Planning and preparation can increase chances of successful outcomes from demonstration plots. This 5-page publication focuses on guiding the successful establishment of demonstration trials and is targeted to county, regional, and state specialized Extension faculty who aim to develop on-farm research and demonstration sites as part of their programs. Written by Marcelo Wallau, Esteban Rios, and Ann Blount, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, January 2021.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag447
Tag: North Florida Research and Education Center
Transitioning from Conventional to Organic Farming Using Conservation Tillage
Organic farming is one of the fastest-growing segments of the agricultural industry in the United States and in Florida. Conservation tillage is often employed to reduce soil erosion, improve physical and biological properties of soil, and increase water use efficiency. This 5-page article aims to provide recommendations to row crop farmers who wish to implement conservation tillage practices during their transition to a certified organic system. Written by D. L. Wright, J. Moyer, D. Treadwell, I. M. Small, and S. George, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, revised November 2020.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag246
Hurricane Preparedness for Forage Crops in the Southeast United States
This 4-page document provides information on preparing forage crops, conserved forage, and grazing areas for potential hurricane damage and alleviating hurricane damage on forage crops and grazing lands in the Southeast United States, with an emphasis on the Florida peninsula and Gulf Coast. Written by José C. B. Dubeux, Jr. and Edward K. Twidwell, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, November 2019.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag439
Bahiagrass (Paspalum notatum Flueggé): Overview and Pasture Management
This 10-page document discusses bahiagrass forage cultivars, forage production, nutritive value, animal performance, planting, pasture renovation, management, and more. Written by Marcelo Wallau, Joao Vendramini, José Dubeux, and Ann Blount, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, revised July 2019.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag342
Estimating Herbage Mass on Pastures to Adjust Stocking Rate
This new 6-page document explains methods to measure forage mass and utilize that information to estimate an adequate stocking rate. Written by Jose Dubeux, Marcelo Wallau, João Vendramini, Liliane Silva, Jane Griffin, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and Erick Santos, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, June 2019.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag434
Overseeding Rhizoma Perennial Peanut Pasture and Hay Fields during the Cool Season
Hay and livestock producers want to know if they can overseed their rhizoma peanut fields with cool-season forages during rhizoma perennial peanut dormancy. This new 5-page document discusses overseeding for hay and overseeding for grazing. Written by Jose Dubeux, Cheryl Mackowiak, Ann Blount, David Wright, and Luana Dantas, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, January 2019.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag426
Forage-Based Heifer Development Program for North Florida
Developing replacement heifers to become productive females in the cow herd is a tremendous investment in a cow-calf operation that takes several years to make a return. Fortunately, there are several options to develop heifers on forage-based programs that can help reduce costs while meeting required industry performance targets. This new 4-page document proposes a model for replacement heifer development based on forage research trials at the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (UF/IFAS NFREC) in Marianna, FL. Written by Jose Dubeux, Nicolas DiLorenzo, Kalyn Waters, and Jane C. Griffin, and published by the UF/IFAS Agronomy Department, October 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag424
Biology and Control of Cogongrass (Imperata cylindrica) in Southern Forests
Cogongrass (Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv.) is a Southeast Asian warm-season perennial grass species that has spread to all continents except Antarctica. It is considered among the worst problematic weeds on a global scale. Control of cogongrass is difficult, especially in forests. This 6-page fact sheet written by Patrick J. Minogue, Brent V. Brodbeck, and James H. Miller and published by the UF/IFAS School of Forest Resources and Conservation presents recommendations for control strategies that will work in mixed pine-hardwood forests and pine forests.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr411
Florida's Bats: The Florida Bonneted Bat
The Florida bonneted bat is one of only two endangered species of bat in Florida and the state’s only endemic flying mammal (“endemic” means that it is found nowhere in the world but in Florida). With a 20-inch wingspan, it is Florida’s largest bat and the third largest of all 48 species of bats in the United States. The Florida bonneted bat was listed as federally endangered in 2013 because of concerns over habitat loss, degradation, and modification caused by humans. Additional concerns include the species’ small population size and restricted range, the small number of known colonies, their slow reproduction, and the relative isolation of separate populations of bonneted bats. This 2-page fact sheet written by Holly K. Ober, Terry Doonan, and Emily Evans, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation explains how to differentiate Florida bonneted bats from velvety free-tailed bats and Brazilian free-tailed bats and explains what to do if you find one of these endangered bats.http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw426
Florida's Bats: Velvety Free-Tailed Bat
The velvety free-tailed bat is found nowhere in the United States but extreme south Florida. These bats emerge from their roosts earlier than most other bats, often shortly before sunset. This 2-page fact sheet written by Holly K. Ober, Terry Doonan, and Emily Evans, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation explains how to differentiate velvety free-tailed bats from Brazilian free-tailed bats and Florida bonneted bats.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw425
Florida's Bats: Brazilian Free-tailed Bat
The Brazilian free-tailed bat lives throughout Florida and is the state’s most common bat. They are important economically because they consume large quantities of insect pests. This 2-page fact sheet written by Holly K. Ober, Terry Doonan, and Emily Evans, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation explains how to differentiate Brazilian free-tailed bats from velvety free-tailed bats and Florida bonneted bats.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw424
Control y Biologia del Helecho Trepador Japones (Lygodium japonicum )
El helecho trepador japonés es una enredadera invasiva no nativa de los Estados Unidos (EEUU) que fue introducida aproximadamente en 1900. Este helecho se ha establecido a lo largo de la llanura costera del sudeste de los EEUU desde los estados de Norte y Sur Carolinas hasta Texas y Arkansas. El helecho trepador japonés es nativo de Asia, en particular Japón así como al oeste de la cordillera de los Himalayas. El área de establecimiento se ha expandido desde la región de la costa del Golfo de México incluyendo TX, AR, LA, MS, AL, FL, GA, SC, NC, y PA. En Florida, el helecho trepador japonés está ampliamente distribuido en el norte y al oeste del estado, mientras que en la parte centro-sur su abundancia es variable. Este helecho está adaptado a lugares soleados o con sombra, y por lo general se localiza en suelos húmedos como los bordes de los pantanos, lagos, arroyos y bosques de tierras altas.
