Rice production in the Everglades Agriculture Area (EAA) of Florida dates back nearly seven decades. For a brief period in the 1950s about 2,000 acres of rice was grown in the EAA. Rice was reintroduced in the EAA in 1977 after it was demonstrated that rice could be successfully incorporated into the sugarcane production cycle during the fallow period. This three-page fact sheet provides a history of rice production in Florida and information about rice varieties grown in Florida. Written by Jehangir H. Bhadha, Luigi Trotta, and Matthew VanWeelden and published by the Soil and Water Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss653
Category: Agriculture
Organic Management of Vegetable Diseases, Part II: Foliar Pathogens
The successful management of both soilborne and foliar diseases requires a multifaceted program, taking into consideration variety selection, cultural methods, biologicals, and chemical applications approved by the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI) and certified organic under the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Organic Program (NOP). This review emphasizes the management of foliar disease and serves as a guide to assist growers in selecting strategies to manage disease in a sustainable system. Written by Gary Vallad and published by the Department of Plant Pathology.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp170
Viburnum Downy Mildew
Downy mildew on viburnum is currently a serious concern throughout Florida. Winters in south Florida combine high humidity with cool nights, creating ideal conditions for disease development. Downy mildews are caused by several different species that tend to be host specific. Plasmopara vibruni is the pathogen that affects viburnum. This five-page fact sheet describes the hosts, symptoms, and management practices for Viburnum Downy Mildew.
Written by A. J. Palmateer and published by the Plant Pathology Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp329
Opinion Leadership and Local Food

Three new articles have been published as part of a new series on Opinion Leadership and Local Food. These articles look at the role opinion leaders, or individuals who have a large amount of influence within their respective social circles, can have on motivating their peers to join in purchasing local food. The articles are as follows:
1. Opinion Leadership and the Perceived Health Benefits of Local Food (http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc266)
2. Opinion Leadership and the Perceived Effects of Local Food on the Local Community (http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc267)
3. Opinion Leadership and the Perceived Economic Benefits of Local Food (http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc268)
Written by Layne S. Marshall, Melissa R. Taylor, and Alexa J. Lamm and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
Worker Protection Standard: Application Exclusion Zone (AEZ)

The Worker Protection Standard (WPS) is a Federal regulation designed to protect agricultural workers (people involved in the production of agricultural plants) and pesticide handlers (people mixing, loading, or applying pesticides or doing other tasks involving direct contact with pesticides).The “Application Exclusion Zone” or AEZ is a new term used in the WPS rule; it refers to the area surrounding the pesticide application equipment. This three-page fact sheet explains this new rule. Written by Fred M. Fishel and Tatiana Sanchez and published by the Agronomy Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi263
The Florida Bull Test 2014/2015
The 2014-2015 Florida Bull Test concluded with the evaluation of 103 bulls. The test assessed the performance potential and breeding soundness of bulls consigned to the program at the UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC). This 9-page fact sheet covers the test procedures, feed efficiency assessment, test rules and regulations, health requirements, test results, and sale summary. Written by Carla D. Sanford, G. Cliff Lamb, and Nicolas DiLorenzo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, June 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an325
How the Veterinary Feed Directive Affects Cattle Owners
The Veterinary Feed Directive is a federal regulation from the Food and Drug Administration that will change the additives that can be included in animal feed, the ways in which cattle producers manage their animals and veterinarians interact with cattle owners, and the products available for use on the ranch. This 3-page fact sheet provides an overview of the new regulation’s nature, functions, requirements, and implications for cattle owners. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, July 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an327
Chilling Injury in Tropical Foliage Plants: III. Dieffenbachia
A chilling temperature is any temperature that is cold enough to cause plant injury but not cold enough to freeze the plant. Chilling injury can occur to tropical foliage plants if greenhouses become too cold or if plants are exposed to chilling temperatures outside of the greenhouse during packing and shipping. Dieffenbachia, commonly known as dumb cane, ranks among the top five most popular foliage plant genera produced and sold in the United States. This four-page fact sheet describes the chilling temperatures of Dieffenbachia cultivars in order to assist growers to better manage greenhouse temperatures. Written by Jianjun Chen and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep530
A Semen Extender for the Short-Term Storage of Fish Sperm
Aquaculturists worldwide use artificial or induced spawning of fish to maximize egg and larval production from fish that cannot normally be bred in captivity. Despite the wide global use of this technique, and much literature published, the success rates of induced spawning are consistently variable. One often overlooked reason for the variable success rates is that successful rates of fertilization, hatching, and larval survival are most dependent on high-quality sperm and the surrounding fluid that supports sperm function. It is difficult to obtain consistent, good-quality spermiations (releases of spermatozoa); to keep sperm alive after collection and during storage and transport; and to freeze large volumes of semen at one time. Therefore, a successful fish breeding program requiring sperm begins with a source of high-quality semen, and its proper collection, handling, and storage. This three-page article written by Frank A. Chapman and published by the Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences in the School of Forest Resources and Conservation describes how to make and use a semen extender that will maximize the volume and preserve the viability of obtained semen.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa193
Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli: Detection, Differentiation, and Implications for Food Safety
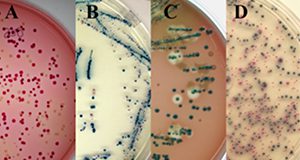
Shiga toxin is a protein found within the genome of a type of virus called a bacteriophage. These bacteriophages can integrate into the genomes of the bacterium E. Coli. Even though most E. coli are benign or even beneficial members of our gut microbial communities, strains carrying Shiga-toxin encoding genes are highly pathogenic in humans and other animals. This six-page fact sheet discusses the two types of Shiga toxins and the best approaches to identifying and determining which Shiga toxin is present. Written by William J. Zaragoza, Max Teplitski, and Clifton K. Fagerquist and published by the Department of Soil and Water Sciences.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss654
Texas Phoenix Palm Decline

Texas Phoenix palm decline is a new disease in Florida, caused by an unculturable bacterium. It is a fatal, systemic disease that kills palms relatively quickly. This six-page fact sheet explains the pathogen and hosts of TPPD, its symptoms, how to diagnose it, and provides disease management practices. Written by Nigel A. Harrison and Monica L. Elliott and published by the Plant Pathology Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp163
Summer Squash Production in Miami-Dade County, Florida

Summer squash is an important vegetable crop in Miami-Dade County. It is grown annually on about 6,000 acres and sold nationwide during the winter in the fresh market. This 16-page fact sheet describes the varieties of summer squash, land preparation and transplanting, what fertilizer to use, irrigation and freeze protection, disease management, insect management, weed management, harvest, and crop rotation. Written by D. Seal, S. Zhang, M. Ozores-Hampton, P. Dittmar, Y. Li, W. Klassen, Q. Wang, and T. Olczyk and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/tr012
Identifying the Attitudes and Preferences of Parents and Children for Seafood: Summary of Focus Group Results

Seafood contains high-quality protein, vitamins, and minerals that have many health benefits, but the average family’s consumption of seafood in the United States remains below recommended levels. To begin to understand how to raise consumption levels, the study described in this three-page fact sheet focused on the influence parents’ seafood consumption habits may have on their children. Written by Anh Sam, Xiang Bi, and Lisa House and published by the Department of Food and Resource Economics.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe992
How to Quantify Nosema Spores Infection Rate in a Honey Bee Colony
Nosema are single-celled fungal parasites that infect various animal hosts. One species, Nosema ceranae, has become the dominant microsporidian infection in western honey bee colonies. When honey bees ingest Nosema spores, many eventually starve to death because the spores replicate in the stomach and hijack the bee’s nutrition. The risk of Nosema infection can be particularly unsettling to beekeepers because colonies often do not show signs of infection until the colony is severely diminished.
This 5-page fact sheet written by Ashley N. Mortensen, Cameron J. Jack, Meghan McConnell, Liana Teigen, and Jamie Ellis and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology explains how to diagnose and quantify Nosema infection in a honey bee colony.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1123
Estimated Costs and Regional Economic Impacts of the Oriental Fruit Fly (Bactrocera dorsalis) Outbreak in Miami-Dade County, Florida
Oriental fruit flies, very destructive pests of fruits, were first detected in the Redland area of Miami-Dade County on August 26, 2015, and as of January 2016, 165 flies had been captured. This triggered an eradication program and establishment of a quarantine area composed of agricultural operations and nonagricultural properties, such as residential and commercial areas. As part of the effort to eradicate the fruit fly, growers and packers in the quarantine area are required to sign a compliance agreement that outlines the procedures necessary for harvesting, handling, and postharvest processing of agricultural products that may serve as hosts for any life cycle of the fruit fly. This 12-page fact sheet written by Sergio Alvarez, Edward A. Evans, and Alan W. Hodges and published by the UF Food and Resource Economics Department provides estimates of the direct and indirect losses to Florida’s agriculture and related sectors as a result of the outbreak and ensuing quarantine and eradication programs.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe988
2016 US Beef Cattle Market Outlook
US cattle markets have experienced a roller coaster ride over the last several years, with cattle prices have been supported by a declining US beef cow herd and strong beef demand. But a turning point in the US cattle industry occurred at the beginning of 2015. This 7-page fact sheet witten by Chris Prevatt and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics includes highlights of the US cattle market’s cycle since 2004 and the estimated outlook for 2016, a brief analysis of the supply situation, food and forage conditions, demand and trade, competing meats, and the 2016 beef price outlook.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe987
Huanglongbing (HLB; citrus greening) and Nutrient Deficiency Identification

Huanglongbing (HLB) is a bacterial disease that is spread by an insect, the Asian citrus psyllid. This two-page fact sheet, which is best viewed as a PDF, http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdffiles/PP/PP32800.pdf, explains how to tell the difference between HLB symptoms and symptoms from nutrient deficiencies. Written by T. Vashisth, M.M. Dewdney, and J.D. Burrow and published by the Plant Pathology Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp328
Pest Identification Guide: Western Flower Thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande)
Western flower thrips transmits the carmovirus Pelargonium flower break virus (PFBV), the ilarvirus Tobacco streak virus (TSV), and the tospoviruses Chrysanthemum stem necrosis virus (CSNV), Groundnut ringspot virus (GRSV), Impatiens necrotic spot virus (INSV), Tomato chlorotic spot virus (TCSV), and Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). This species is primarily a flower feeder, so most damage would be expected on the flower or fruit. Learn to identify the western flower thrips with this two-page illustrated guide written by Jeffrey D. Cluever and Hugh A. Smith and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1127
Citrus Nutrition UF/IFAS Grower Trials (Pamphlet)
Interested in learning more about citrus nutrition grower trials? This two-page pamphlet provides information on the goals, objectives, benefits, and considerations of the trials as well as specific information about trials being held from 2015-2017. The pamphlet also contains a sign up form for the trials. Written by Tripti Vashisth and Jamie D. Burrow and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1283
Pest Identification Guide: Melon Thrips Thrips palmi Karny

Melon thrips transmits Calla lily chlorotic spot virus (CCSV), Groundnut bud necrosis virus (GBNV), Melon yellow spot virus (MYSV), Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), and Watermelon silver mottle virus (WSMoV). This species is primarily a foliage feeder (except in pepper and eggplant, where flowers are more preferred). Feeding on the leaves results in yellowing followed by death of leaf. Leaf feeding can also cause terminal growth to be discolored, stunted, and malformed. Feeding on fruit may cause scarring and malformed fruit. Learn to identify the melon thrips with this two-page illustrated guide written by Jeffrey D. Cluever and Hugh A. Smith and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology.
edis.ifas.ufl.edu/IN1126











