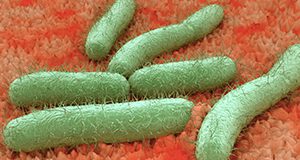
The bacterium Clostridium perfringens causes one of the most common types of foodborne gastroenteritis in the United States, often referred to as perfringens food poisoning. It is associated with consuming contaminated food that contains great numbers of vegetative cells and spores that will produce toxin inside the intestine. This six-page fact sheet describes the bacterium, outbreaks associated with it, and how to prevent illness from this bacterium. Written by Keith R. Schnedier, Renee Goodrich-Schneider, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Bruna Bertoldi and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs101
Tag: Food Science and Human Nutrition Department
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Bacillus cereus
Ingesting foods contaminated with Bacillus cereus bacteria can lead to nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Though B. cereus is commonly found in many types of fresh and processed foods, proper cooking, handling, and storage can minimize the risk of contamination. This 5-page fact sheet explains how B. cereus is transmitted, what foods it is commonly associated with, the methods used to prevent contamination, and good practices for receiving, handling, processing, and storing food. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée Goodrich Schneider, Rachael Silverberg, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Bruna Bertoldi, and published by the Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs269
Protein and the Older Adult

Protein is a nutrient that provides energy for our bodies and is involved in many vital functions, such as repair, maintenance, and immune function. This three-page document discusses the protein requirements for older adults. Written by Amanda L. Ford and Wendy J. Dahl and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs290
Citrus Flavonoid Effects on Obesity
The increased prevalence of obesity in recent decades has sparked tremendous concern worldwide. A type of phytochemical, called flavanoids, has been shown in clinical trials to provide significan benefits to overall health because of their antioxidant abilities. Flavanoids are especially abundant in citrus species. This two-page fact sheets describes the health benefits of citrus flavanoids. Written by Yu Wang and Laura Reuss and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs285
Preventing Foodborne Illness: E. coli O157:H7
This seven-page fact sheet discusses the common foodborne pathogen E. coli O157:H7, especially as it concerns food handlers, processors and retailers. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée Goodrich Schneider, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Bruna Bertoldi and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs097
Coconut Oil: A Heart Healthy Fat?
There are many claims about the health benefits of coconut oil. But what is the evidence behind these health claims? Read this five-page fact sheet to learn more about coconut oil and how it might affect heart health. Written by Wendy M. Gans and Gail P.A. Kauwell and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs289
Alimentos en Pure: Prueba de Textura con la Prueba de Desplome
This is the Spanish version of FS276 Pureed Foods: Texture Testing with the Slump Test. For individuals with dysphagia, the texture of puréed foods is extremely important. If the puréed foods are either too thick or too thin, it can make it more difficult to swallow. The slump test is a quick, easy, and inexpensive way to assess the texture of foods. This four-page fact sheet describes the slump test, how to perform a slump test, and how the slump test can be used to evaluate the texture of puréed foods. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs288
Chronic Kidney Disease: Potassium and Your Diet
Potassium is an essential mineral required for normal body function. It helps maintain normal blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, muscle and nerve function, as well as bone density. This three-page fact sheet describes potassium and its normal dietary importance, as well as the impact potassium levels have on those with Chronic Kidney Disease. Written by Ashley R. Kendall, Nancy J. Gal, and Wendy J. Dahl and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs287
A Guide to Probiotics and Health
Probiotics are beneficial for gastrointestinal wellness, immunity, and a variety of other health outcomes. There are hundreds of probiotic supplements available in the marketplace and choosing a supplement can be challenging. This six-page fact sheet provides a summary of the health benefits of probiotics that are backed by a high level of scientific evidence. Written by Wendy J. Dahl and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs286
A Guide to Tracking Physical Activity

Being physically active is fun, has many physical and mental health benefits, and can help maintain a healthy weight. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend that adults be purposefully active for at least 150 minutes per week for overall health and wellness. One proven strategy to make sure you reach your activity goal is to track your energy expenditure. This three-page fact sheet explains the different free and low cost cell phone apps, websites, and portable devices available for tracking physical activity. Written by Madison K. Keesling and Anne E. Mathews and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs283
Body Fat and Health: How Can I Tell if I am at Risk for Health Problems?
Obesity is called an epidemic because there is a high rate of obesity in the United States. In fact, over 30% of all US adults were obese as of 2012, and more than two-thirds are either overweight or obese. This is concerning because excess body fat is linked to poor health and chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease. The amount of excess body fat a person has is commonly sorted into weight status categories using Body Mass Index. This three-page fact sheet describes the body mass index and how to calculate it. Written by Kohrine A. Counts and Anne E. Mathews and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs284
Facts about Fats and Oils
Fats and oils are important for good health. Fats provide your body with energy while oils are needed in the diet in small amounts because they are a major source of Vitamin E, which has antioxidant properties. This four-page fact sheet describes the different types of fats and oils and tips for choosing the healthiest types.Written by Tiffany N. Stodtko and Wendy J. Dahl and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs281
Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Olive Extracts

Olive oil is known for its health benefits. There are three common types of olive oil, namely virgin olive oil, refined olive oil, and olive pomace oil. Each has its unique processing method, flavor characteristics, composition, and food applications. This five-page fact sheet describes each of the types of olive oil and their pros and cons. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, Michael A. Tandlich, and Julie England and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs282
De Compras para la Salud: Cereales de Desayuno
It is no secret that breakfast is an important meal. Eating breakfast provides you with physical and mental energy to start the day, along with vitamins and minerals. Cereal is a quick, versatile, and budget-friendly breakfast choice. The benefits of eating a healthy cereal include increased fiber intake and lower body weight. But navigating the cereal aisle at your local grocery store can be an overwhelming experience. This three-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Shopping for Health: Breakfast Cereals, http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs274. Written by Jenna Seckar and Wendy J. Dahl and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs280
De Compras para la Salud: Aperitivos
At first glance, you might think that snacking should be avoided because of the extra calories they can add to your diet. However, studies have shown there may be benefits when healthy snack choices are made. Read this article to learn about the benefits of healthy snacks and to learn healthy snack shopping tips. Includes recipes for homemade crispy kale chips and peanut butter and jelly yogurt. This four-page fact sheet is the Spanish langauge version of FS279 Shopping For Health: Snack Foods. Written by Carley Rusch and Wendy J. Dahl and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs279
Understanding Dietary Supplements
More than half of adults in the United States take at least one dietary supplement. It is important to know in what situations supplements may be effective for improving health and wellness. This three-page fact sheet describes dietary supplements, when to use them, and how to evaluate their safety and efficacy. Written by Daniel Staub and Anne Mathews and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs278
Preventing Foodborne and Non-foodborne Illness: Vibrio vulnificus
 Vibrio vulnificus occurs naturally in warm brackish and saltwater environments. During the warmer months, this bacterium can reach particularly high concentrations in filter-feeding shellfish that inhabit coastal waters. Foodborne illness from V. vulnificus is almost exclusively associated with consumption of raw oysters. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses risk of infection, times to seek medical treatment, symptoms, activities related to illness, foods commonly associated with the bacterium, handling and storage of seafood and shellfish, and methods of prevention. Written by Anita C. Wright, Renée M. Goodrich, Michael A. Hubbard, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Food Science and Human Nutrition Department. Original publication date: July 2009. Revised October 2015.
Vibrio vulnificus occurs naturally in warm brackish and saltwater environments. During the warmer months, this bacterium can reach particularly high concentrations in filter-feeding shellfish that inhabit coastal waters. Foodborne illness from V. vulnificus is almost exclusively associated with consumption of raw oysters. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses risk of infection, times to seek medical treatment, symptoms, activities related to illness, foods commonly associated with the bacterium, handling and storage of seafood and shellfish, and methods of prevention. Written by Anita C. Wright, Renée M. Goodrich, Michael A. Hubbard, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Food Science and Human Nutrition Department. Original publication date: July 2009. Revised October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs147
Pureed Foods: Texture Testing with the Slump Test

For individuals with dysphagia, the texture of puréed foods is extremely important. If the puréed foods are either too thick or too thin, it can make it more difficult to swallow. The slump test is a quick, easy, and inexpensive way to assess the texture of foods. This four-page fact sheet describes the slump test, how to perform a slump test, and how the slump test can be used to evaluate the texture of puréed foods. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs276
De Compras Para la Salud: Mariscos

El marisco es un término general para todo tip de pescados y mariscos (USDA 2010). Los mariscos son parte del “grupo de alimentos de proteína” de MyPlate y también proporciona otros nutrientes necesarios para una buena salud (USDA 2011). Como hay muchos beneficios para la salud associados con la inclusión de los mariscos en la dieta, se recomienda que los adultos consuman al menos ocho onzas de una variedad de mariscos cada semana. Mientras que comer más mariscos se recomienda como parte de una dieta saludable, es importante tener en cuenta su presupuesto al hacer compras de mariscos. Este artículo explica los beneficios para la salud de los mariscos y ofrece algunas estrategias para ahorrar dinero para hacer los mariscos más asequible. This four page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs247, written by Michelle Brown and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs275
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Typhoid Fever: Salmonella Typhi
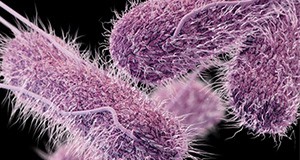
Typhoid fever is a blood infection caused by the consumption of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Salmonella enterica.Typhoid fever is easily controlled and relatively uncommon in the United States, but an estimated 21.5 million people per year are affected by typhoid fever in developing nations including regions in Asia, Africa, and South America. Many of the cases of typhoid fever in the United States are acquired through international travel to these regions. This four-page fact sheet explains the causes and symptoms of typhoid fever, as well as describing who is at risk, what foods have commonly been associated with typhoid fever, and how to implement certain sanitation methods to prevent the spread of typhoid fever. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée Goodrich Schneider, and Rachael Silverberg, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs125