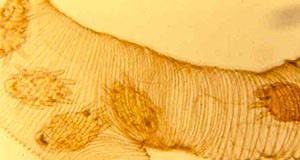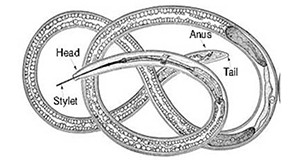
Dagger nematodes parasitize plants. They cause economic damage and death of host crops through feeding on the roots and by spreading viral mosaic and wilting diseases, but field studies have shown that some control measures targeting reduction in the population of dagger nematodes can be effective in controlling viral diseases in susceptible crops. This 7-page fact sheet was written by William K. Heve, William T. Crow, and Tesfamarian Mengistu, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1097
Category: Agriculture
Summary of 2013/14 Production Costs for Indian River Fresh Market Grapefruit and Southwest Florida Juice Oranges

This 10-page report, developed through interviews with growers who managed their own citrus groves, outlines the cost of production budgets for fresh grapefruit and juice oranges grown during the 2013/14 season. The Florida citrus industry is on a steep learning curve as it collectively tries to maintain economically sustainable fruit yields from HLB-infected trees. Growers are experimenting with new materials and management strategies to reduce psyllid populations and improve a tree’s overall nutritional health. As a result, production costs have increased threefold since 2004. Between the 2012/13 and the 2013/14 seasons, production costs increased 30% and 34% for fresh grapefruit and juice oranges, respectively. Since 2004, production costs for fresh grapefruit have increased 182%, while costs to grow juice oranges have increased 211%.
Written by Fritz Roka, Ariel Singerman, and Ronald Muraro, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe968
Doveweed (Murdannia nudiflora) Control in Warm-Season Turfgrass Species
 Doveweed is an aggressive, naturalized summer annual weed that rapidly invades warm-season turfgrass species, especially in residential lawns, and few herbicides can effectively control it. Because of these challenges, a well-designed management strategy is necessary for doveweed control. This 4-page fact sheet describes identification, growth requirements, chemical control and cultural practices. Written by Ramon G. Leon and Bryan Unruh, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, June 2015.
Doveweed is an aggressive, naturalized summer annual weed that rapidly invades warm-season turfgrass species, especially in residential lawns, and few herbicides can effectively control it. Because of these challenges, a well-designed management strategy is necessary for doveweed control. This 4-page fact sheet describes identification, growth requirements, chemical control and cultural practices. Written by Ramon G. Leon and Bryan Unruh, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag395
Can Calcium Propionate Help Maintain Calcium Concentrations and Prevent Metritis in Dairy Cows with Dystocia?
Studies have suggested that giving dairy cows supplemental calcium may reduce the incidence of metritis. This study tested this hypothesis with cows at the UF Dairy Unit and found that calcium supplements actually did not benefit postpartum health and are not recommended as means of metritis prevention. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Klibs N. Galvao, Mauricio Benzaquen, and Carlos A. Risco, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine—Large Animal Clinical Sciences, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm223
Commercial Production of Ornamental Tropical Foliage Plants: Micropropagation
 Florida nursery operators need to understand plant propagation principles and techniques so they can grow enough plants for sale. Micropropagation is a way to culture plant tissue to rapidly propagate a large number of plants. This 4-page fact sheet presents an overview of micropropagation to help growers evaluate it as a propagation technique for their own nursery operations. Written by J. Chen and R. J. Henny, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, May 2015. (Photo: J. Chen, UF/IFAS)
Florida nursery operators need to understand plant propagation principles and techniques so they can grow enough plants for sale. Micropropagation is a way to culture plant tissue to rapidly propagate a large number of plants. This 4-page fact sheet presents an overview of micropropagation to help growers evaluate it as a propagation technique for their own nursery operations. Written by J. Chen and R. J. Henny, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, May 2015. (Photo: J. Chen, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep520
Biology and Management of Long-Stalked Phyllanthus in Ornamental Crop Production
This 5-page fact sheet discusses the characteristics of long-stalked phyllanthus and explains how to control its growth in a nursery environment. Written by Theresa Chormanski, Chris Marble, and Lyn Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep518
Florida Citrus Rootstock Selection Guide, 3rd Edition
Information about citrus rootstocks has become an important part of understanding and managing citrus greening (Huanglongbing or HLB). This selection guide covers 20 characteristics of 45 citrus rootstocks and explains its methodology in detail. This 3-page fact sheet was written by William S. Castle, Kim D. Bowman, Jude W. Grosser, Stephen H. Futch, and James H. Graham and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, May 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1260
Biology and Management of Mulberry Weed (Fatoua villosa) in Ornamental Crop Production
This 4-page fact sheet discusses the characteristics of mulberry weed (Fatoua villosa) and explains how to control its growth in a nursery environment. Written by Chris Marble and Shawn Steed, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep517
How to Dissect Honey Bees (Apis mellifera L.) to Detect Tracheal Mites (Acarapis woodi Rennie)
Tracheal mites are parasites of the western honey bee and negatively impact the health and productivity of an infested colony. This 6-page fact sheet details the method of dissecting honey bees in order to diagnose tracheal mites. Written by John Bonkowski, Ashley N. Mortensen, and James D Ellis, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1072
Observation Bee Hives

