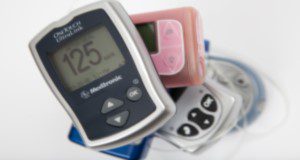
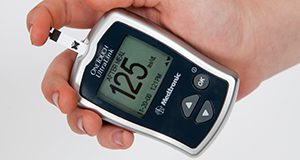
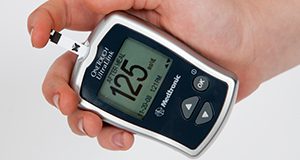
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is considered a public health issue within the United States because an estimated 37 million adults or 15% of the population have this disease. CKD is a disease characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function. Early prevention techniques such as a well-balanced diet reduce the progression of this disease. The purpose of this new 6-page article is to provide an overview of CKD and nutritional considerations. Written by Sofia Acevedo, Danielle Aycart, and Jeanette Andrade, and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs429
Tag: Diabetes
Reducing Your Risk for Type 2 Diabetes: The Power of Food
Type 2 diabetes is a medical condition where you have too much sugar in your blood. According to the Centers for Disease Control, nearly 1 in 10 adults have Type 2 diabetes and 1 in 3 adults have pre-diabetes. This new 14-page publication of the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department describes the modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes and tips to reduce your risk for diabetes. It also includes several example recipes. Written by Elena Torna, Jodi Fitzgerald, Danielle Nelson, Madison Woodard, and Jeanette Andrade.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs397
Dietas populares: Dieta cetogénica
La dieta cetogénica es una dieta alta en grasas y muy baja en carbohidratos. El primer uso documentado de la dieta cetogénica fue en 1921 para tratar la epilepsia en niños. En los últimos años, la dieta cetogénica ha ganado un resurgimiento como un medio potencial para perder peso. La dieta cetogénica se ha vuelto popular debido al respaldo de las celebridades y las influencias de las redes sociales, pero ¿es segura y efectiva?
This new 4-page article is the Spanish translation of FSHN20-44/FS403, Popular Diets: Ketogenic Diet. Written by Kelsey Gemmill, Daniela Rivero-Mendoza, and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs416
Planificacion de comidas para la diabetes: manejo de la ingesta de carbohidratos
Mantener una ingesta constante de carbohidratos durante todo el día es un método eficaz de planificación de comidas para ayudar a mantener su objetivo de niveles de glucosa en sangre. Los alimentos que contienen carbohidratos tienen el mayor efecto sobre los niveles de glucosa en sangre en comparación con los alimentos que contienen principalmente proteínas o grasas. Los carbohidratos en los alimentos que contribuyen a la glucosa en la sangre incluyen azúcares y almidones. Los alimentos que contienen carbohidratos se dividen en grupos según su similar contenido de carbohidratos por porción. La cantidad de carbohidratos que consuma se basa en sus objetivos de tratamiento de la diabetes y la tolerancia a los carbohidratos.
This new 2-page article is the Spanish translation of FSHN20-1/FS324, Diabetes Meal Planning: Managing Your Carbohydrate Intake, written by Nancy J. Gal and Wendy J. Dahl, translated by Daniela Rivero Mendoza, and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs377
Planificacion de menu para adultos con diabetes
La nutrición, la actividad física y la medicación son los tres componentes principales de un plan de manejo de la diabetes. Según la Asociación Americana de Diabetes, no existe un plan específico de comidas para la diabetes. Si tiene diabetes, es importante desempeñar un papel activo en su autocontrol diario. Al trabajar con un Dietista Nutricionista Registrado (RDN), preferiblemente uno que sea un educador certificado en diabetes (CDE), puede desarrollar un plan de nutrición personalizado basado en sus objetivos de tratamiento, medicamentos y preferencias personales.
This new 2-page article is a translation of FSHN19-3/FS323, Meal Planning for Adults with Diabetes, written by Nancy J. Gal and Wendy J. Dahl, translated by Daniela Rivero Mendoza, and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs376
Meal Planning for Adults with Diabetes
Nutrition, physical activity, and medication are the three main components of a diabetes management plan. According to the Americans Diabetes Association, there is no one diabetes meal plan; rather, it is a healthful eating pattern specifically designed to meet your individual needs. This new 2-page publication of the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department provides some basic tips for creating a personalized meal plan for adults with diabetes. Written by Nancy J. Gal and Wendy J. Dahl.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs323
Diabetes Meal Planning: Managing Your Carbohydrate Intake
If you have diabetes, maintaining a consistent carbohydrate intake throughout the day is an effective meal-planning method to help maintain your target blood glucose levels. Foods that contain carbohydrates have the greatest effect on blood glucose levels compared to foods that contain primarily protein or fat. Carbohydrates in foods that contribute to blood glucose includes sugars and starches. The amount of carbohydrate you consume is based on your diabetes treatment goals and carbohydrate tolerance. This new 3-page publication of the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, written by Nancy J. Gal and Wendy J. Dahl, provides a strategy for planning your daily menu to manage your carbohydrate intake.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs324
Symptoms and Treatment of Low Blood Glucose
Low blood glucose, also called hypoglycemia, can be life-threatening for people with diabetes. It can be caused by eating too little food, taking too much insulin or other diabetes medication, or being extra active. If left untreated, low blood glucose can progress to diabetic coma. Everyone with diabetes needs to know the symptoms of low blood glucose so they can take action right away. This 2-page fact sheet discusses preparation, symptoms, and treatment. Written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised February 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy521
Sick Day Management for Adults with Diabetes Who Take Insulin
When people have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and take multiple daily insulin injections, their blood glucose levels can rise drastically due to a cold or another minor illness. This can result in serious health problems. The best way for people with diabetes to prevent a minor illness from becoming a major illness is to have a personalized sick day plan designed with their health care provider before they become ill. This 4-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses ways in which illness affects diabetes control, development of a sick day plan, times to call your health care provider, checking blood glucose and urine ketones, medicines, and diet. Written by Nancy J. Gal and Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised June 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1281
Vida Saludable: Diabetes
La diabetes es una condición que ocurre cuando el cuerpo tiene dificultad para producir o utilizar la insulina. La insulina es una hormona que controla la cantidad de glucosa (azúcar) en nuestra sangre, informándole a las células cuanta glucosa pueden dejar entrar. Cuando una persona tiene diabetes, el cuerpo no produce o produce poca insulina, o produce una insulina que no funciona bien. Esto resulta en altos niveles de glucosa en la sangre. Controlar los niveles de glucosa en la sangre reduce el riesgo de otras complicaciones.
This 2-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses diabetes and management techniques. Written by Linda B. Bobroff and Paulina Wittkowsky, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised June 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy081
Vida Saludable: Diabetes
La diabetes es una condición en la que el cuerpo tiene dificultad de producir o utilizar la insulina. La insulina es una hormona que controla la cantidad de glucosa (azúcar) en nuestra sangre. Cuando una persona tiene diabetes, el cuerpo no produce insulina o produce muy poca insulina o una insulina que no funciona bien. Esto resulta en altos niveles de glucosa en la sangre.
This 4-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses diabetes, possible consequences of high blood glucose, risk factors, healthy weights, symptoms, control methods, and ways to choose a healthy diet. Written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised October 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy079
Vida Saludable: Fuentes de informacion sobre la diabetes
Muchos recursos sobre la diabetes se encuentra en línea.
This 2-page fact sheet provides a list of resources with information on diabetes. Written by Linda B. Bobroff and Paulina Wittkowsky, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised August 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy083
Diabetes-Related Websites
Managing diabetes requires learning about your disease, making positive lifestyle choices, and being a partner with your health care team. Finding and using current and reliable sources of health information on the Internet also helps you make choices that support your health while avoiding potentially harmful products and practices. This 1-page fact sheet is a major revision that provides links to government, educational, and recognized professional websites on diabetes. Written by Linda B. Bobroff and Nancy J. Gal, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences. Revised May 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1103
Vivir con Diabetes
La diabetes es una enfermedad que afecta a más de 29 millones de estadounidenses. Aunque no existe cura para tipo 1 o tipo 2 diabetes, con los cuidados necesarios se puede controlar la enfermedad.
This 5-page fact sheet is the Spanish version of Living with Diabetes. This major revision provides an overview of diabetes, a list of people at high risk of developing the disease, and a description of each type of diabetes. It also discusses tests, possible health problems, control of blood glucose, and diabetes management. Written by Nancy J. Gal and Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised May 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy924
Healthy Living: Taking Care from Head to Toe
If you have diabetes, pay special attention to your skin, eyes, teeth, gums, and feet. These areas are at high risk for complications. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that gives helpful information on ways to take care of these areas to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. Written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, revised May 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy886
Healthy Living: Diabetes
Diabetes is a serious health condition that occurs when a person’s body has difficulty making or using insulin, which results in high blood glucose (blood sugar) and can lead to other complications. This 3-page facts sheet covers the effects of high blood glucose, who is at risk, the symptoms and management of the condition, and additional resources for those with or at risk of developing diabetes. Written by Linda B. Bobroff, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Paulina Wittkowsky, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy078
Vida Saludable: Examinando el nivel de glucosa en la sangre
 Examinar el nivel de glucosa en su sangre es una parte importante en el manejo de la diabetes. El conocer los valores de glucosa en su sangre le indica que tan eficiente está funcionando su plan de cuidado y si debe hacer algún cambio. ¡Continúe leyendo para aprender más!
Examinar el nivel de glucosa en su sangre es una parte importante en el manejo de la diabetes. El conocer los valores de glucosa en su sangre le indica que tan eficiente está funcionando su plan de cuidado y si debe hacer algún cambio. ¡Continúe leyendo para aprender más!
This 4-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Healthy Living: Checking Blood Glucose. Written by Jennifer Hillan and Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, January 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy908
Alimentacion Saludable: Nutricion y diabetes
 Una dieta saludable, junto con ejercicio y medicinas, pueden ayudar a controlar la diabetes y reducir el riesgo de complicaciones. Un estilo de vida saludable también ayuda a personas con alto riesgo de diabetes a reducir las probabilidades de padecer de esta enfermedad. Para una dieta saludable, siga estos consejos. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff, Jennifer Hillan, y Emily Minton, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2015.
Una dieta saludable, junto con ejercicio y medicinas, pueden ayudar a controlar la diabetes y reducir el riesgo de complicaciones. Un estilo de vida saludable también ayuda a personas con alto riesgo de diabetes a reducir las probabilidades de padecer de esta enfermedad. Para una dieta saludable, siga estos consejos. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff, Jennifer Hillan, y Emily Minton, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy665
Healthy Living: Checking Blood Glucose
 Checking your blood glucose levels is an important part of managing diabetes. Your blood glucose values let you know how well your care plan is working and if you need to make any changes. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jennifer Hillan and Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2015.(Photo iStock/Thinkstock.com)
Checking your blood glucose levels is an important part of managing diabetes. Your blood glucose values let you know how well your care plan is working and if you need to make any changes. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jennifer Hillan and Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2015.(Photo iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy868
Healthy Living: Diabetes Warning Signs
 Could you have diabetes and not know it? It is possible. More than one-fourth of the people who have diabetes don’t know they have the disease! Treating and managing diabetes greatly decreases the risk of diabetes-related health problems. Review the list of warning signs below and check any that you have experienced. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, July 2014.
Could you have diabetes and not know it? It is possible. More than one-fourth of the people who have diabetes don’t know they have the disease! Treating and managing diabetes greatly decreases the risk of diabetes-related health problems. Review the list of warning signs below and check any that you have experienced. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy084