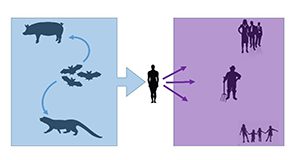
Bats benefit both natural ecosystems and people. Viruses that live in bats can harm people, but transmission of these pathogens from bats to humans can occur only when humans come too close to bats. Recently, misguided attempts to preserve human health have led to persecution of bats. In fact, however, what will keep people healthy is to protect bats and their habitat. This 4-page fact sheet written by Holly K. Ober and Samantha M. Wisely and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation explains how protecting bat roosts can reduce the likelihood of future zoonotic disease pandemics while also increasing the natural pest reduction services bats provide as they consume insects that cause damage to agronomic crops as well as the mosquitoes that transmit diseases like Zika, dengue, malaria, and chikungunya. Finally, protecting bat roosts keeps bats safely distanced from people, whereas destroying their homes risks the health of both people and bats because it forces bats into closer proximity to people.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw473
Author: Susan Gildersleeve
Yellow-Legged Hornet (suggested common name), Vespa velutina (Lepeletier 1836) (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Vespidae)
The yellow-legged hornet, Vespa velutina (Lepeletier), is a pest of concern outside of its native range. Vespa velutina is native to Southeast Asia and has invaded several regions in Europe, first appearing in France in 2004. As a generalist predator, they are a pest of honey bees and a major concern to many beekeepers. Vespa velutina has not been intercepted in North America, but it is believed to have high invasion potential. This 5-page fact sheet written by Krystal Ashman, Oliver Keller, and Cameron Jack and published by the UF/IFAS Entomology and Nematology Department describes the hornet and explains its live cycle, biology, and some of its predatory strategies.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1282
Asian Giant Hornet, Vespa mandarinia Smith (1852) (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Vespidae)
Vespa mandarinia Smith, commonly called the Asian giant hornet, is the largest hornet in the world. Its size and distinctive markings make it easily distinguishable from other Asian hornet species. Not only is the wasp occasionally life-threatening to humans, it can decimate a number of insect colonies, most notably wild and farmed honey bees. Vespa mandarinia is native to Japan and occurs in several countries in Asia. The first Vespa madarinia hornet detected in the United States was in Washington State in 2019. This 5-page fact sheet written by Caitlin Gill, Cameron Jack, and Andrea Lucky and published by the UF/IFAS Entomology and Nematology Department describes the hornet, its biology, its predatory strategies, and its medical significance. The fact sheet also provides some strategies for management of this dangerous and destructive hornet.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1281
Cultivo de ciruelas en Florida
Las ciruelas podrían ser un cultivo potencial para los productores y propietarios de viviendas en Florida y otras áreas de invierno templado en toda la costa del Golfo, pero muchas variedades de ciruelas de la costa oeste no funcionarán de manera consistente en Florida para producir fruta. Sin embargo, el programa de mejoramiento de fruta de hueso de la Universidad de Florida ha desarrollado cultivares que mejoran el potencial para el cultivo de ciruelas en Florida y otras áreas de invierno templado que tienen alta presión de enfermedades. Estos cultivares se recomiendan para probar en Florida. Los nombres de todos los cultivares de ciruela de la Universidad de Florida comienzan con el prefijo 'Gulf'. Estos cultivares son ciruelas de tipo japonés (Prunus salicina Lindl.) y tienen resistencia al escaldado de hojas de ciruela (Xylella fastidiosa) y a la bacteriosis o cribado (Xanthomonas campestris). El tamaño del fruto es satisfactorio (aproximadamente 1½ a 2 pulgadas de diámetro) con buena calidad del fruto. Maduran a principios o finales de mayo, aproximadamente dos semanas antes de que las ciruelas de otras áreas lleguen al Mercado.
This new 14-page fact sheet is the Spanish translation of HS895/HS250, Growing Plums in Florida, written by A. Sarkhosh, M. Olmstead, E. P. Miller, P. C. Andersen, and J. G. Williamson, translated by Tatiana Sanchez, and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1364
Indoor Vertical Farming Systems for Food Security and Resource Sustainability
Indoor vertical farming has been gaining increased popularity worldwide as a method of addressing food security while satisfying sustainability needs. This 5-page fact sheet written by Jiangxiao Qiu, Haimanote K. Bayabil, and Yuncong Li and published by the UF/IFAS School of Forest Resources and Conservation provides a comprehensive summary of the current status of indoor vertical farming in the United States and globally, commercial derivatives, major sustainability benefits and limitations and challenges. Learn about the limitations and challenges of the industry as well as the potential benefits both for food security and resource sustainability.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr429
Wading Birds of Northern Belize
Belize is home to over 605 bird species, many of them wading birds popular with bird watchers who enjoy their bright colors and charismatic behavior. Bird-watching is a major contributor to successful wildlife conservation and is important as native habitat loses ground to development. This 4-page fact sheet written by Venetia S. Briggs-Gonzalez, Jorge E. Ruano, Justin R. Dalaba and Frank J. Mazzotti and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation presents photos and descriptions that will help identify some common and some rare wading birds.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw469
White-tailed Deer of Florida

The white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) is the most economically important big game mammal in North America and Florida. This 12-page fact sheet written by Raoul K. Boughton, Bethany Wight, Samantha Wisely, Karen Hood, and Martin B. Main and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation provides an overview of the various subspecies of white-tailed deer with populations in Florida and describes their history, biology, and management.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw121
Diarrhea in Farmed White-tailed Deer Fawns
Diarrheal diseases, commonly called scour, are common in newborn ruminant farm animals including deer fawns. The clinical presentation can range from mild diarrhea without systemic disease to profuse, acute diarrhea associated with rapid dehydration and death, sometimes within hours of onset. Determining the particular agents associated with an outbreak of diarrhea is important for both prevention and treatment. This 5-page fact sheet written by Juan M. Campos Krauer and Samantha M. Wisely and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation focuses on disease in fawns caused by pathogenic types of Escherichia coli, describes the pathogens and how they infect fawns, and includes advice about treatment and prevention.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw463
Citrus Pest Quick Guide: Asian Citrus Psyllid (Diaphorina citri Kuwayama)
A one-page quick guide written by and published by the Entomology and Nematology Department presents the life cycle of the Asian citrus psyllid and provides several photos of the pest and the damage it causes to assist in identification.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1271
Citrus Pest Quick Guide: Citrus Leafminer (Phyllocnistis citrella Stainton)

A one-page quick guide written by Lauren M. Diepenbrock and Jamie D. Burrow and published by the Entomology and Nematology Department presents the life cycle of the citrus leafminer and provides several photos of the pest and the damage it causes to assist in identification.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1254
Sheep Bot Fly Oestrus ovis Linnaeus (1761) (Insecta: Diptera: Oestridae)
The sheep bot fly, Oestrus ovis, is an obligate parasite found all over the world. It cannot complete its life cycle without parasitizing the nasal passages, frontal and maxillary cavities, and sinuses of sheep. Unlike other flies, females do not lay eggs, instead depositing droplets containing live larvae into the nostrils of sheep. This 4-page fact sheet written by Hannah A. Sholar and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman and published by the UF/IFAS Entomology and Nematology Department describes the life cycle of the pest and its veterinary significance and management.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1267
Sea Turtle Conservation: 10 Ways You Can Help
All of Florida’s five species of sea turtles are in danger of extinction, largely as a result of people’s actions. Fortunately, however, there are simple steps Florida’s residents and visitors can take to help these remarkable animals. This illustrated 4-page fact sheet written by Jessica E. Swindall, Holly K. Ober, Margaret M. Lamont, and Raymond R. Carthy and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation provides 10 easy-to-follow suggestions for ways people can reduce harm to sea turtles.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw466
Cost of Producing Fresh Market Grapefruit in Indian River in 2018/19

This 4-page fact sheet written by Ariel Singerman and published by the UF/IFAS Food and Resource Economics Department presents the cost of production per acre for growing fresh grapefruit in the Indian River region during 2018/19. Estimates reflect costs and cultural practices for a panel of growers, particularly important information at this time because, since citrus greening (HLB) was found, growers have been modifying their practices from year to year in an attempt to cope with the disease.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe1078
Quantum GIS (QGIS): An Introduction to a Free Alternative to More Costly GIS Platforms
Geographic information system (GIS) software packages can be prohibitively expensive, causing many to shy away from mapping and spatial analysis. This 7-page fact sheet written by Jeffry M. Flenniken, Steven Stuglik, and Basil V. Iannone III and published by the UF/IFAS School of Forest Resources and Conservation introduces the reader to a free GIS software package called Quantum GIS (QGIS), walking the reader through simple GIS processes that can be used to visualize spatial patterns of importance to a variety of fields, including natural resources, agriculture, and urban planning. Learn how to create a land-cover map for a county of interest and create heatmaps that illustrate the density of a given attribute (Florida Springs for this example). This publication will benefit those interested in incorporating GIS into their work but who are unable to afford expensive proprietary GIS software packages, as well as anyone interested in learning a new GIS software package.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr428
Cost of Producing Processed Oranges in Southwest Florida in 2018/19
This 4-page fact sheet written by Ariel Singerman and published by the UF/IFAS Food and Resource Economics Department estimates the cost of production per acre for processed oranges grown in southwest Florida in 2018/19 based on a survey of southwest Florida growers.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe1077
How Effective and Humane Is Trap-Neuter-Release (TNR) for Feral Cats?
As the number of feral cats continues to increase, land managers, public health officials, and private citizens are voicing concerns about how to address the nuisance and public health impacts, as well as animal welfare concerns, that feral cats create. Trap-neuter-release programs aimed at reducing feral cat populations without euthanasia are gaining popularity in the United States. But do they work? Authors Mark Hostetler, Samantha M. Wisely, Steve Johnson, Elizabeth F. Pienaar, and Martin Main discuss the pros and cons of trap-neuter-release programs in this 8-page fact sheet published by the UF/IFAS Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw468
Fish Population Recruitment: What Recruitment Means and Why It Matters

Recruitment, the process by which small fish transition to older, larger life stages, is probably the most important process that regulates populations of fish, but it is complicated to understand. This 6-page fact sheet written by Edward V. Camp, Robert N. M. Ahrens, Angela B. Collins, and Kai Lorenzen and published by the UF/IFAS Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, School of Forest Resources and Conservation explains the recruitment process in fish populations and why recruitment is so important to fisheries science and management.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa222
Brown Dog Tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus Latreille (Arachnida: Acari: Ixodidae)
The brown dog tick is unusual among ticks in that it can complete its entire life cycle indoors as well as outdoors. Brown dog tick infestations can develop in dog kennels and residences, where populations can reach dramatic levels and cause dog diseases. This 6-page fact sheet written by and published by the UF/IFAS provides the distribution, description and identification, life cycle, and management of the brown dog tick as well as its hosts and the medical and veterinary significance of this troublesome pest.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in378
Termite Prevention and Control
This 16-page guide written by F. M. Oi, J. Davis, J. McConnell, J. Corbus, N. Nelson, and M. Atkinson and published by the UF/IFAS Entomology and Nematology Department is intended to help homeowners make informed choices about the best termite protection for their homes.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1277
Insect Bite Hypersensitivity in Horses
Allergic skin disease is a very common cause of itching in horses. The itching can severely affect the horse’s quality of life, leading to the horse wounding itself by biting or scratching, and it can reduce the utility of the horse. This 4-page fact sheet written by Rosanna Marsella, Nicky Craig, Carissa Wickens, and Samantha Brooks and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences explains how to manage allergic skin disease, control itching, treat secondary infections, and prevent the insect bites in the first place.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an359