The use of observation bee hives continues to interest a variety of people. This is not surprising. The observation hive is one of the primary research and educational tools in apiculture. It is both educational and entertaining. Observation bee hives can be used to enhance public relations and marketing programs. But a great deal of time and energy is needed to set up a hive and keep it going. Maintenance can be expensive and time consuming, especially if the hive is to be used as a permanent display for the general public. This 3-page fact sheet provides sources for building observation hives and tips for maintenance. Written by David Hall, James D. Ellis, and Malcolm Sanford, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, March 2015. (UF/IFAS photo by Tyler Jones)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg320
Snap Bean Soil Fertility Program in Miami-Dade County
In terms of acreage, snap beans are the most commonly grown vegetable in Miami-Dade County. This 2-page facts sheet outlines the impact of fertilizer use and local weather and soil on snap bean production in this region. Written by Monica Ozores-Hampton, Qiang Zhu, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, May 2015. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1261
Sample Pollination Agreement
 The key to a prospering pollination service is proper promotion, honest, quality service, and a written contract. This contract would detail the expectations of both the beekeeper and the grower. This 4-page fact sheet provides a suggested pollination agreement. Written by Malcolm T. Sanford, Jeanette Klopchin, and James Ellis, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, March 2015. (UF/IFAS Photo: Thomas Wright)
The key to a prospering pollination service is proper promotion, honest, quality service, and a written contract. This contract would detail the expectations of both the beekeeper and the grower. This 4-page fact sheet provides a suggested pollination agreement. Written by Malcolm T. Sanford, Jeanette Klopchin, and James Ellis, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, March 2015. (UF/IFAS Photo: Thomas Wright)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/aa169
Thrips in Florida Strawberry Crops
 Strawberries grown in Florida are attacked by several pests, including flower thrips. Western flower thrips and common blossom thrips (both invasive) can cause damage to strawberries in Florida; but, while the native Florida flower thrips is commonly found in strawberry blossoms, it hasn’t been established that it can cause economic damage to strawberry. This 9-page fact sheet describes thrips damage, characteristics to distinguish among the three species, and methods of control. Written by Jeff D. Cluever, Hugh A. Smith, Joe E. Funderburk, and Galen Frantz, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2015. (Photo: H. A. Smith)
Strawberries grown in Florida are attacked by several pests, including flower thrips. Western flower thrips and common blossom thrips (both invasive) can cause damage to strawberries in Florida; but, while the native Florida flower thrips is commonly found in strawberry blossoms, it hasn’t been established that it can cause economic damage to strawberry. This 9-page fact sheet describes thrips damage, characteristics to distinguish among the three species, and methods of control. Written by Jeff D. Cluever, Hugh A. Smith, Joe E. Funderburk, and Galen Frantz, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2015. (Photo: H. A. Smith)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1078
SmartIrrigation Avocado App: A Step-by-Step Guide
 UF’s SmartIrrigation Avocado for iOS and Android platforms provides a simple ET-based method to schedule irrigation and is expected to provide 20% to 50% water savings based on findings with other schedule tools. This 6-page fact sheet provides configuration instructions and main menu features. Written by D. Mbabazi, K. W. Migliaccio, J. H. Crane, J. H. Debastiani Andreis, C. Fraisse, L. Zotarelli, and K. T. Morgan, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, May 2015.
UF’s SmartIrrigation Avocado for iOS and Android platforms provides a simple ET-based method to schedule irrigation and is expected to provide 20% to 50% water savings based on findings with other schedule tools. This 6-page fact sheet provides configuration instructions and main menu features. Written by D. Mbabazi, K. W. Migliaccio, J. H. Crane, J. H. Debastiani Andreis, C. Fraisse, L. Zotarelli, and K. T. Morgan, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, May 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae513
Rose Rosette Disease: A New Disease of Roses in Florida
Rose rosette disease is an incurable, destructive disease that affects both wild and cultivated roses. Over the past several decades, the disease has spread over much of the U.S., though it was first observed in Florida in 2013. This 6-page fact sheet describes the symptoms and diagnosis of the disease, as well as the cultural, chemical, and, possibly, biological controls that can minimize its spread. Written by Binoy Babu, Mathews L. Paret, Tim Schubert, Carlye Baker, Gary Knox, Fanny Iriarte, James Aldrich, Laura Ritchie, Carrie L. Harmon, and Svetlana Y. Folimonova, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, May 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp317
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: What the Future Could Hold for Bs2 Tomatoes
 Bs2 tomatoes are transgenic tomatoes that have been engineered to contain the Bs2 gene from pepper. As such, they are considered a genetically modified (GM) food, or a genetically modified organism (GMO). Numerous trials conducted by University of Florida researchers have shown the benefits of these cultivars for bacterial spot disease management, and growers and industry members recognize the potential for Bs2 tomatoes to make Florida tomato production more sustainable. This 4-page fact sheet discusses the benefits that might be realized by the adoption of Bs2 tomato varieties, and the challenges standing in the way of their commercial production. Written by S. F. Hutton, J. W. Scott, J. B. Jones, R. E. Stall, G. E. Vallad, B. J. Staskawicz, and D. M. Horvath , and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2015.
Bs2 tomatoes are transgenic tomatoes that have been engineered to contain the Bs2 gene from pepper. As such, they are considered a genetically modified (GM) food, or a genetically modified organism (GMO). Numerous trials conducted by University of Florida researchers have shown the benefits of these cultivars for bacterial spot disease management, and growers and industry members recognize the potential for Bs2 tomatoes to make Florida tomato production more sustainable. This 4-page fact sheet discusses the benefits that might be realized by the adoption of Bs2 tomato varieties, and the challenges standing in the way of their commercial production. Written by S. F. Hutton, J. W. Scott, J. B. Jones, R. E. Stall, G. E. Vallad, B. J. Staskawicz, and D. M. Horvath , and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1259
Bot Canker of Oak in Florida Caused by Diplodia corticola and D. quercivora
 This 6-page fact sheet describes the emergence of these two pathogens of oak and grapevine in North America and Florida; the signs and symptoms of infection; mechanism of host disease and death; fungal morphology; origin, host range, and classification; and management options. Written by Sonja Mullerin and Jason A. Smith, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, March 2015. (Photo: Jason Smith, UF/IFAS)
This 6-page fact sheet describes the emergence of these two pathogens of oak and grapevine in North America and Florida; the signs and symptoms of infection; mechanism of host disease and death; fungal morphology; origin, host range, and classification; and management options. Written by Sonja Mullerin and Jason A. Smith, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, March 2015. (Photo: Jason Smith, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr386
Pest Management of Peppers in Miami-Dade County, Florida

Pest management of peppers in Miami-Dade County is challenging because of a climate favorable to pests. To assist local pepper growers in maintaining crop productivity and improving the quality of produce, this publication illustrates common pests including major diseases and insects and recommends Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques, including host resistance, cultivation, sanitation, and physical, mechanical, biological, and chemical approaches, for effective pest management. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Qingren Wang, Shouan Zhang, Dakshina Seal, and Teresa Olczyk, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, February 2015. (Photo: Shouan Zhang)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp316
Pesticide Storage: Keep It in the Container
 Accidents happen quickly, and so do accidents with pesticides. Anyone storing pesticides, especially in the presence of children, needs to take precautions by keeping them in their proper, original containers. Several people have died when they unknowingly drank pesticides from containers that originally held soda, other beverages, or foodstuffs. In particular, the herbicide paraquat is highly toxic to humans; one small accidental sip can be fatal, and there is no antidote. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Fred Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2015. (Photo: Fred Fishel)
Accidents happen quickly, and so do accidents with pesticides. Anyone storing pesticides, especially in the presence of children, needs to take precautions by keeping them in their proper, original containers. Several people have died when they unknowingly drank pesticides from containers that originally held soda, other beverages, or foodstuffs. In particular, the herbicide paraquat is highly toxic to humans; one small accidental sip can be fatal, and there is no antidote. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Fred Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2015. (Photo: Fred Fishel)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi255
The Role and Impact of Technology on Supply-Chain Management in the Food Industry
 In competitive markets, innovations such as electronic devices, information technology, and green and sustainable technologies can provide a competitive advantage in managing the supply chain, and determine which operations succeed and which fail. The information in this article is intended to provide insight regarding the potential benefits and limitations of these technologies so that firms in the food industry can make more informed decisions on which technologies should be incorporated into their own systems and to what degree. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Jonathan A. Watson, Allen F. Wysocki, and Ray A. Bucklin, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, April 2015. (UF/IFAS photo: Thomas Wright)
In competitive markets, innovations such as electronic devices, information technology, and green and sustainable technologies can provide a competitive advantage in managing the supply chain, and determine which operations succeed and which fail. The information in this article is intended to provide insight regarding the potential benefits and limitations of these technologies so that firms in the food industry can make more informed decisions on which technologies should be incorporated into their own systems and to what degree. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Jonathan A. Watson, Allen F. Wysocki, and Ray A. Bucklin, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, April 2015. (UF/IFAS photo: Thomas Wright)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae511