Young citrus trees require optimal irrigation management for vigorous vegetative growth, leaf flushing, and establishment of a dense canopy. Poor irrigation practices, such as infrequent irrigation or irrigating without using irrigation scheduling tools, could be costly. Besides excessive loss of water and nutrients, the growth of young trees might be impacted by an excess or deficit of water. Crop water stress in young trees directly affects yield and fruit quality. This new 2-page publication of the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences, written by Davie Kadyampakeni and Sandra Guzmán, covers some strategies for optimizing young tree care and irrigation management to in turn optimize grove efficiency and productivity.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss701
Tag: fertigation
Tomato Production in Florida Using Fertigation Technology
Tomato is in high demand because of its taste and health benefits. In Florida, tomato is the number one vegetable crop in terms of both acreage and value. Because of its high value and wide acreage, it is important for tomato production to be efficient in its water and nutrient use, which may be improved through fertigation practices. Therefore, the objective of this new 7-page article is to disseminate research-based methods of tomato production utilizing fertigation to enhance yield and nutrient use efficiency. Written by Mary Dixon and Guodong Liu, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1392
Implementing the Five Rs of Nutrient Stewardship for Fertigation in Florida’s Vegetable Production
The five Rs of nutrient stewardship is a mnemonic device used to emphasize accuracy and precision for nutrient management so as to apply the (1) right source of fertilizer at the (2) right rate at the (3) right time in the (4) right place with the (5) right irrigation. Because the majority of Florida’s soils are sandy, this fifth R is imperative for sustainable nutrient management for commercial crop production. These main points of nutrient management (source, rate, time, place, irrigation) may help enhance sustainability by reducing pollution by eutrophication, nitrogen loss through ammonia volatilization, and climate change from soil greenhouse gas emission. This new 8-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department was written by Mary Dixon and Guodong Liu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1386
Fertigation via Center Pivot Irrigation for Commercial Potato Production in Florida
Potatoes are an important crop in the United States, and Florida is ranked the 7th producer nationwide for potato production. In Florida, potatoes are mainly planted on sandy soils with low nutrient- and water-holding capacities. Nitrogen is the most limiting nutrient in these soils. Adopting efficient fertilization methods such as fertigation is imperative for minimizing leaching and improving use efficiency of nitrogen. This new 12-page article provides step-by-step guidelines for fertigation practices for commercial potato production. Written by Xiangju Fu, Guodong Liu, Lincoln Zotarelli, Steven Sargent, Kati Migliaccio, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1361
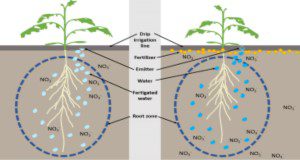
Fertigation for Citrus Trees
Microirrigation is an important component of citrus production systems in Florida. For citrus trees, microirrigation is more desirable than other irrigation methods for several reasons: water conservation, fertilizer management efficiency, and freeze protection. Research has shown that when microirrigation systems are properly managed, water savings can amount to as much as 80% compared with subirrigation and 50% compared with overhead sprinkler irrigation. Research has also shown the important advantage of microsprinklers for freeze protection of citrus. This 4-page fact sheet discusses fertilizer solubility and some common fertigation materials. It also offers a fertigation summary. Written by Mongi Zekri, Arnold Schumann, Tripti Vashisth, Davie Kadyampakeni, Kelly Morgan, Brian Boman, and Tom Obreza, and published by the UF Horticultural Sciences Department, September 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1306