This 6-page fact sheet was written by Elsa D. Chevasco, Patrick J. Minogue, Kimberly K. Bohn, and Francisco Escobedo, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, November 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr344
The Florida Bull Test 2014/2015
The 2014-2015 Florida Bull Test concluded with the evaluation of 103 bulls. The test assessed the performance potential and breeding soundness of bulls consigned to the program at the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC). This 9-page fact sheet covers the test procedures, feed efficiency assessment, test rules and regulations, health requirements, test results, and sale summary. Written by Carla D. Sanford, G. Cliff Lamb, and Nicolas DiLorenzo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, June 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an325
Carinata, the Jet Fuel Cover Crop: 2016 Production Recommendations for the Southeastern United States

Carinata has been grown commercially for several years on the Canadian prairie and more recently in the US northern plains as a summer crop. For the past four years, UF has been conducting research to evaluate various management practices that allow incorporation of carinata into current cropping systems as a winter crop with minimal modification to existing infrastructure in the southeastern US. This 8-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses carinata characteristics, biology, nutrient management, tillage, variety selection, planting dates, seeding depth, seeding rate, row spacing, weed management, disease management, insect management, harvest management, economics, and crop insurance. Written by Ramdeo Seepaul, Christine M. Bliss, David L. Wright, Jim J. Marois, Ramon G. Leon, Nicholas Dufault, Sheeja George, and Steve M. Olson, and published by the UF Agronomy Department, December 2014. Revised October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag389
Temporary Food Plot Deterrents for Deer: Do They Work?

Many Floridians enjoy the opportunity to hunt, watch, or photograph white-tailed deer. Hunters and landowners often plant cool season forage plots both to attract wildlife and to provide a dependable food source. But where there is a high deer population or scarce food resources, deer may forage on food plots as soon as the plants emerge and before they become established. This fact sheet presents the results of research conducted at the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center in Quincy into the effectiveness of various strategies hunters and landowners can use to temporarily limit access to new food plots until the plants are well established and strong enough to attract and sustain hungry deer through the winter. Written by Holly Ober, Cheryl Mackowiak, and Ann Blount and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw410
Biology, Control and Invasive Potential of Giant Reed (Arundo donax L.) in Florida

Arundo donax (L.), also known as giant reed, is a tall, fast-growing, bamboo-like grass that under ideal conditions can reach a height of up to 30 feet and a stem diameter up to 1.5 inches. Giant reed is invasive and difficult to control and has caused economic losses in California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. This species was introduced to Florida over 100 years ago and is currently naturalized in at least 26 of the 67 Florida counties. So far giant reed has not proved problematic in Florida, but recent permitting of its planting for bioenergy feed stock may increase the risk that it could naturalize into plant communities in Florida and other southeastern states and potentially cause economic losses as well as harm to native species and habitats. This 5-page fact sheet written by Pat Minogue and Seth Wright and published by the School of Forest Resources and Conservation describes the biology of this species and explains some strategies for its control.
edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr396
The Economic Impact of Feed Efficiency in Beef Cattle
 A well-run, profitable business is usually more efficient than its competitors. In the case of the beef cattle industry, competition can come from two sources: other producers who sell similar classes of cattle, and other protein-producing species, such as pork and poultry. Measuring efficiency across the entire integrated beef system can be difficult due to the differing classes of cattle, breed differences, and ways in which the biological systems interact. There are a multitude of measures of efficiency in beef production, with feed efficiency being one of the most economic. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that covers feed to gain ratio and residual feed intake in beef cattle. Written by Travis D. Maddock, Darren D. Henry, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences. Original publication date: May 2009. Revised October 2015.
A well-run, profitable business is usually more efficient than its competitors. In the case of the beef cattle industry, competition can come from two sources: other producers who sell similar classes of cattle, and other protein-producing species, such as pork and poultry. Measuring efficiency across the entire integrated beef system can be difficult due to the differing classes of cattle, breed differences, and ways in which the biological systems interact. There are a multitude of measures of efficiency in beef production, with feed efficiency being one of the most economic. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that covers feed to gain ratio and residual feed intake in beef cattle. Written by Travis D. Maddock, Darren D. Henry, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences. Original publication date: May 2009. Revised October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an217
Parana Pine, Araucaria angustifolia: An Ancient-Looking Conifer for Modern Landscapes
 Paraná pine is a primitive-looking conifer valued for its unusual horizontal branching, interesting triangular-shaped needles, and neat, symmetrical form. The primitive appearance of this evergreen tree results from its resemblance to and relationship with an ancient group of Araucaria-related conifers that dominated forests more than 145 million years ago. This tree once covered vast areas in southern Brazil, Argentina and Paraguay. Native Americans harvest the seeds for food. It was an important timber tree for European settlers, and it was logged extensively through the 20th century. Now one of the rarest trees in Brazil, Paraná pine is considered critically endangered due to habitat loss and exploitation. This evergreen conifer grows too large for most residential situations, but is best used as an accent or conversation piece in large-scale landscapes. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Gary W. Knox, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, November 2014.
Paraná pine is a primitive-looking conifer valued for its unusual horizontal branching, interesting triangular-shaped needles, and neat, symmetrical form. The primitive appearance of this evergreen tree results from its resemblance to and relationship with an ancient group of Araucaria-related conifers that dominated forests more than 145 million years ago. This tree once covered vast areas in southern Brazil, Argentina and Paraguay. Native Americans harvest the seeds for food. It was an important timber tree for European settlers, and it was logged extensively through the 20th century. Now one of the rarest trees in Brazil, Paraná pine is considered critically endangered due to habitat loss and exploitation. This evergreen conifer grows too large for most residential situations, but is best used as an accent or conversation piece in large-scale landscapes. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Gary W. Knox, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep509
Understanding Pregnancy Diagnosis in Beef Cattle
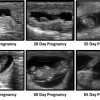 Because 55 to 70 percent of the input costs associated with a beef cattle operation are related to nutrition, culling open (non-pregnant) cows after the breeding season can save as much as $200 per head that can be diverted to the purchase or development of replacement females, sire selection, increased nutritional management, and other management-related costs. Pregnancy diagnosis can be performed simply during vaccination or at the time of weaning. There are three practical methods: rectal palpation, transrectal ultrasonography, or blood test. This 5-page fact sheet was written by G. Cliff Lamb, Darren D. Henry, Vitor R. G. Mercadante, and Doug E. Mayo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
Because 55 to 70 percent of the input costs associated with a beef cattle operation are related to nutrition, culling open (non-pregnant) cows after the breeding season can save as much as $200 per head that can be diverted to the purchase or development of replacement females, sire selection, increased nutritional management, and other management-related costs. Pregnancy diagnosis can be performed simply during vaccination or at the time of weaning. There are three practical methods: rectal palpation, transrectal ultrasonography, or blood test. This 5-page fact sheet was written by G. Cliff Lamb, Darren D. Henry, Vitor R. G. Mercadante, and Doug E. Mayo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an314
Potential Bull Buyers Perceive Increased Value to their Operations When Purchasing Bulls from the Florida Bull Test
 Since its beginning in 2000, the Florida Bull Test has been under constant evolution to achieve its goal of helping producers select high-quality sires, thereby improving production and profitability of beef cattle producers in Florida and the Southeast United States. A survey of potential buyers before the 2014 sale succeeded in identifying which characteristics of bulls are most important to buyers purchasing bulls: purchasing bulls from the Florida Bull Test increases the value of calves sired by improving performance, genetics, and feed efficiency of their herds. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, Darren D. Henry, Francine M. Ciriaco, Paula M. Mercadante, Tessa Schulmeister, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
Since its beginning in 2000, the Florida Bull Test has been under constant evolution to achieve its goal of helping producers select high-quality sires, thereby improving production and profitability of beef cattle producers in Florida and the Southeast United States. A survey of potential buyers before the 2014 sale succeeded in identifying which characteristics of bulls are most important to buyers purchasing bulls: purchasing bulls from the Florida Bull Test increases the value of calves sired by improving performance, genetics, and feed efficiency of their herds. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, Darren D. Henry, Francine M. Ciriaco, Paula M. Mercadante, Tessa Schulmeister, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an313












