The booming craft beer industry, rising prices of hops, and demand for locally-produced ingredients have recently increased interest in local hop production among growers and brewers. This article describes crop management practices and labor inputs required for small-scale hop production in Florida, with the aim of assisting growers with investment and farm management decisions. It is part of a larger series that will review the challenges of hop production in Florida, based on research experience at the UF/IFAS Gulf Coast Research and Education Center in Balm, FL. This new 6-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department was written by Shinsuke Agehara, Mariel Gallardo, Aleyda Acosta-Rangel, Zhanao Deng, Jack Rechcigl, Tianyuan Luo, and Qi Qiu.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1409
Tag: Shinsuke Agehara
Construcción del Sistema de Tutorado para Lúpulo y su Establecimiento en Florida
El lúpulo (Humulus lupulus L.) es un ingrediente esencial en la elaboración de cerveza, que agrega amargura y sabor a la cerveza. Impulsada por el reciente movimiento de la cerveza artesanal, la producción de lúpulo se está expandiendo hacia estados no tradicionales en la producción de lúpulo. En Florida, aunque la producción comercial de lúpulo es casi inexistente, la cantidad de cervecerías artesanales aumentó de 45 en 2011 a 285 en 2018, y el impacto económico de la industria de la cerveza artesanal en Florida supera los $3 mil millones. Este nuevo artículo de 7 páginas, escrito por Shinsuke Agehara, Aleyda Acosta-Rangel, Zhanao Deng, Jack Rechcigl y Simon Bollin, traducido por Mariel Gallardo y publicado por el Horticultural Sciences Department de UF/IFAS, proporciona pautas y consideraciones para construir el sistema de tutorado para lúpulo y su establecimiento en Florida, utilizando como modelo, el campo de investigación del UF/IFAS Gulf Coast Research and Education Center (GCREC).
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1408
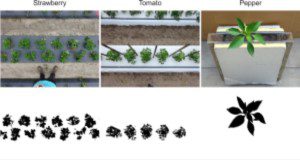
Useful Image-Based Techniques for Manual and Automatic Counting Using ImageJ for Horticultural Research
Counts (e.g., number of leaves, fruits, seeds, or plants) are a common type of data gathered in horticultural research. In many instances, using ImageJ can increase the ease and accuracy of gathering count data. When image processing can easily separate objects of interest from the background, automatic counting with ImageJ can eliminate tedious manual counting processes. Furthermore, additional plant growth data, such as leaf area, plant width, and canopy area, can be collected from the same image. The image processing and analysis techniques introduced in this article are easily accessible and simple to use and thus can be adopted not only by researchers, but also by Extension agents and students. This new 10-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department is part of a series introducing various image-based measurements with ImageJ for horticultural research. Written by Lillian Pride and Shinsuke Agehara.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1405
A Simple, Inexpensive, and Portable Image-Based Technique for Nondestructive Leaf Area Measurements
This new 6-page article, part of a series introducing various image-based measurements for horticultural research, introduces a simple, inexpensive, and portable image-based technique for nondestructive leaf area measurements. It uses an imaging apparatus made with ordinary office supplies to obtain leaf images in greenhouse or field environments. Leaf images are then processed and analyzed to measure leaf area using ImageJ, an open-source image processing program. Because both image capture and analysis are performed nondestructively, leaf area can be measured on the same leaf repeatedly, enabling the monitoring of leaf growth over time, as well as photosynthesis and transpiration. This technique is particularly useful to researchers and students studying leaf growth and physiology in greenhouse or field environments. Written by Shinsuke Agehara, Lillian Pride, Mariel Gallardo, and Jose Hernandez-Monterroza, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1395
Métodos para el establecimiento de trasplantes de fresa en Florida
Florida es el segundo productor de fresa más grade de los Estados Unidos, con un valor estimado de $337 millones. La siembra inicia entre finales de septiembre y mediados de octubre, en momentos donde las altas temperaturas representan un reto significativo para la sobrevivencia de los trasplantes, y por tanto también para el rendimiento y la calidad. El propósito principal de esta publicación es proporcionar recomendaciones basadas en resultados de investigación sobre métodos de establecimientos de trasplantes para productores de fresas en la Florida.
This new 5-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department is the Spanish translation of HS1376, Methods for Strawberry Transplant Establishment in Florida. Written by Emmanuel Torres-Quezada, Lincoln Zotarelli, Vance M. Whitaker, and Shinsuke Agehara.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1378
Methods for Strawberry Transplant Establishment in Florida
Florida is the second largest strawberry producer in the United States, with an annual farm gate value of about $300 million. Planting occurs from late September through late October, and high air temperatures pose significant challenges for transplant establishment and thus yield and fruit quality. The primary purpose of this new 4-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department is to provide research-based recommendations on transplant establishment methods for strawberry growers in Florida. The techniques presented are overhead irrigation application methods and practices, strawberry plugs and bare-root transplants, crop protectants, and reflective mulching. Written by Emmanuel Torres-Quezada, Lincoln Zotarelli, Vance M. Whitaker, and Shinsuke Agehara.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1376
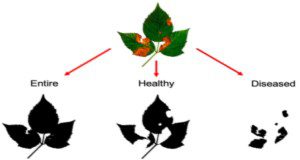
How to Measure Leaf Disease Damage Using Image Analysis in ImageJ
This new 13-page article introduces simple image processing and analysis techniques to quantify leaf disease damage using ImageJ, an open-source image processing program. These techniques are not meant to replace crop scouting or disease diagnosis by a plant diagnostic laboratory, but rather to provide a supplemental tool for making quantitative measurements of leaf disease damage. Similar techniques are also available for plant growth assessment, including plant height, plant width, and canopy cover area. The image processing and analysis techniques introduced in this article are fairly simple to use and thus can be adopted not only by researchers, but also by producers, crop consultants, Extension agents, and students. Written by Lillian Pride, Gary Vallad, and Shinsuke Agehara, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1382
Selection and Preparation of Planting Material for Successful Hop Production in Florida
Hops (Humulus lupulus L.), an essential ingredient in beer, have potential to develop as a viable alternative crop in Florida. In our surveys, many breweries have expressed strong interest in using locally grown hops. However, hop production is plagued by many diseases, most of which were inadvertently introduced through the movement of contaminated planting material. The primary purposes of this new 7-page article are to prevent the introduction of these diseases into the state and to provide recommendations for selecting and preparing planting material for successful hop production in Florida. This publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department is part of a larger series that will review the challenges of hop production, based on research experience at the UF/IFAS Gulf Coast Research and Education Center (UF/IFAS GCREC) in Balm, FL.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1381
Using Supplemental Lighting to Control Flowering of Hops in Florida
Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) are an emerging crop in Florida. Florida’s craft beer industry has experienced significant growth over the last 10 years, with 285 breweries producing 42.6 million gallons of beer and generating an economic impact of $3.6 billion in 2018. To respond to their strong demand for locally grown hops, an interdisciplinary hops research team is currently studying optimum crop management practices at the UF/IFAS Gulf Coast Research and Education Center (UF/IFAS GCREC). In Florida, the major yield-limiting factor is premature flowering induced by inadequate day length. This new 4-page article, written by Shinsuke Agehara and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, provides guidelines for supplemental lighting to control flowering of hops in Florida.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1365
Hop Yard Establishment and Trellis Construction in Florida
Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) are an essential ingredient in brewing, adding bitterness and flavor to beer. Driven by the recent craft beer movement, hop production is expanding into nontraditional hop-producing states. In Florida, while commercial hop production is almost nonexistent, the number of craft breweries in Florida increased from 45 in 2011 to 285 in 2018, and the economic impact of Florida’s craft beer industry exceeds $3 billion. This new 7-page article, written by Shinsuke Agehara, Aleyda Acosta-Rangel, Zhanao Deng, Jack Rechcigl, and Simon Bollin and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, provides guidelines and considerations for building a hop yard in Florida, using the UF/IFAS Gulf Coast Research and Education Center’s research hop yard as a model.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1354
Simple Imaging Techniques for Plant Growth Assessment
Quantification of plant phenotypic traits, such as height, width, stem diameter, and leaf area, is often performed manually in the field; however, these measurements can be performed more quickly and precisely through simple imaging techniques using an image processing program. This new 5-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, written by Shinsuke Agehara, describes simple imaging techniques for plant growth assessment using the public domain program ImageJ.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1353
Choosing the Right Blackberry Cultivar in Subtropical Florida
Blackberry (Rubus spp.) is a deciduous berry crop and the fourth most economically important berry crop in the United States. Driven by the growing demand for blackberries, production recently expanded to the southeastern United States. In Florida, however, commercial blackberry production is limited primarily to small commercial U-pick operations. The main challenges include insufficient chill hours and poor fruit quality associated with the subtropical climate. This new 6-page article, a publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, will discuss important cultivar selection criteria and recommended blackberry cultivars in subtropical Florida. Written by Shinsuke Agehara, Syuan-You Lin, and Zhanao Deng.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1352
Guidelines for Pomegranate Nutrient Management in Florida
Many Florida growers are interested in the potential of pomegranate as an alternative fruit crop. The first flush of flowers produces the best quality fruit, and climatic conditions have a great impact on the timing of flowering. Proper fertilization is critical to promote healthy canopy development, minimize nutrient disorders, and maximize fruit yield and quality. This new 5-page article, written by Shinsuke Agehara, Weining Wang, and Ali Sarkhosh and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, provides guidelines for pomegranate nutrient management in Florida.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1347
Florida Brilliance Strawberry
‘Florida Brilliance’ is a new short-day strawberry cultivar released by the University of Florida and commercialized in 2018. This 4-page document describes important attributes of this cultivar and makes management recommendations for growers. Written by Vance Whitaker, Natalia A. Peres, and Shinsuke Agehara and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, October 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1322
'Florida Beauty' Strawberry
‘Florida Beauty’ is a new strawberry cultivar released by the University of Florida and commercialized in 2017. This 4-page document describes the characteristics, performance, growth, and management of this cultivar. Written by Vance M. Whitaker, Natalia A. Peres, and Shinsuke Agehara and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, November 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1307
Production Guidelines for Globe Artichoke in Florida
Globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus L.) belongs to a genus of thistle-like plants in the sunflower (Asteracae) family and is cultivated for its flower buds. This four-page fact sheet discusses production guidelines for artichoke in Florida. Written by Shinsuke Agehara and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1289