Plant-parasitic nematodes are among the least understood and most difficult pests to manage on turfgrass in Florida. They are very small, and most can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. They use a stylet to puncture plant cells, to inject digestive juices into them, and to ingest plant fluids. The most reliable way to determine whether plant-parasitic nematodes are involved in a turf problem is to have a nematode assay conducted by a professional nematode diagnostic lab. This 6-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ng039
Tag: William T. Crow
Nematode Management on Athletic Fields
Turfgrasses are essential components of many athletic fields, racetracks, and parks. Plant-parasitic nematodes can damage athletic fields by weakening turf root systems and causing turf to pull up during play, which can create dangerous conditions for players. To help keep turf–and athletes–healthy, this 7-page fact sheet written by William T. Crow and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology explains how to spot and manage a nematode problem in an athletic field.
edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in126
Nematode Management for Golf Courses in Florida
UF/IFAS is committed to providing the most current information on the notoriously difficult problem of managing nematodes on golf courses. This publication is updated and revised whenever there is a breaking development, to bring you the new information and management advice. Nine pages, revised in January 2017 by William T. Crow and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in124
Dagger Nematode Xiphinema spp. (Cobb, 1913) Inglis, 1983 (Nematoda: Enoplea: Dorylaimia: Dorylaimina: Xiphinematinae)
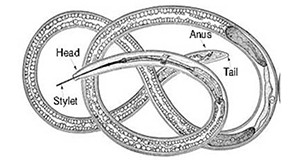
Dagger nematodes parasitize plants. They cause economic damage and death of host crops through feeding on the roots and by spreading viral mosaic and wilting diseases, but field studies have shown that some control measures targeting reduction in the population of dagger nematodes can be effective in controlling viral diseases in susceptible crops. This 7-page fact sheet was written by William K. Heve, William T. Crow, and Tesfamarian Mengistu, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1097
Sting Nematode Belonolaimus longicaudatus Rau (Nematoda: Tylenchida: Belonolaimidae)
 Among the most destructive plant-parasitic nematodes to a wide range of plants, Belonolaimus longicaudatus damages plant roots. When the plants cannot take up water and nutrients from the soil, they become stunted, wilt, and with severe infestation, die. Florida is considered to be the point-of-origin for Belonolaimus longicaudatus and therefore this nematode exhibits a great deal of diversity in morphology, host preference, and genetics in our region. This 6-page fact sheet was written by W. T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, March 2015. (Photo W. T. Crow, UF/IFAS)
Among the most destructive plant-parasitic nematodes to a wide range of plants, Belonolaimus longicaudatus damages plant roots. When the plants cannot take up water and nutrients from the soil, they become stunted, wilt, and with severe infestation, die. Florida is considered to be the point-of-origin for Belonolaimus longicaudatus and therefore this nematode exhibits a great deal of diversity in morphology, host preference, and genetics in our region. This 6-page fact sheet was written by W. T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, March 2015. (Photo W. T. Crow, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1080
Nematode Management for Bedding Plants
 Florida is the “land of flowers.” Surely, one of the things that Florida is known for is the beauty of its vegetation. Due to the tropical and subtropical environment, color can abound in Florida landscapes year-round. Unfortunately, plants are not the only organisms that enjoy the mild climate. Due to warm temperatures, sandy soil, and humidity, Florida has more than its fair share of pests and pathogens that attack bedding plants. Plant-parasitic nematodes can be among the most damaging and hard-to-control of these organisms. This 11-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, February 2014.
Florida is the “land of flowers.” Surely, one of the things that Florida is known for is the beauty of its vegetation. Due to the tropical and subtropical environment, color can abound in Florida landscapes year-round. Unfortunately, plants are not the only organisms that enjoy the mild climate. Due to warm temperatures, sandy soil, and humidity, Florida has more than its fair share of pests and pathogens that attack bedding plants. Plant-parasitic nematodes can be among the most damaging and hard-to-control of these organisms. This 11-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in470
Nematode Management in Residential Lawns (ENY006/NG039)
 Plant-parasitic nematodes are among the least understood and most difficult pests to manage on turfgrass in Florida. They are very small, and most can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. They use a stylet to puncture plant cells, to inject digestive juices into them, and to ingest plant fluids. The most reliable way to determine whether plant-parasitic nematodes are involved in a turf problem is to have a nematode assay conducted by a professional nematode diagnostic lab. This 6-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2013.
Plant-parasitic nematodes are among the least understood and most difficult pests to manage on turfgrass in Florida. They are very small, and most can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. They use a stylet to puncture plant cells, to inject digestive juices into them, and to ingest plant fluids. The most reliable way to determine whether plant-parasitic nematodes are involved in a turf problem is to have a nematode assay conducted by a professional nematode diagnostic lab. This 6-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ng039
Nematode Management for Golf Courses in Florida (ENY008/IN124)
 Of all the pests that commonly affect golf course turf in Florida, nematodes are probably the least understood and most difficult to manage. Nematode problems are more common and more severe in Florida than in most other states because our climate and soils provide a perfect habitat for many of the most destructive nematode species. This 8-page fact sheet explains what plant-parasitic nematodes are, how they affect turf, how to tell if they are a problem, and how to manage them. Written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2013.
Of all the pests that commonly affect golf course turf in Florida, nematodes are probably the least understood and most difficult to manage. Nematode problems are more common and more severe in Florida than in most other states because our climate and soils provide a perfect habitat for many of the most destructive nematode species. This 8-page fact sheet explains what plant-parasitic nematodes are, how they affect turf, how to tell if they are a problem, and how to manage them. Written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in124
Amaryllis Lesion Nematode, Pratylenchus hippeastri Inserra et al., 2006 (Nematoda: Tylenchida: Pratylenchidae) (EENY546/IN975)
 Amaryllis lesion nematode is an important nematode pest of amaryllis in Florida. It reduces plant vigor, flower yield, and bulb size. As the nematodes tunnel through the root, the damaged cells die and collapse, forming lesions on the exterior and the interior of the root tissue. This 4-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2013.
Amaryllis lesion nematode is an important nematode pest of amaryllis in Florida. It reduces plant vigor, flower yield, and bulb size. As the nematodes tunnel through the root, the damaged cells die and collapse, forming lesions on the exterior and the interior of the root tissue. This 4-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in975
Spiral Nematode, Helicotylenchus pseudorobustus (Steiner, 1941) Golden, 1956 (Nematoda: Tylenchida: Hoplolaimidae) (EENY544/IN973)
 Spiral nematodes of the genus Helicotylenchus are among the most ubiquitous plant-parasitic nematodes worldwide. Helicotylenchus pseudorobustus is a species common in Florida and the southeastern United States and is frequently found associated with turfgrasses and other grass hosts in the region. On most plants, it is not considered particularly damaging, but recent research has shown that this species suppresses growth of certain turfgrass hosts. Seashore paspalum, a turfgrass used in tropical and subtropical regions, is particularly susceptible to infestation. This 4-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2013.
Spiral nematodes of the genus Helicotylenchus are among the most ubiquitous plant-parasitic nematodes worldwide. Helicotylenchus pseudorobustus is a species common in Florida and the southeastern United States and is frequently found associated with turfgrasses and other grass hosts in the region. On most plants, it is not considered particularly damaging, but recent research has shown that this species suppresses growth of certain turfgrass hosts. Seashore paspalum, a turfgrass used in tropical and subtropical regions, is particularly susceptible to infestation. This 4-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in973
Burrowing Nematode Radopholus similis (Cobb, 1893) Thorne, 1949 (Nematoda: Secernentea: Tylenchida: Pratylenchidae: Pratylenchinae) (EENY542/IN969)
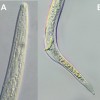 The burrowing nematode is the most economically important nematode parasite of banana in the world. Infection causes toppling disease of banana, yellows disease of pepper and spreading decline of citrus. These diseases are the result of burrowing nematode infection destroying root tissue, leaving plants with little to no support or ability to take up water and translocate nutrients. Because of the damage that it causes to citrus, ornamentals and other agricultural industries, worldwide, burrowing nematode is one of the most regulated nematode plant pests. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Nicholas Sekora and William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, November 2012.
The burrowing nematode is the most economically important nematode parasite of banana in the world. Infection causes toppling disease of banana, yellows disease of pepper and spreading decline of citrus. These diseases are the result of burrowing nematode infection destroying root tissue, leaving plants with little to no support or ability to take up water and translocate nutrients. Because of the damage that it causes to citrus, ornamentals and other agricultural industries, worldwide, burrowing nematode is one of the most regulated nematode plant pests. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Nicholas Sekora and William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in969
Earthworm, suborder Crassiclitellata, cohort Terrimegadrili (Jamieson, 1988) (EENY532/IN946)
 Like insects, earthworms are among the animals most frequently encountered by many Floridians. Our kids play with them, dissect them in middle school biology, we fish with them, they crawl across our sidewalks and live in our flower pots. Despite this, their ecological and economic importance often goes unrecognized. Earthworms have several important ecological roles. Additionally, some species are used commercially for bait, animal feed, environmental remediation, and composting. This 6-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2012.
Like insects, earthworms are among the animals most frequently encountered by many Floridians. Our kids play with them, dissect them in middle school biology, we fish with them, they crawl across our sidewalks and live in our flower pots. Despite this, their ecological and economic importance often goes unrecognized. Earthworms have several important ecological roles. Additionally, some species are used commercially for bait, animal feed, environmental remediation, and composting. This 6-page fact sheet was written by William T. Crow, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in946
EENY008/IN124 Nematode Management for Golf Courses
Revised! EENY008, a 9-page illustrated fact sheet by William T. Crow, answers explains what plant-parasitic nematodes are, how they affect turf, how to know if they are a problem, and how to manage them on a golf course. Published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in124

