent, Kati Migliaccio, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1361
Bok Choy, an Asian Leafy Green Vegetable Emerging in Florida
Asian vegetable crops are rapidly expanding in Florida in the last decade due to their health benefits combined with their high profitability. These crops can help increase vegetable growers’ income and diversify Florida’s crop production, and they are new to most Floridians. This new 5-page article provides a general overview of bok choy for vegetable growers, crop consultants, certified crop advisors, Extension agents, and graduate students. Written by Hai Liu and Guodong Liu and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1337
UF/IFAS Standardized Nutrient Recommendations for Vegetable Crop Production in Florida
Soil testing is a scientific tool for effective nutrient management that provides an estimate or an index of the available nutrient-supplying capacity of the soil. This 9-page publication presents the fertilization recommendations for vegetable crops based on soil tests performed by the IFAS Extension Soil Testing Laboratory (ESTL). Written by Rao Mylavarapu, George Hochmuth, and Guodong Liu and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences, December 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/cv002
Luffa: an Asian Vegetable Emerging in Florida
Luffa is the genus name of several tropical and subtropical plants in the cucumber family. Alternatively spelled “Loofa” or “Loofah,” the name is derived from the plant’s use as a material for sponges and dish cloths for bathing and cleaning dishes. This six page fact sheet describes the two types of Luffa, how to cultivate them, and what they can be used for. Written by Yucong Xie, Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, and Kati Migliaccio and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1285
Pond Apple: A Tree Species Adapted to Salt Stresses

Soil salinity is a naturally ocurring problem for growers, gardeners, and homeowners in Florida. As sea-levels rise, seawater intrusion causes salt stress to plants grown in coastal lowland areas. This three-page fact sheet introduces a salt-tolerant species, pond apple (Annona glabra L.), which has great potential to be used in high-salinity coastal landscapes. Written by Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, Kimberly Moore, and Kim Gabel and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1281
How to Chemigate Salinity-Stressed Plants with Hydrogen Peroxide to Increase Survival and Growth Rates
Man-made activities can induce climate change and global sea-level rise, posing threats to the survival and growth of coastal vegetation in Florida. This three-page fact sheet explains how to ensure plant survival and facilitate the growth of coastal vegetation threatened by sea-level rise and the resulting oxygen deficiencies and saline stresses. Written by Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, Kimberly Moore, Kim Gabel, Lei Wu, and Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1280
Tong Hao: an Asian Vegetable Emerging in Florida

Tong Hao (Glebionis coronaria) is a member of the daisy family and therefore a relative of lettuce. It is an important vegetable in Asian communities. Grown in China for more than 900 years, Tong Hao is a branched annual leafy herb that can be cooked and eaten. This four-page fact sheet provides background information about Tong Hao, including information on growing, harvesting, and cooking it. Written by Guodong Liu, Qingren Wang, Bonnie Wells, Yuncong Li, and David Dinkins, and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1276
Practices to Minimize Flooding Damage to Commercial Vegetable Production

Flooding is a major risk for commercial vegetable production in south Florida, especially in the south Dade County area. Flooding causes oxygen deficiency, or hypoxic stress, causing the plants to produce less energy. This shortage in energy prevents the absorption of nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. This four-page fact sheet discusses several different management practices for overcoming flood damage, including the use of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers, oxygen fertilizers, growth regulators, and fungicides. Written by Goudong Liu, Yuncong Li, and Xiangju Fu, and published by the Soil and Water Science Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss425
Implementing the Four Rs (4Rs) in Nutrient Stewardship for Tomato Production
 Fertilization plays a critical role in tomato production across the state of Florida. However, appropriate fertilization management depends on four major components (4Rs): right source, right rate, right placement, and right timing. Farming practices that follow the 4Rs can provide nutrients for optimal tomato productivity while minimizing the risk of nutrient losses and adverse environmental effects, both of which are important to the development of agricultural sustainability. This 6-page fact sheet discusses the 4Rs as well as conventional dry source fertilizers, controlled-release or slow-release source fertilizers, and liquid source fertilizers. Written by Qingren Wang, Guodong Liu, Kelly Morgan, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2015.
Fertilization plays a critical role in tomato production across the state of Florida. However, appropriate fertilization management depends on four major components (4Rs): right source, right rate, right placement, and right timing. Farming practices that follow the 4Rs can provide nutrients for optimal tomato productivity while minimizing the risk of nutrient losses and adverse environmental effects, both of which are important to the development of agricultural sustainability. This 6-page fact sheet discusses the 4Rs as well as conventional dry source fertilizers, controlled-release or slow-release source fertilizers, and liquid source fertilizers. Written by Qingren Wang, Guodong Liu, Kelly Morgan, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1269
Bitter Melon: An Asian Vegetable Emerging in Florida
 Bitter melon is a tropical and subtropical vegetable crop with long climbing vines which is widely cultivated in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean. The unripe fruit is used as a vegetable with a pleasantly bitter taste. This 7-page fact sheet provides an overview of this plant as well as recommendations for individuals in Florida who are interested in growing it. Written by Guodong Liu, Qingren Wang, Yuncong Li, David Dinkins, Bonnie Wells, and Yuqi Cui, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, December 2015.
Bitter melon is a tropical and subtropical vegetable crop with long climbing vines which is widely cultivated in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean. The unripe fruit is used as a vegetable with a pleasantly bitter taste. This 7-page fact sheet provides an overview of this plant as well as recommendations for individuals in Florida who are interested in growing it. Written by Guodong Liu, Qingren Wang, Yuncong Li, David Dinkins, Bonnie Wells, and Yuqi Cui, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, December 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1271
Long Squash: An Asian Vegetable Emerging in Florida
 Long squash is an annual, vigorous, and herbaceous crop that was brought to the Americas by Paleoindian populations from Asia before the arrival of Columbus. This 4-page fact sheet provides an overview of this plant as well as recommendations for individuals in Florida who are interested in growing it. Written by Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, David Dinkins, Bonnie Wells, Qingren Wang, and Yuqi Cui, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, December 2015.
Long squash is an annual, vigorous, and herbaceous crop that was brought to the Americas by Paleoindian populations from Asia before the arrival of Columbus. This 4-page fact sheet provides an overview of this plant as well as recommendations for individuals in Florida who are interested in growing it. Written by Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, David Dinkins, Bonnie Wells, Qingren Wang, and Yuqi Cui, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, December 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1272