 Since its beginning in 2000, the Florida Bull Test has been under constant evolution to achieve its goal of helping producers select high-quality sires, thereby improving production and profitability of beef cattle producers in Florida and the Southeast United States. A survey of potential buyers before the 2014 sale succeeded in identifying which characteristics of bulls are most important to buyers purchasing bulls: purchasing bulls from the Florida Bull Test increases the value of calves sired by improving performance, genetics, and feed efficiency of their herds. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, Darren D. Henry, Francine M. Ciriaco, Paula M. Mercadante, Tessa Schulmeister, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
Since its beginning in 2000, the Florida Bull Test has been under constant evolution to achieve its goal of helping producers select high-quality sires, thereby improving production and profitability of beef cattle producers in Florida and the Southeast United States. A survey of potential buyers before the 2014 sale succeeded in identifying which characteristics of bulls are most important to buyers purchasing bulls: purchasing bulls from the Florida Bull Test increases the value of calves sired by improving performance, genetics, and feed efficiency of their herds. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, Darren D. Henry, Francine M. Ciriaco, Paula M. Mercadante, Tessa Schulmeister, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an313
Tag: Vitor Mercadante
Understanding Pregnancy Diagnosis in Beef Cattle
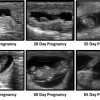 Because 55 to 70 percent of the input costs associated with a beef cattle operation are related to nutrition, culling open (non-pregnant) cows after the breeding season can save as much as $200 per head that can be diverted to the purchase or development of replacement females, sire selection, increased nutritional management, and other management-related costs. Pregnancy diagnosis can be performed simply during vaccination or at the time of weaning. There are three practical methods: rectal palpation, transrectal ultrasonography, or blood test. This 5-page fact sheet was written by G. Cliff Lamb, Darren D. Henry, Vitor R. G. Mercadante, and Doug E. Mayo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
Because 55 to 70 percent of the input costs associated with a beef cattle operation are related to nutrition, culling open (non-pregnant) cows after the breeding season can save as much as $200 per head that can be diverted to the purchase or development of replacement females, sire selection, increased nutritional management, and other management-related costs. Pregnancy diagnosis can be performed simply during vaccination or at the time of weaning. There are three practical methods: rectal palpation, transrectal ultrasonography, or blood test. This 5-page fact sheet was written by G. Cliff Lamb, Darren D. Henry, Vitor R. G. Mercadante, and Doug E. Mayo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an314
The Florida Bull Test, 2013-2014
 The 2013-2014 Florida Bull Test was a 112-day performance test and a breeding soundness evaluation of each bull that qualified for the auction. Table 1 summarizes feed efficiency data; Table 2 individual feed intake and feed efficiency; and Table 3 individual animal performance. This 10-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, G. Cliff Lamb, and Nicolas DiLorenzo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, May 2014.
The 2013-2014 Florida Bull Test was a 112-day performance test and a breeding soundness evaluation of each bull that qualified for the auction. Table 1 summarizes feed efficiency data; Table 2 individual feed intake and feed efficiency; and Table 3 individual animal performance. This 10-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, G. Cliff Lamb, and Nicolas DiLorenzo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an301
Management of Postpartum Anestrus in Beef Cows (AN277)
 It is estimated that in Florida alone the cost of infertility of beef cows exceeds $86 million annually. Infertility occurs when cows become pregnant but fail to calve, become pregnant late in the breeding season and fall out of the annual production cycle or fail to become pregnant during the breeding season. The latter two causes of infertility are a direct result of the length of the post-partum interval. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Kalyn Bischoff, Vitor Mercadante, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, March 2012.
It is estimated that in Florida alone the cost of infertility of beef cows exceeds $86 million annually. Infertility occurs when cows become pregnant but fail to calve, become pregnant late in the breeding season and fall out of the annual production cycle or fail to become pregnant during the breeding season. The latter two causes of infertility are a direct result of the length of the post-partum interval. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Kalyn Bischoff, Vitor Mercadante, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, March 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an277