Southern highbush blueberries combine the fruit quality and productivity of highbush blueberries with the low chilling requirement necessary to produce a crop in the Florida climate. Written by J. G. Williamson, D. A. Phillips, P. M. Lyrene, and P. R. Munoz and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, this 13-page major revision describes current and historical southern highbush blueberry cultivars released by the University of Florida.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1245
Tag: Gulf Coast REC
Charcoal Rot of Strawberries Caused by Macrophomina phaseolina
Charcoal rot is caused by Macrophomina phaseolina and has become more prevalent in Florida strawberry fields since methyl bromide was phased out. This 4-page publication describes the symptoms, development, and control of charcoal rot in strawberry fields. Written by N. A. Peres, J. S. Baggio, and J. C. Mertely and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Plant Pathology, February 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp161
Production Guidelines for Globe Artichoke in Florida
Globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus L.) belongs to a genus of thistle-like plants in the sunflower (Asteracae) family and is cultivated for its flower buds. This four-page fact sheet discusses production guidelines for artichoke in Florida. Written by Shinsuke Agehara and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1289
How to Use a Dichotomous Key: A Tutorial Featuring 10 Common Shade Trees of the Tampa Bay Area
A dichotomous key is a tool used to help identify an unknown organism. This twelve-page fact sheet features a key of leaf characteristics for ten common broadleaf trees in the Tampa Bay Area. Accurately navigating this series of paired, either-or choices about leaf characteristics will lead the reader to identify the correct tree from the group of ten. Written by Andrew K. Koeser, Gitta Hasing, Michael G. Andreu, and Melissa H. Friedman and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep510
10 Common Palms of the Tampa Bay Area
Palms often serve as key specimens in urban landscape designs. Despite this, their identity is often unknown to Florida’s new, seasonal, and even long-term residents. This ten-page fact sheet serves as a quick reference for some of the most common palms found in North and Central Florida and the Tampa Bay Area in particular. Written by Gitta Hasing, Andrew K. Koeser, Melissa H. Friedman, and Timothy K. Broschat and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep506
Ten Common Conifers of the Tampa Bay Area
Conifers are cone-bearing trees often identified by their needles. In addition to their value as landscape trees and lumber and paper sources, they are popular around the holidays as Christmas trees.
This 6-page guide written by Andrew K. Koeser, Holly Finley, Gitta Hasing, Gary W. Knox, and Melissa H. Friedman and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department will assist you in identifying the 10 most common conifers that grow in the Tampa Bay area of Florida. It is an efficient resource for master gardeners, novice tree inventory crews, 4-H forestry teams, and others interested in basic conifer identification.
Ten Common Flowering Trees of the Tampa Bay Area
Blooming trees serve as key focal points in the urban landscape. Florida’s flowering trees can be quite spectacular and leave you wondering, Wow, what tree is that?
This 7-page guide written by Gitta Hasing, Andrew K. Koeser, Gary W. Knox, and Melissa H. Friedman and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department will assist you in identifying the 10 most common flowering trees that grow in the Tampa Bay area of Florida. It is an efficient resource for master gardeners, novice tree inventory crews, 4-H forestry teams, and others interested in basic flowering tree identification.
edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep505
Contaminants in the Urban Environment: Dioxins
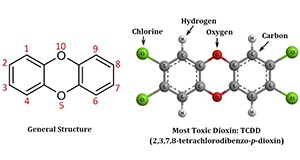 Dioxins are among the most toxic chemicals on the earth. They are by-products of a number of human activities such as combustion of fuels and wastes containing polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorine bleaching of paper products, and selected industrial processes. Current releases of dioxins by humans are due to the combustion of fuels and burning of household trash. The good news is that levels of dioxins in the environment have decreased in the United States throughout the past 30 years due to the improved emission controls and regulatory activities. But dioxins break down slowly, so they remain in the environment for a long time and accumulate in the food chain. Long-term exposure to dioxins can harm immune system, nervous system, endocrine system, and reproductive functions. This 7-page fact sheet discusses the sources, emission trends, and impacts of dioxins as well as the ways to minimize exposure to dioxins. Written by Yun-Ya Yang and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, July 2015.
Dioxins are among the most toxic chemicals on the earth. They are by-products of a number of human activities such as combustion of fuels and wastes containing polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorine bleaching of paper products, and selected industrial processes. Current releases of dioxins by humans are due to the combustion of fuels and burning of household trash. The good news is that levels of dioxins in the environment have decreased in the United States throughout the past 30 years due to the improved emission controls and regulatory activities. But dioxins break down slowly, so they remain in the environment for a long time and accumulate in the food chain. Long-term exposure to dioxins can harm immune system, nervous system, endocrine system, and reproductive functions. This 7-page fact sheet discusses the sources, emission trends, and impacts of dioxins as well as the ways to minimize exposure to dioxins. Written by Yun-Ya Yang and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss642
Thrips in Florida Strawberry Crops
 Strawberries grown in Florida are attacked by several pests, including flower thrips. Western flower thrips and common blossom thrips (both invasive) can cause damage to strawberries in Florida; but, while the native Florida flower thrips is commonly found in strawberry blossoms, it hasn’t been established that it can cause economic damage to strawberry. This 9-page fact sheet describes thrips damage, characteristics to distinguish among the three species, and methods of control. Written by Jeff D. Cluever, Hugh A. Smith, Joe E. Funderburk, and Galen Frantz, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2015. (Photo: H. A. Smith)
Strawberries grown in Florida are attacked by several pests, including flower thrips. Western flower thrips and common blossom thrips (both invasive) can cause damage to strawberries in Florida; but, while the native Florida flower thrips is commonly found in strawberry blossoms, it hasn’t been established that it can cause economic damage to strawberry. This 9-page fact sheet describes thrips damage, characteristics to distinguish among the three species, and methods of control. Written by Jeff D. Cluever, Hugh A. Smith, Joe E. Funderburk, and Galen Frantz, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2015. (Photo: H. A. Smith)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1078
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: What the Future Could Hold for Bs2 Tomatoes
 Bs2 tomatoes are transgenic tomatoes that have been engineered to contain the Bs2 gene from pepper. As such, they are considered a genetically modified (GM) food, or a genetically modified organism (GMO). Numerous trials conducted by University of Florida researchers have shown the benefits of these cultivars for bacterial spot disease management, and growers and industry members recognize the potential for Bs2 tomatoes to make Florida tomato production more sustainable. This 4-page fact sheet discusses the benefits that might be realized by the adoption of Bs2 tomato varieties, and the challenges standing in the way of their commercial production. Written by S. F. Hutton, J. W. Scott, J. B. Jones, R. E. Stall, G. E. Vallad, B. J. Staskawicz, and D. M. Horvath , and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2015.
Bs2 tomatoes are transgenic tomatoes that have been engineered to contain the Bs2 gene from pepper. As such, they are considered a genetically modified (GM) food, or a genetically modified organism (GMO). Numerous trials conducted by University of Florida researchers have shown the benefits of these cultivars for bacterial spot disease management, and growers and industry members recognize the potential for Bs2 tomatoes to make Florida tomato production more sustainable. This 4-page fact sheet discusses the benefits that might be realized by the adoption of Bs2 tomato varieties, and the challenges standing in the way of their commercial production. Written by S. F. Hutton, J. W. Scott, J. B. Jones, R. E. Stall, G. E. Vallad, B. J. Staskawicz, and D. M. Horvath , and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1259
Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis [Pergande])
 One of many species of thrips found in Florida, Frankliniella occidentalis is a pest of several crops throughout Florida and the world, causing injury by feeding and by transmission of plant viruses. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Jeffrey D. Cluever, Hugh A. Smith, Joseph E. Funderburk, and Galen Frantz, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2015. (Photo: Lyle Buss)
One of many species of thrips found in Florida, Frankliniella occidentalis is a pest of several crops throughout Florida and the world, causing injury by feeding and by transmission of plant viruses. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Jeffrey D. Cluever, Hugh A. Smith, Joseph E. Funderburk, and Galen Frantz, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2015. (Photo: Lyle Buss)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1089
Is My Tree Safe? Recognizing Conditions that Increase the Likelihood of Tree Failure
 Urban trees provide shade and beauty and the urban forest as a whole provides a wealth of benefits to neighborhoods and residents. But stresses from the urban environment may lead to problems that pose an unacceptable safety risk to people and property. It is a landowner’s responsibility to ensure that the trees on their property are safe. A key step in reducing the potential for tree-related injury or property damage is learning to identify common tree defects associated with increased risk of failure. This 5-page fact sheet highlights seven easily reconizable tree defects that homeowners and non-professionals in public agencies. may encounter in Florida. Written by Drew C. McLean, Andrew K. Koeser, Robert J. Northrop, and Gitta Hasing, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, October 2014. (Photo by Gitta Hasing)
Urban trees provide shade and beauty and the urban forest as a whole provides a wealth of benefits to neighborhoods and residents. But stresses from the urban environment may lead to problems that pose an unacceptable safety risk to people and property. It is a landowner’s responsibility to ensure that the trees on their property are safe. A key step in reducing the potential for tree-related injury or property damage is learning to identify common tree defects associated with increased risk of failure. This 5-page fact sheet highlights seven easily reconizable tree defects that homeowners and non-professionals in public agencies. may encounter in Florida. Written by Drew C. McLean, Andrew K. Koeser, Robert J. Northrop, and Gitta Hasing, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, October 2014. (Photo by Gitta Hasing)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep507
Sensation™ Brand 'Florida127' Strawberry
 ‘Florida127’ is a new strawberry cultivar released from the University of Florida in 2013, the fruit of which are eligible for marketing under the Sensation™ brand. It is a short-day plant adapted to annual, winter plasticulture growing systems. The plant is moderately compact, robust, and upright with long pedicels, making the fruit easy to harvest. This 4-page fact sheet provides information and recommendations based on several years of testing in field plots in west-central Florida. Comparisons are made to ‘Florida Radiance’ and ‘Strawberry Festival’ for disease resistance. Written by Vance M. Whitaker, Craig K. Chandler, and Natalia A. Peres, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014. (Photo by Vance M. Whitaker)
‘Florida127’ is a new strawberry cultivar released from the University of Florida in 2013, the fruit of which are eligible for marketing under the Sensation™ brand. It is a short-day plant adapted to annual, winter plasticulture growing systems. The plant is moderately compact, robust, and upright with long pedicels, making the fruit easy to harvest. This 4-page fact sheet provides information and recommendations based on several years of testing in field plots in west-central Florida. Comparisons are made to ‘Florida Radiance’ and ‘Strawberry Festival’ for disease resistance. Written by Vance M. Whitaker, Craig K. Chandler, and Natalia A. Peres, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014. (Photo by Vance M. Whitaker)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1256
Biology and Management of Common Purslane in Fruiting Vegetables, Cucurbits, and Strawberries
 Purslane occurs throughout the year in Florida. It produces thousands of seeds per plant, which germinate readily, but can also persist in the soil for up to 15 years. Vegetative shoot fragments can survive on the soil surface for extended periods of time, then re-root when exposed to moisture and can even flower and produce seeds after they have been pulled from the soil. This characteristic enables purslane to persist and spread following cultivation. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Nathan S. Boyd, Andrew W. MacRae, Rick Kelly, and Ixchel M. Hernandez, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2014.
Purslane occurs throughout the year in Florida. It produces thousands of seeds per plant, which germinate readily, but can also persist in the soil for up to 15 years. Vegetative shoot fragments can survive on the soil surface for extended periods of time, then re-root when exposed to moisture and can even flower and produce seeds after they have been pulled from the soil. This characteristic enables purslane to persist and spread following cultivation. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Nathan S. Boyd, Andrew W. MacRae, Rick Kelly, and Ixchel M. Hernandez, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1238
Protected Culture for Vegetable and Small Fruit Crops: Southern Highbush Blueberry Cultivars under High Tunnels
 High tunnels have been proposed as an alternative for freeze protection and to increase fruit earliness of southern highbush blueberry. But there is no information about the effect of this type of structure on southern highbush blueberry fruit earliness under subtropical Florida conditions. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of 2-year study in a commercial southern highbush blueberry farm in North Central Florida to compare early fruit weight in high tunnels to that of open fields. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Bielinski M. Santos and Teresa P. Salame-Donoso, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2013.
High tunnels have been proposed as an alternative for freeze protection and to increase fruit earliness of southern highbush blueberry. But there is no information about the effect of this type of structure on southern highbush blueberry fruit earliness under subtropical Florida conditions. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of 2-year study in a commercial southern highbush blueberry farm in North Central Florida to compare early fruit weight in high tunnels to that of open fields. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Bielinski M. Santos and Teresa P. Salame-Donoso, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1226
’Fairytale Princess’ and ’Red Hot’: Red Lance-leaved Caladium Cultivars
 Caladiums are valued in landscapes and containers for their colorful and variable-shaped leaves. Two types of caladium cultivars exist in commercial production: fancy- and lance-leaved. ‘Florida Sweetheart’ is the most popular lance-leaved commercial cultivar of all colors. It produces wide lance leaves with a rosy color and relatively large tubers. ‘Florida Red Ruffles’ is the most popular red, lance-leaved commercial cultivar among caladium growers, greenhouse growers, and nurseries. It has excellent sunburn tolerance. Both cultivars were introduced by the University of Florida (UF) caladium breeding program. This 9-page fact sheet was written by Zhanao Deng, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2013.
