- Atlantic St. John’s Wort, Hypericum tenuifolium Synonym: Hypericum reductum
- Beach Morning-glory Ipomoea imperati and Railroad Vine Ipomoea pes-caprae subsp. brasiliensis
- Bitter Panicgrass, Bitter Panicum, Panicum amarum
- Coastal Groundcherry, Physalis angustifolia
- Coastal Sand Frostweed, Crocanthemum arenicola Synonym: Helianthemum arenicola
- Coastalplain Honeycombhead, Balduina angustifolia
- False Rosemary, Conradina canescens
- Florida Rosemary, Ceratiola ericoides
- Goldenaster, Chrysopsis
- Gopher Apple, Geobalanus oblongifolius Synonym: Licania michauxii
- Gulf Bluestem, Maritime Bluestem, Schizachyrium maritimum
- Gulf Coast Lupine, Lupinus westianus var. westianus
- Inkberry, Ilex glabra
- Myrtle Oak, Quercus myrtifolia
- October Flower, Polygonella polygama
- Sand Live Oak, Quercus geminata
- Sandhill Milikweed, Asclepias humistrata
- Sea Oats, Uniola paniculata
- Seabeach Evening Primrose, Oenothera humifusa
- Seacoast Marshelder, Iva imbricata
- Seaside Goldenrod, Solidago sempervirens
- Squareflower, Paronychia erecta
- Wax Myrtle, Morella cerifera Synonym: Myrica cerifera
- Woody Goldenrod, Chrysoma pauciflosculosa
- Yaupon, Ilex vomitoria
Tag: Florida Sea Grant
Natural Climate Variability Can Influence Cyanobacteria Blooms in Florida Lakes and Reservoirs
During the summer, many of Florida's nutrient-enriched lakes and reservoirs experience proliferations of cyanobacteria commonly called “blooms.”. Cyanobacteria are natural in Florida lakes and reservoirs, but when they grow to high levels and bloom, they become a big problem. They look awful, smell bad, and can poison fish and other animals in the water. To help resource managers considering costly remediation projects or evaluating the effectiveness of nutrient reduction strategies to manage the problem, this 7-page fact sheet presents the results from 15 years of studies observing three large, nutrient-rich lakes in Florida (Lake Harris, Lake George, and Lake Okeechobee) to study the relationship between rainfall and cyanobacteria blooms and learn causes of year-to-year bloom variability. Written by Karl E. Havens, Mark V. Hoyer, and Edward J. Phlips and published by the Florida Sea Grant College Program
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg142
Frequently Asked Questions about Vibrio in Florida

Florida is a tropical paradise that attracts marine enthusiasts and seafood lovers from around the world. Its extensive waterways not only offer unique areas for us to explore but also provide essential habitat for marine life, including marine bacteria that keep the habitat in healthy balance by breaking down organic matter and providing food for larger organisms. One type of marine bacteria known as Vibrio sometimes causes infections and seafood sickness in people with weakened immune systems, but Vibrio should not keep Floridians and visitors from enjoying their favorite activities because Vibrio infections are rare and easy to prevent. This 7-page fact sheet written by Gabby Barbarite, Peter J McCarthy, Holly Abeels, and Anita Wrightwill and published by the Florida Sea Grant College Program will help you ensure that your time on the water is as safe and enjoyable as possible.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/SG140
Basics of the National Flood Insurance Program

Established by Congress in 1968 because the private market stopped offering flood insurance, the NFIP provides federally backed flood insurance to property owners in participating communities. This 10-page fact sheet covers topics such as: why buy flood insurance, recent changes, flood zones and insurance rate maps, ways to reduce premiums, rate increases for pre-1974 structures, and actions communities can take to lower citizen premiums related to climate change and sea-level rise. Written by Thomas Ruppert and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg139
Lionfish: Is It Safe to Eat?

Lionfish is not a traditional or likely seafood selection, but growing interest in response to the invasive and increasing abundance has stirred recreational and commercial interest. This prolific, invasive fish is threatening reefs and coastal fisheries in ocean waters throughout the Caribbean Seas and neighboring regions, and eating lionfish is being encouraged as one of the best options to mitigate the its harmful impact. This 4-page fact sheet discusses the risks in handling and consuming lionfish, and offers recommendations for avoiding risk, for both recreational and commercial harvesters. Written by Steve Otwell, and published by Florida Sea Grant, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg135
Climate Change: Effects on Salinity in Florida's Estuaries and Responses of Oysters, Seagrass, and Other Biota
 Florida’s economically important estuaries could be heavily impacted by sea-level rise and altered river flow, both caused by climate change. The resulting higher salinity, or saltiness of the water, could harm plants and animals, alter fish and bird habitat, and reduce the capacity of estuaries to provide such important services as seafood production and the protection of shorelines from erosion. This 6-page fact sheet explains the importance of estuaries, salinity in estuaries, and provides examples of stress from extreme high salinity. Then it explores the projected change in climate that could affect salinity in estuaries, how plants and animals would be affected, mitigating effects, and other impacts of climate change on estuaries. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
Florida’s economically important estuaries could be heavily impacted by sea-level rise and altered river flow, both caused by climate change. The resulting higher salinity, or saltiness of the water, could harm plants and animals, alter fish and bird habitat, and reduce the capacity of estuaries to provide such important services as seafood production and the protection of shorelines from erosion. This 6-page fact sheet explains the importance of estuaries, salinity in estuaries, and provides examples of stress from extreme high salinity. Then it explores the projected change in climate that could affect salinity in estuaries, how plants and animals would be affected, mitigating effects, and other impacts of climate change on estuaries. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg138
Climate Change and Ecosystem Services of Florida's Largest Water Body: Lake Okeechobee
 Future climate change could result in higher temperatures and greater evaporative water loss in Florida. If these changes are not compensated for by more rainfall, the state’s largest water body, Lake Okeechobee, could experience prolonged periods of very low water levels and catastrophic loss of its ecosystem services, which are the benefits that people receive from ecosystems. This 6-page fact sheet provides background, optimal and actual water levels, projected changes in South Florida climate & their effects on water levels in Lake Okeechobee, their effects on ecosystem services, and possible remedies. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
Future climate change could result in higher temperatures and greater evaporative water loss in Florida. If these changes are not compensated for by more rainfall, the state’s largest water body, Lake Okeechobee, could experience prolonged periods of very low water levels and catastrophic loss of its ecosystem services, which are the benefits that people receive from ecosystems. This 6-page fact sheet provides background, optimal and actual water levels, projected changes in South Florida climate & their effects on water levels in Lake Okeechobee, their effects on ecosystem services, and possible remedies. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg137
Climate Change and the Occurrence of Harmful Microorganisms in Florida's Ocean and Coastal Waters
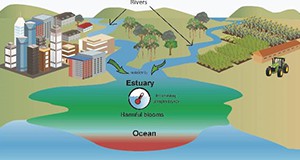 Climate change is expected to result in increased temperatures of nearshore ocean water, and this could lead to increased growth of harmful microorganisms. These include algae that form noxious or toxic blooms, including red tides, and bacteria and other pathogens. This situation could have negative consequences in regard to human health and also Florida’s ocean-related economy. This 6-page fact sheet discusses projected ocean temperatures, how harmful microorganisms living in the ocean might respond, and how this might affect people, and identifies actions that could be taken to reduce these impacts. Written by Karl Havens, and published by Florida Sea Grant, June 2015.
Climate change is expected to result in increased temperatures of nearshore ocean water, and this could lead to increased growth of harmful microorganisms. These include algae that form noxious or toxic blooms, including red tides, and bacteria and other pathogens. This situation could have negative consequences in regard to human health and also Florida’s ocean-related economy. This 6-page fact sheet discusses projected ocean temperatures, how harmful microorganisms living in the ocean might respond, and how this might affect people, and identifies actions that could be taken to reduce these impacts. Written by Karl Havens, and published by Florida Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg136
Ecosystem Services Valuation for Estuarine and Coastal Restoration in Florida
 Throughout Florida’s history, humans have altered the coastlines, leading to large-scale degradation of coastal ecosystems. This has led to the loss of associated ecosystem services, including products such as food and timber and processes like coastal protection and disease control. Unfortunately, ecosystem restoration efforts have not always been a priority for coastal management. This 10-page literature review surveys the available ecosystem-service valuation literature for five of Florida’s coastal natural communities–oyster reefs, beach dunes, mangrove forests, seagrass beds, and salt marshes–to facilitate the quantification of ecosystem services to provide a better measure of the full impact of restoration efforts. Written by Susanna Blair, Carrie Adams, Tom Ankersen, Maia McGuire, and David Kaplan, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, November 2014. (UF/IFAS photo by Tyler Jones)
Throughout Florida’s history, humans have altered the coastlines, leading to large-scale degradation of coastal ecosystems. This has led to the loss of associated ecosystem services, including products such as food and timber and processes like coastal protection and disease control. Unfortunately, ecosystem restoration efforts have not always been a priority for coastal management. This 10-page literature review surveys the available ecosystem-service valuation literature for five of Florida’s coastal natural communities–oyster reefs, beach dunes, mangrove forests, seagrass beds, and salt marshes–to facilitate the quantification of ecosystem services to provide a better measure of the full impact of restoration efforts. Written by Susanna Blair, Carrie Adams, Tom Ankersen, Maia McGuire, and David Kaplan, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, November 2014. (UF/IFAS photo by Tyler Jones)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg134
Maps of Charlotte County General Permit Trafficshed Channels and Secondary Channels
 This 33-page collection of maps depicts channels included in the Charlotte County General Permit (GP)1. Each map shows either channel segments within a GP trafficshed or segments in a GP secondary channel system. Written by Robert A. Swett, David A. Fann, and Elizabeth Staugler, and published on EDIS by Florida Sea Grant, October 2014.
This 33-page collection of maps depicts channels included in the Charlotte County General Permit (GP)1. Each map shows either channel segments within a GP trafficshed or segments in a GP secondary channel system. Written by Robert A. Swett, David A. Fann, and Elizabeth Staugler, and published on EDIS by Florida Sea Grant, October 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg133
The Potential of Sea-level Rise on Florida’s Coastal Ecosystems
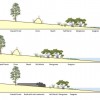 Sea-level rise may have significant effects on Florida’s coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems are the foundation upon which much of Florida’s natural beauty and economy are based. Understanding what changes may happen in the future can help us plan for those changes and, to the extent possible, lessen the impacts of those changes. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Whitney Gray, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, October 2013.
Sea-level rise may have significant effects on Florida’s coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems are the foundation upon which much of Florida’s natural beauty and economy are based. Understanding what changes may happen in the future can help us plan for those changes and, to the extent possible, lessen the impacts of those changes. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Whitney Gray, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg131
Common Sharks of Florida
 Florida’s shark population is diverse and includes species that range in size from only a few feet to more than 40 feet in total length. Experts caution sea-goers to beware of sharks 6 feet or longer due to the damage they can cause in a single bite. Among the species that grow to this size and have been known to attack humans are bull sharks, tiger sharks and great white sharks. Whites are seasonal visitors to Florida waters, and bulls and tigers are year-round residents, along with these other common species. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Florida Sea Grant, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, September 2014.
Florida’s shark population is diverse and includes species that range in size from only a few feet to more than 40 feet in total length. Experts caution sea-goers to beware of sharks 6 feet or longer due to the damage they can cause in a single bite. Among the species that grow to this size and have been known to attack humans are bull sharks, tiger sharks and great white sharks. Whites are seasonal visitors to Florida waters, and bulls and tigers are year-round residents, along with these other common species. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Florida Sea Grant, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg062
Invasive Species of Florida’s Coastal Waters: The Red Lionfish (Pterois volitans) and Devil Firefish (P. miles)
 Two species of Indo-Pacific lionfish (Pterois volitans and P. miles) are the first reported non-native marine fish to become established in the Atlantic Ocean. Genetic studies indicate that lionfish in the Atlantic are likely all descendants of a few individuals, consistent with the widely held belief that lionfish were introduced into the Atlantic as a result of accidental or deliberate release of aquarium pets. Regardless of the method of introduction, the prolific spread of these invasive species in the Atlantic Ocean ecosystem is cause for concern. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Maia McGuire and Jeffrey HIll, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, January 2013.
Two species of Indo-Pacific lionfish (Pterois volitans and P. miles) are the first reported non-native marine fish to become established in the Atlantic Ocean. Genetic studies indicate that lionfish in the Atlantic are likely all descendants of a few individuals, consistent with the widely held belief that lionfish were introduced into the Atlantic as a result of accidental or deliberate release of aquarium pets. Regardless of the method of introduction, the prolific spread of these invasive species in the Atlantic Ocean ecosystem is cause for concern. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Maia McGuire and Jeffrey HIll, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg132
A Multi-Disciplinary Review of Current Sea-Level Change Research in Florida (TP193/SG125)
 Sea-level rise is an issue of paramount importance for the state of Florida due to its lengthy coastline, low relief, high coastal population density, ecologically and economically vital beaches, estuaries, and wetlands, and porous limestone geology. The rate of sea-level rise in Florida generally follows the global average (~3 mm per year) and is slowly gaining public attention as a significant threat to the natural and socioeconomic future of the state. This 18-page multi-disciplinary review provides an annotated bibliographic summary of current peer-reviewed literature regarding sea-level rise in Florida. Written by Anna Cathey Linhoss, Lisa Gardner Chambers, Kevin Wozniak, and Tom Ankersen, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, February 2013.
Sea-level rise is an issue of paramount importance for the state of Florida due to its lengthy coastline, low relief, high coastal population density, ecologically and economically vital beaches, estuaries, and wetlands, and porous limestone geology. The rate of sea-level rise in Florida generally follows the global average (~3 mm per year) and is slowly gaining public attention as a significant threat to the natural and socioeconomic future of the state. This 18-page multi-disciplinary review provides an annotated bibliographic summary of current peer-reviewed literature regarding sea-level rise in Florida. Written by Anna Cathey Linhoss, Lisa Gardner Chambers, Kevin Wozniak, and Tom Ankersen, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, February 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg125
Deep Problems in Shallow Lakes: Why Controlling Phosphorus Inputs May Not Restore Water Quality (SGEF198/SG128)
 Florida’s thousands of lakes are shallower than most people realize, and some unique properties of shallow lakes make them challenging to restore if they have been degraded by nutrients or other pollutants.This 4-page fact sheet examines how water managers track nutrients as they cycle through Florida’s lakes. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, January 2013.
Florida’s thousands of lakes are shallower than most people realize, and some unique properties of shallow lakes make them challenging to restore if they have been degraded by nutrients or other pollutants.This 4-page fact sheet examines how water managers track nutrients as they cycle through Florida’s lakes. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg128
Effects of Climate Change on the Eutrophication of Lakes and Estuaries (SGEF189/SG127)
 Recent research suggests that climate change will reinforce the negative consequences of man-made eutrophication and make it more difficult to improve water quality in lakes and estuaries.This 3-page fact sheet was written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, September 2012.
Recent research suggests that climate change will reinforce the negative consequences of man-made eutrophication and make it more difficult to improve water quality in lakes and estuaries.This 3-page fact sheet was written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, September 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg127
Guidelines and Management Practices for Artificial Reef Siting, Use, Construction, and Anchoring in Southeast Florida (TP176/SG101)
 Coral reefs are one of southeast Florida’s most highly valued ocean resources. Despite their economic and ecological importance, they continue to face damage and destruction from human activity. “Artificial reefs” can help restore damaged coral reefs or mitigate their loss. Hundreds these natural and man-made structures have been deployed in southeast Florida coastal waters over the last 30 years. However, construction practices, design features and use patterns associated with this reef-building all have the potential to affect coral ecosystems. This 162-page guide describes artificial reef science and technology as a means of helping practitioners with varied backgrounds, skills and experience achieve responsible and sustainable reef development. Written by William Lindberg and William Seaman, and published by the UF Florida Sea Grant Program, June 2012.
Coral reefs are one of southeast Florida’s most highly valued ocean resources. Despite their economic and ecological importance, they continue to face damage and destruction from human activity. “Artificial reefs” can help restore damaged coral reefs or mitigate their loss. Hundreds these natural and man-made structures have been deployed in southeast Florida coastal waters over the last 30 years. However, construction practices, design features and use patterns associated with this reef-building all have the potential to affect coral ecosystems. This 162-page guide describes artificial reef science and technology as a means of helping practitioners with varied backgrounds, skills and experience achieve responsible and sustainable reef development. Written by William Lindberg and William Seaman, and published by the UF Florida Sea Grant Program, June 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg101
Rethinking the Role of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Eutrophication of Aquatic Ecosystems (SGEF190/SG118)
 For many years, environmental agencies have sought to improve the water quality of lakes and estuaries by reducing inputs of phosphorus. New research indicates that we must reduce both phosphorus and nitrogen to reverse eutrophication symptoms. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Karl Havens and Thomas Frazer, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2012.
For many years, environmental agencies have sought to improve the water quality of lakes and estuaries by reducing inputs of phosphorus. New research indicates that we must reduce both phosphorus and nitrogen to reverse eutrophication symptoms. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Karl Havens and Thomas Frazer, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg118
Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning (SGEF178/SG111)
 Coastal and marine spatial planning can assist Florida’s residents and visitors with balancing the many uses and activities associated with our coastal and ocean resources. One example at work in Florida is the Regional Waterway Management System in southwest Florida, an objective approach to waterway planning and permitting based on mapped channel depths. Marine spatial planning has also successfully allowed shipping lanes near Boston Harbor to be reconfigured to reduce collisions with endangered North Atlantic right whales, which migrate northward to feed from their calving grounds off the Florida and Georgia coasts. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Robert A. Swett , and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, July 2010.
Coastal and marine spatial planning can assist Florida’s residents and visitors with balancing the many uses and activities associated with our coastal and ocean resources. One example at work in Florida is the Regional Waterway Management System in southwest Florida, an objective approach to waterway planning and permitting based on mapped channel depths. Marine spatial planning has also successfully allowed shipping lanes near Boston Harbor to be reconfigured to reduce collisions with endangered North Atlantic right whales, which migrate northward to feed from their calving grounds off the Florida and Georgia coasts. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Robert A. Swett , and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, July 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg111
Common Sharks of Florida (SGEF146/SG062)
 Florida’s shark population is diverse and includes species that range in size from only a few feet to more than 40 feet in total length. The following species are among the most common. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Florida Sea Grant, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, December 2011.
Florida’s shark population is diverse and includes species that range in size from only a few feet to more than 40 feet in total length. The following species are among the most common. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Florida Sea Grant, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, December 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg062