The UF/IFAS Plant Science Research and Education Unit (PSREU) in Citra, FL developed an in-laboratory calibration protocol for CS616 TDR sensors for sandy soils, which are typical of north central Florida. This new 7-page fact sheet discusses the reflectometer, field site, calibration protocol, and calibration coefficients. Written by Tara Bongiovanni, Pang-Wei Liu, Daniel Preston, Johanna Montanez, Courtnay Cardozo, Steven Feagle, and Jasmeet Judge, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, February 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae519
Category: Water
Florida Rainfall Data Sources and Types
This new 5-page document introduces the sources, providers, and types of rainfall data available to Florida researchers and residents to promote understanding of the rainfall data and their application in studies and daily life. Written by Meijing Zhang, Young Gu Her, Kati Migliaccio, and Clyde Fraisse, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, January 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae517
Water Conservation and Extension Participants: An Interesting Synergy
The home landscape is a place where there is a great opportunity for people to adopt irrigation practices and technologies that conserve water. However, a large portion of residents lack the required knowledge and skills to adopt some of those practices. This three-page fact sheet discusses using innovative evaluation approaches to demonstrate the impacts of statewide urban water conservation programs. Written by Laura A. Warner, Sebastian Galindo-Gonzalez, and Anil Kumar Chaudhary and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc278
Estimating Benefits of Residential Outdoor Water Conservation: A Step-by-Step Guide
This 9-page fact sheet written by Tatiana Borisova, Laura A. Warner, Jennison Searcy, Anil Kumar Chaudhary, and Michael Dukes and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics in February 2017 was developed to help Extension agents, water-conservation managers, and homeowners estimate the economic benefits of residential outdoor water conservation. It provides guidance for reporting benefits, including lowered utility bills for homeowners, reduced water-delivery costs for utilities, and increased water supply. This publication also offers an example of an impact statement.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe1009
Household Water Usage and Irrigation Practices
Water pollution and drought in the United States have made water scarcity a widespread concern. Currently, residential consumers account for most urban water use, and meaningful programs that lead to water conservation rely on a comprehensive understanding of how consumers use water inside and outside their homes. This 5-page fact sheet written by Hayk Khachatryan, Alicia Rihn, and Michael Dukes and published by the Department of Food and Resource Economics outlines University of Florida researchers’ assessments of current US household indoor and outdoor water use to assist policy makers and researchers with creating incentives for homeowners to conserve water.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe996
Natural Climate Variability Can Influence Cyanobacteria Blooms in Florida Lakes and Reservoirs
During the summer, many of Florida's nutrient-enriched lakes and reservoirs experience proliferations of cyanobacteria commonly called “blooms.”. Cyanobacteria are natural in Florida lakes and reservoirs, but when they grow to high levels and bloom, they become a big problem. They look awful, smell bad, and can poison fish and other animals in the water. To help resource managers considering costly remediation projects or evaluating the effectiveness of nutrient reduction strategies to manage the problem, this 7-page fact sheet presents the results from 15 years of studies observing three large, nutrient-rich lakes in Florida (Lake Harris, Lake George, and Lake Okeechobee) to study the relationship between rainfall and cyanobacteria blooms and learn causes of year-to-year bloom variability. Written by Karl E. Havens, Mark V. Hoyer, and Edward J. Phlips and published by the Florida Sea Grant College Program
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg142
Engaging High Water Users in Water Conservation #3: High Water Users' Opportunities to Learn about Water Conservation
Homeowners who use excessive amounts of water to irrigate their landscapes have specified demographic characteristics and have been identified as high water users. This three-page fact sheet is the third in a series discussing how Extension can improve high water users' engagement in water conservation, focusing on how to effectively communicate with high water users about water conservation education. Written by Pei-wen Huang and Alexa J. Lamm and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc257
Engaging High Water Users in Water Conservation #2: High Water Users' Water-related Behaviors and Willingness to Act
Approximately 50% of Floridians’ daily water consumption is used for outdoor purposes, such as landscape irrigation; this is 20% higher than the national average. In order to alleviate the pressure on the precious water resources in Florida from various demands, increased public awareness and engagement in water conservation is needed especially among high water users. This four-page fact sheet is the second in a series discussing how Extension can improve high water users’ engagement in water conservation with a focus on high water users’ water-related behavior and willingness to act. Written by Pei-wen Huang and Alexa J. Lamm and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc256
Engaging High Water Users in Water Conservation #1: High Water Users' Experiences and Perceptions of Water
Florida has an abundance of water, but still faces an increased pressure on water resources because of a growing population, prosperous tourism, and an active agricultural industry. This five-page fact sheet is the first in a series discussing how Extension can improve high water users' engagement in water conservation by focusing on high water users' characteristics, experiences with water issues, and perceptions of water. Written by Pei-wen Huang and Alexa J. Lamm and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc255
Encouraging Landscape Water-Conservation Behaviors #4: Florida Homeowners' Reactions to Messages that Encourage Landscape Water Conservation Practice Adoption
This is the fourth publication in a series focused on improving and encouraging water conservation among Florida residents who use irrigation in their home landscape. This four-page fact sheet examines the impact of differently framed messages on Florida residents’ attitudes toward good irrigation practices and their perceived ability to implement those practices. Written by Joy Rumble, Laura A. Warner, Courtney Owens, Alexa Lamm, and Randall Cantrell and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc202
Differences in Perceptions of Agricultural Water Use between the General Public and Local Officials
Due to the scarcity of water resources among states and the influx of people, balancing agriculture and public water needs has become a contentious issue. Therefore, dialogue msut take place to educate and inform the general public and local officials about the reality of agricultural water use. This is the second article in a series describing the differences in perceptions of agricultural water use in Florida between the general public and local officials. This four-page fact sheet identifies the differens among groups for agricultural water use and provides ways to change Extension programming according to these differences. Written by Courtney T. Owens, Alexa J. Lamm, and Ricky W. Telg and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc249
Encouraging Landscape Water-Conservation Behaviors: Applying Audience Segmentation to Water Conservation Activities in the Landscape—Defining Segments of the Florida Homeowner Audience and Implications for Extension Programming
This is the second publication in a series focusing on encouraging water conservation among Florida residents who use irrigation in their home landscapes. This six-page fact sheet examines one approach to segmenting Florida residents who use irrigation in the home landscape. It also describes how segmentation can be used to encourage water conservation practices. Written by Laura A. Warner, Emmett Martin, Alexa J. Lamm, Joy N. Rumble, and Esen Momol and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc200
Attitudes and Perceptions of Agricultural Water Use in Florida Expressed by the General Public and Local Officials
The use of water has become increasingly contentious because an increased population is sharing a decreasing amount of water. Water remains Florida’s most plentiful natural resource but is at risk as the agriculture industry and Floridians demand more water for a variety of uses. This four-page fact sheet discusses the media’s influence on perceptions of agricultural water use, the measurement of attitudes and perception towards agricultural water use, and ways to educate the general public and local officials on this issue. Written by Courtney T. Owens, Alexa J. Lamm, and Ricky W. Telg, and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communication.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc248
How the General Public and Local Officials Prefer to Learn about Agricultural Water Use in Florida

Water is a precious resource that is invaluable to the state of Florida. The amount of water being used daily in the state is estimated at 14.3 million gallons. Part of a series dedicated to describing the preferred ways of learning about agricultural water use in Florida, this study can be used to assist Extension educators and the agricultural industry at large in the development of strategies meant to inform people about the realities of water use. This three-page fact sheet helps Extension educators understand preferred learning mediums so they can provide useful information about agricultural water use. Written by Courtney T. Owens, Alexa J. Lamm, and Ricky W. Telg and published by the Agricultural Education and Communication Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc247
Nitrogen Fertilizer Recommendations for Sugarcane Production for Sugar on Florida Sand Soils

Sands used in sugarcane production in Florida have low levels of organic matter, silt, and clay, and they provide little N through mineralization of organic matter and possess a low capacity for N retention as a result. Because these soils are highly leachable, N must be managed well to ensure adequate nutrition for the crop as well as protection of groundwater. This new 4-page fact sheet is part of the Sugarcane Handbook, and it discusses sand soils used in sugarcane production, sugar yield response to nitrogen, and revised nitrogen recommendations. Written by J. Mabry McCray, Kelly T. Morgan, and Les Baucum, and published by the UF Agronomy Department, February 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc101
Basics of Quantifying N Sources and Fates on the University of Florida Campus
 Landscapes, recreational areas, and sports fields are important parts of the University of Florida campus that receive nitrogen (N) fertilization to maintain the health and quality of their plants. However, nitrogen can be lost from the landscape through runoff in storm water or leaching into groundwater, both fates leading to pollution of the receiving water bodies. Human activities can also cause losses of nitrogen. Therefore, educating people about nitrogen cycling in the urban environment is critical for the development of solutions to the environmental problems caused by nitrogen loss. This 5-page fact sheet discusses nitrogen mass budgets, land uses in a major university, and nitrogen sources and fates associated with different land uses on campus. Written by Jiexuan Luo and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science.
Landscapes, recreational areas, and sports fields are important parts of the University of Florida campus that receive nitrogen (N) fertilization to maintain the health and quality of their plants. However, nitrogen can be lost from the landscape through runoff in storm water or leaching into groundwater, both fates leading to pollution of the receiving water bodies. Human activities can also cause losses of nitrogen. Therefore, educating people about nitrogen cycling in the urban environment is critical for the development of solutions to the environmental problems caused by nitrogen loss. This 5-page fact sheet discusses nitrogen mass budgets, land uses in a major university, and nitrogen sources and fates associated with different land uses on campus. Written by Jiexuan Luo and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss641
School Garden: Plastic Wading Pool Hydroponics
 School gardens are a great way to get youth interested in where their food comes from. Hydroponics, or the cultivation of plants in liquid nutrient solutions rather than in soil, is a fascinating way to teach students about food systems. This 4-page fact sheet lists the materials, tools, and construction steps needed to grow a variety of crops in a wading pool hydroponic garden. Written by Edmund L. Thralls, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, October 2015.
School gardens are a great way to get youth interested in where their food comes from. Hydroponics, or the cultivation of plants in liquid nutrient solutions rather than in soil, is a fascinating way to teach students about food systems. This 4-page fact sheet lists the materials, tools, and construction steps needed to grow a variety of crops in a wading pool hydroponic garden. Written by Edmund L. Thralls, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep525
Arrow Arum: Peltandra virginica
 Arrow arum is a native aquatic and wetland plant that is a welcome addition to water gardens, aquatic ponds, and wetland restoration and mitigation sites. The species is broadly adapted and extremely common throughout Florida, and its perennial nature assures a stellar performance year after year. This new 3-page fact sheet provides an overview of this plant and discusses its distribution, habitat, propagation, and other uses. Written by Kimberly A. Moore, Luci E. Fisher, Carl J. Della Torre III, and Lyn A. Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2015.
Arrow arum is a native aquatic and wetland plant that is a welcome addition to water gardens, aquatic ponds, and wetland restoration and mitigation sites. The species is broadly adapted and extremely common throughout Florida, and its perennial nature assures a stellar performance year after year. This new 3-page fact sheet provides an overview of this plant and discusses its distribution, habitat, propagation, and other uses. Written by Kimberly A. Moore, Luci E. Fisher, Carl J. Della Torre III, and Lyn A. Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag400
Contaminants in the Urban Environment: Microplastics
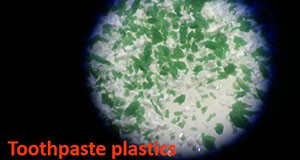
Plastic, plastic everywhere! We live in a world where we are surrounded by plastic: from packaging materials and cutlery to plastic appliances and medical devices. Since the mid-twentieth century, plastic has been a boon to humanity and an integral part of our modern lives. However, plastic debris is a major concern due to its abundance and persistence in the environment. Plastic contaminants not only include plastic debris characterized by large size but also small pieces of plastic in the millimeter size range; these inconspicuous “microplastics” have become a major concern because of their widespread presence in different environments and diverse organisms. This six-page fact sheet discusses the sources of microplastics, their effects on the environment, and ways to minimize microplastics pollution and exposure. Written by Yun-Ya Yang, Ignacio A. Rodriquez, Maia McGuire, and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the Soil and Water Science Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss649
Preventing Foodborne and Non-foodborne Illness: Vibrio parahaemolyticus
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a naturally occurring bacterium that inhabits coastal brackish marine waters throughout the world and is commonly found in the United States and Canada. If ingested in sufficient numbers, this bacterium can cause illness such as gastroenteritis with symptoms such as cramps, vomiting, and nausea. Illnesses linked with this organism are usually associated with the consumption of raw or improperly cooked seafood, particularly raw oysters. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses Vibrio parahaemolyticus, illness caused by the bacterium, factors that increase risk of infection, methods of infection, seafood and shellfish handling recommendations, and prevention. Written by Anita C. Wright, Renée M. Goodrich, Michael A. Hubbard, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition. Original publication date: July 2009. Revised October 2015.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a naturally occurring bacterium that inhabits coastal brackish marine waters throughout the world and is commonly found in the United States and Canada. If ingested in sufficient numbers, this bacterium can cause illness such as gastroenteritis with symptoms such as cramps, vomiting, and nausea. Illnesses linked with this organism are usually associated with the consumption of raw or improperly cooked seafood, particularly raw oysters. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses Vibrio parahaemolyticus, illness caused by the bacterium, factors that increase risk of infection, methods of infection, seafood and shellfish handling recommendations, and prevention. Written by Anita C. Wright, Renée M. Goodrich, Michael A. Hubbard, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition. Original publication date: July 2009. Revised October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs146