Caladiums are valued in landscapes and containers for their colorful and variable-shaped leaves. Two types of caladium cultivars exist in commercial production: fancy- and lance-leaved. ‘Florida Sweetheart’ is the most popular lance-leaved commercial cultivar of all colors. It produces wide lance leaves with a rosy color and relatively large tubers. ‘Florida Red Ruffles’ is the most popular red, lance-leaved commercial cultivar among caladium growers, greenhouse growers, and nurseries. It has excellent sunburn tolerance. Both cultivars were introduced by the University of Florida (UF) caladium breeding program. This 9-page fact sheet was written by Zhanao Deng, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep481
New Gerbera Daisy Varieties for Large Containers and Flower Gardens
 Gerbera daisy is one of the most popular flowers in the United States. Recently, interest has increased in growing gerberas in large containers for indoor or outdoor use. ‘Funtastic™ Tangerine Eye’ and ‘Funtastic™ Golden Eye’ have been selected and tested specifically for use in large containers. These cultivars produce large, powdery mildew-resistant plants and large, attractive flowers in orange-red or yellow-orange that complement the existing Funtastic™ series of gerbera cultivars. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Zhanao Deng, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2013.
Gerbera daisy is one of the most popular flowers in the United States. Recently, interest has increased in growing gerberas in large containers for indoor or outdoor use. ‘Funtastic™ Tangerine Eye’ and ‘Funtastic™ Golden Eye’ have been selected and tested specifically for use in large containers. These cultivars produce large, powdery mildew-resistant plants and large, attractive flowers in orange-red or yellow-orange that complement the existing Funtastic™ series of gerbera cultivars. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Zhanao Deng, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep482
Protected Culture for Vegetable and Small Fruit Crops: Types of Structures
 A protective structure is defined as any structure designed to modify the environment in which plants are grown. Protective structures, such as greenhouses, screen houses, and tunnels, are known worldwide as production systems for high-quality vegetable and fruit crops. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Bielinski M. Santos, Gary Vallad, and Emmanuel A. Torres-Quezada, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2013.
A protective structure is defined as any structure designed to modify the environment in which plants are grown. Protective structures, such as greenhouses, screen houses, and tunnels, are known worldwide as production systems for high-quality vegetable and fruit crops. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Bielinski M. Santos, Gary Vallad, and Emmanuel A. Torres-Quezada, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1224
Colletotrichum Crown Rot (Anthracnose Crown Rot) of Strawberries (PP238/PP156)
 Colletotrichum crown rot is caused by the fungi Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Colletotrichum fragariae. Both pathogens kill strawberry plants by aggressively invading crown tissue. Crown rot is a serious disease in warm production regions, such as those in the southeastern United States. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Natalia A. Peres and Steven J. MacKenzie, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, September 2012.
Colletotrichum crown rot is caused by the fungi Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Colletotrichum fragariae. Both pathogens kill strawberry plants by aggressively invading crown tissue. Crown rot is a serious disease in warm production regions, such as those in the southeastern United States. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Natalia A. Peres and Steven J. MacKenzie, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, September 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp156
'Strawberry Star': A Spotted, Fancy-Leaved Caladium for Use in Containers and Landscapes (ENH1201/EP462)
 'Strawberry Star' is a fancy-leaved variety with a primarily white leaf face and attractive red spots. It is similar to 'Marie Moir' in leaf color and coloration pattern but different from 'Marie Moir' in petiole color. Compared to 'Marie Moir', 'Strawberry Star' sprouts earlier, produces high-quality container plants, demonstrates better landscape performance, and yields more tubers. These improvements make 'Strawberry Star' a desirable replacement for 'Marie Moir' and an additional sun-tolerant variety for the landscape plant palette. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Zhanao Deng, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2012.
'Strawberry Star' is a fancy-leaved variety with a primarily white leaf face and attractive red spots. It is similar to 'Marie Moir' in leaf color and coloration pattern but different from 'Marie Moir' in petiole color. Compared to 'Marie Moir', 'Strawberry Star' sprouts earlier, produces high-quality container plants, demonstrates better landscape performance, and yields more tubers. These improvements make 'Strawberry Star' a desirable replacement for 'Marie Moir' and an additional sun-tolerant variety for the landscape plant palette. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Zhanao Deng, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep462






