
The jalapeño is derived from the Capsicum genus of the family Solanaceae. Jalapeños are members of a diverse group, which also include ancho poblano, cayenne, serrano, Anaheim, banana, Asian, habanero, and Hungarian wax peppers. Hot peppers are classified by their heat and shape. The heat of the pepper comes from the chemical compound capsaicin, which is measured by the Scoville scale. This 8-page fact sheet is a guide of jalapeño and other hot pepper varieties used in Florida was written by Monica Ozores-Hampton and Gene McAvoy, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1241
Author: dihagan
African malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae Giles (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae)
 Anopheles gambiae Giles is commonly called the African malaria mosquito because it is the most efficient vector of human malaria in the Afrotropical Region. They are considered to be one of the world’s most important human malaria vectors because of their susceptibility to the Plasmodium parasite, their preference for humans as a host, and their indoor-feeding behavior. Due to their short development time and their preference for developmental habitats near human dwellings, Anopheles gambiae are considered effective vectors of human malaria, as well as lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis). This 6-page fact sheet was written by Sabrina A. White and Phillip E. Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2014.
Anopheles gambiae Giles is commonly called the African malaria mosquito because it is the most efficient vector of human malaria in the Afrotropical Region. They are considered to be one of the world’s most important human malaria vectors because of their susceptibility to the Plasmodium parasite, their preference for humans as a host, and their indoor-feeding behavior. Due to their short development time and their preference for developmental habitats near human dwellings, Anopheles gambiae are considered effective vectors of human malaria, as well as lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis). This 6-page fact sheet was written by Sabrina A. White and Phillip E. Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1048
Growth Stages and Tuber Development of FL1867 Potato under Full and Reduced Irrigation Scheduling
 The potato cultivar ‘Frito Lay 1867’ (‘FL 1867’) is a popular chipping variety grown across Florida and the southern United States. Knowledge of the timing and duration of the tuber initiation and tuber bulking stages for ‘FL 1867’ is critical for timing fertilizer and irrigation applications. So to evaluate the start and length of the tuber initiation and tuber bulking stages under Florida growing conditions, ‘FL 1867’ plants were dug up and photographed on a weekly basis from a commercial field near Live Oak, FL in 2012. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Seth A. Byrd, Diane L. Rowland, and Lincoln Zotarelli, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
The potato cultivar ‘Frito Lay 1867’ (‘FL 1867’) is a popular chipping variety grown across Florida and the southern United States. Knowledge of the timing and duration of the tuber initiation and tuber bulking stages for ‘FL 1867’ is critical for timing fertilizer and irrigation applications. So to evaluate the start and length of the tuber initiation and tuber bulking stages under Florida growing conditions, ‘FL 1867’ plants were dug up and photographed on a weekly basis from a commercial field near Live Oak, FL in 2012. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Seth A. Byrd, Diane L. Rowland, and Lincoln Zotarelli, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag388
Pool Chemicals and Personal Safety
 Pool chemicals are among the most common household substances and are used to protect health in recreational waters. Pool chemicals containing chlorine safeguard against recreational-water illnesses caused by disease-causing pathogens, such as the diarrhea-causing Cryptosporidium. They also enhance disinfection by regulating water pH. But even though these materials are regularly handled by homeowners, most don’t ever realize that they are handling pesticides. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Fred Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
Pool chemicals are among the most common household substances and are used to protect health in recreational waters. Pool chemicals containing chlorine safeguard against recreational-water illnesses caused by disease-causing pathogens, such as the diarrhea-causing Cryptosporidium. They also enhance disinfection by regulating water pH. But even though these materials are regularly handled by homeowners, most don’t ever realize that they are handling pesticides. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Fred Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi253
University of Florida Potato Variety Trial Program: 'Elkton' Commercial Evaluation
 The ‘Elkton’ chipping potato variety was tested on a commercial scale at two growers’ farms in Florida during the 2011 season. The average yield of ‘Elkton’ in the commercial trials ranged between 295 and 324 cwt/ac, an average of 11 percent higher than that of the standard ‘Atlantic,’ and comparable to the yield range obtained in 19 trials conducted over a nine-year period by the University of Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Lincoln Zotarelli, Douglas Gergela, and Dana Fourman, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014.
The ‘Elkton’ chipping potato variety was tested on a commercial scale at two growers’ farms in Florida during the 2011 season. The average yield of ‘Elkton’ in the commercial trials ranged between 295 and 324 cwt/ac, an average of 11 percent higher than that of the standard ‘Atlantic,’ and comparable to the yield range obtained in 19 trials conducted over a nine-year period by the University of Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Lincoln Zotarelli, Douglas Gergela, and Dana Fourman, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1253
Sugarcane Orange Rust
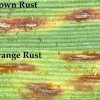 In June 2007, rust symptoms were observed on sugarcane cultivar CP80-1743 about six miles east of Belle Glade, Florida. The disease was confirmed as orange rust of sugarcane. It is hypothesized that rust spores were blown into the region as a disperse spore cloud from an unknown source rather than spread from a single or several small focal points. This 7-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, S. Sood, J. C. Comstock, R. N. Raid, N. C. Glynn, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2014.
In June 2007, rust symptoms were observed on sugarcane cultivar CP80-1743 about six miles east of Belle Glade, Florida. The disease was confirmed as orange rust of sugarcane. It is hypothesized that rust spores were blown into the region as a disperse spore cloud from an unknown source rather than spread from a single or several small focal points. This 7-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, S. Sood, J. C. Comstock, R. N. Raid, N. C. Glynn, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc099
Food Safety at Tailgating
 While tailgating can be a great fun for family and friends, you need to make plans and take on-site precautions to keep your food safe during these events. Since refrigerators and running water are not always available for the events, you should familiarize yourself with the safe food handling practices for these outdoor events and plan ahead so you will be prepared with enough coolers/ice and all the tools you need to keep and cook your food safely. This 3-page fact sheet provides information on safe food practices for tailgating and other outdoor sporting events. Written by Soohyoun Ahn, Amarat H. Simonne, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2014.
While tailgating can be a great fun for family and friends, you need to make plans and take on-site precautions to keep your food safe during these events. Since refrigerators and running water are not always available for the events, you should familiarize yourself with the safe food handling practices for these outdoor events and plan ahead so you will be prepared with enough coolers/ice and all the tools you need to keep and cook your food safely. This 3-page fact sheet provides information on safe food practices for tailgating and other outdoor sporting events. Written by Soohyoun Ahn, Amarat H. Simonne, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs256
A Practical Guide for Aquaponics as an Alternative Enterprise
 Aquaponics is an intensive sustainable agricultural production system that connects hydroponic and aquaculture systems to produce multiple cash crops with reduced water and fertilizer inputs. It is highly suited for small farm producers targeting local markets and agritourism opportunities. This 10-page fact sheet was written by Richard Tyson and Eric Simonne, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, September 2014.
Aquaponics is an intensive sustainable agricultural production system that connects hydroponic and aquaculture systems to produce multiple cash crops with reduced water and fertilizer inputs. It is highly suited for small farm producers targeting local markets and agritourism opportunities. This 10-page fact sheet was written by Richard Tyson and Eric Simonne, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1252
Conventional and Specialty Eggplant Varieties in Florida
 Eggplants are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae. Cultural practices employed in eggplant production are similar to tomatoes and peppers. In south Florida, where winters are mild and freezes are infrequent, eggplants are planted from August to March. This 5-page fact sheet is a guide to eggplant varieties commonly used in Florida. Written by Monica Ozores-Hampton, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014.
Eggplants are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae. Cultural practices employed in eggplant production are similar to tomatoes and peppers. In south Florida, where winters are mild and freezes are infrequent, eggplants are planted from August to March. This 5-page fact sheet is a guide to eggplant varieties commonly used in Florida. Written by Monica Ozores-Hampton, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1243
Effect of Anovulation and Subclinical Endometritis on Fertility of Lactating Dairy Cows: Why Are Dairy Cows Not Getting Pregnant: Lack of Cyclicity, Uterine Disease, or Both?
 Virtually all Holstein dairy cows have the first wave of follicle growth starting two weeks postpartum, with about 30% of these cows ovulating within 21 days in milk. This 3-page fact sheet presents the results of a recent paper that evaluated the individual and combined effects of anovulation and subclinical endometritis on reproductive performance of dairy cows. Written by Klibs N. Galvão and Achilles Vieira-Neto, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine-Large Animal Clinical Sciences, May 2014.
Virtually all Holstein dairy cows have the first wave of follicle growth starting two weeks postpartum, with about 30% of these cows ovulating within 21 days in milk. This 3-page fact sheet presents the results of a recent paper that evaluated the individual and combined effects of anovulation and subclinical endometritis on reproductive performance of dairy cows. Written by Klibs N. Galvão and Achilles Vieira-Neto, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine-Large Animal Clinical Sciences, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm222
Consuming local vegetables from our local growers
 In recent years, consumers increasingly are seeking out locally grown foods, due to concern for freshness, food safety, and the carbon footprint associated with food sourced from distant places. This 5-page fact sheet promotes local vegetable consumption by pointing out some of the advantages, benefits, and business opportunities associated with local vegetable production and consumption. Written by Qingren Wang, Edward A. Evans, Margie Pikarsky, and Teresa Olczyk, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, September 2014.
In recent years, consumers increasingly are seeking out locally grown foods, due to concern for freshness, food safety, and the carbon footprint associated with food sourced from distant places. This 5-page fact sheet promotes local vegetable consumption by pointing out some of the advantages, benefits, and business opportunities associated with local vegetable production and consumption. Written by Qingren Wang, Edward A. Evans, Margie Pikarsky, and Teresa Olczyk, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1251
Acoelorrhaphe wrightii: Paurotis Palm
 The paurotis or Everglades palm is a clustering, fan-leaved palm with very slender stems. It can reach heights up to 30 feet, with a spread of 20 feet. The light green leaves have blades about 2 feet across on spiny petioles up to 3 feet long. The stems are covered with fibers and persistent leaf bases. In the spring paurotis palms produce large inflorescences of creamy white flowers that extend well beyond the foliage. These are followed in the summer by ¼-inch round fruits that pass through green and orange stages but turn black when completely ripe. Paurotis palms are rather slow-growing and are not tolerant of salt spray. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Timothy K. Broschat, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2014.
The paurotis or Everglades palm is a clustering, fan-leaved palm with very slender stems. It can reach heights up to 30 feet, with a spread of 20 feet. The light green leaves have blades about 2 feet across on spiny petioles up to 3 feet long. The stems are covered with fibers and persistent leaf bases. In the spring paurotis palms produce large inflorescences of creamy white flowers that extend well beyond the foliage. These are followed in the summer by ¼-inch round fruits that pass through green and orange stages but turn black when completely ripe. Paurotis palms are rather slow-growing and are not tolerant of salt spray. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Timothy K. Broschat, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/st058
An Overview of Carbon Markets for Florida Forest Landowners
 Payments for sequestering carbon in forests can be an important supplemental income source in the southern US which includes one-third of the contiguous US forest carbon stocks and supplies 16% of the world’s wood. It is difficult to understand the carbon market and certification options available to Florida forest landowners and the possible risks of participating in them. To address this need, UF/IFAS forest management specialists provide this overview of forest carbon markets in the United States as of 2014 and compare key features of the four major carbon offset certification options. This 9-page fact sheet was written by José R. Soto, Francisco J. Escobedo, and Damian C. Adams, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, July 2014.
Payments for sequestering carbon in forests can be an important supplemental income source in the southern US which includes one-third of the contiguous US forest carbon stocks and supplies 16% of the world’s wood. It is difficult to understand the carbon market and certification options available to Florida forest landowners and the possible risks of participating in them. To address this need, UF/IFAS forest management specialists provide this overview of forest carbon markets in the United States as of 2014 and compare key features of the four major carbon offset certification options. This 9-page fact sheet was written by José R. Soto, Francisco J. Escobedo, and Damian C. Adams, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr387
Datos sobre el fosforo
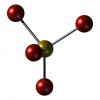 El fósforo es un mineral que se encuentra en todas las células del cuerpo, por lo general en forma de fosfato. Es el segundo mineral más abundante en el cuerpo después del calcio. Alrededor del 85% del fósforo se almacena en los huesos y dientes. Es importante para la formación de huesos y dientes, además de la reparación de huesos.
El fósforo es un mineral que se encuentra en todas las células del cuerpo, por lo general en forma de fosfato. Es el segundo mineral más abundante en el cuerpo después del calcio. Alrededor del 85% del fósforo se almacena en los huesos y dientes. Es importante para la formación de huesos y dientes, además de la reparación de huesos.
This 3-page fact sheet was written by Nancy J. Gal y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, August 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs252
Citrus Mechanical Harvesting Systems–Continuous Canopy Shakers
 Mechanization has been the hallmark of American agriculture. Nearly 100 percent of the agronomic crops grown in the United States are plowed, planted, and harvested with mechanical equipment. Mechanical harvesting equipment for sweet oranges has been studied extensively since the 1970s and during the 2005/06 harvest season, trunk and canopy shakers harvested more than 36,000 acres of Florida citrus. Mechanically harvested citrus acreage, however, has decreased significantly since 2005. During the 2012/13 season, less than 9,000 acres were mechanically harvested (FDOC 2013). Nevertheless, development and adoption of mechanical harvesting technology is important to the long-term economic sustainability of the Florida orange juice processing industry. This 5-page fact sheet describing canopy shakerswas written by F.M. Roka, R.J. Ehsani, S.H. Futch, and B.R. Hyman, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, August 2014.
Mechanization has been the hallmark of American agriculture. Nearly 100 percent of the agronomic crops grown in the United States are plowed, planted, and harvested with mechanical equipment. Mechanical harvesting equipment for sweet oranges has been studied extensively since the 1970s and during the 2005/06 harvest season, trunk and canopy shakers harvested more than 36,000 acres of Florida citrus. Mechanically harvested citrus acreage, however, has decreased significantly since 2005. During the 2012/13 season, less than 9,000 acres were mechanically harvested (FDOC 2013). Nevertheless, development and adoption of mechanical harvesting technology is important to the long-term economic sustainability of the Florida orange juice processing industry. This 5-page fact sheet describing canopy shakerswas written by F.M. Roka, R.J. Ehsani, S.H. Futch, and B.R. Hyman, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, August 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe951
Citrus Mechanical Harvesting Systems–Trunk Shakers
 While citrus growers are rightfully concerned about restoring the health of their HLB-infected trees, more study and consideration should be given to mechanical harvesting. The costs to grow and harvest citrus have been escalating significantly since 2006, and the cost savings potential from mechanical harvesting technologies can help Florida growers remain economically viable. This 4-page fact sheet was written by F.M. Roka, R.J. Ehsani, S.H. Futch, and B.R. Hyman, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, August 2014.
While citrus growers are rightfully concerned about restoring the health of their HLB-infected trees, more study and consideration should be given to mechanical harvesting. The costs to grow and harvest citrus have been escalating significantly since 2006, and the cost savings potential from mechanical harvesting technologies can help Florida growers remain economically viable. This 4-page fact sheet was written by F.M. Roka, R.J. Ehsani, S.H. Futch, and B.R. Hyman, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, August 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe950
Running a Smooth 4-H Business Meeting
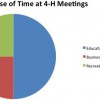 A quality 4-H club meeting consists of three main parts: (1) the business meeting, (2) an educational component, and (3) a recreational component. This 4-page fact sheet focuses on running a smooth 4-H business meeting. Written by Chris DeCubellis, and published by the UF Department of 4-H Youth Development, July 2014.
A quality 4-H club meeting consists of three main parts: (1) the business meeting, (2) an educational component, and (3) a recreational component. This 4-page fact sheet focuses on running a smooth 4-H business meeting. Written by Chris DeCubellis, and published by the UF Department of 4-H Youth Development, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/4h344
Waterhyacinth: Florida's Worst Floating Weed
 Waterhyacinth is one of the world’s worst aquatic weeds and is Florida’s most intensively managed floating plant. Dense mats formed by this species interfere with human uses of water bodies and disrupt ecosystems by preventing penetration of light and oxygen into the water column. This attractive, free-floating aquatic plant grows throughout the year in southern Florida but often dies back during the winter in the northern parts of the state. Waterhyacinth is cultivated as a water garden and pond plant, but cultivation, sale, and possession of this noxious weed is prohibited in Florida. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Lyn A. Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
Waterhyacinth is one of the world’s worst aquatic weeds and is Florida’s most intensively managed floating plant. Dense mats formed by this species interfere with human uses of water bodies and disrupt ecosystems by preventing penetration of light and oxygen into the water column. This attractive, free-floating aquatic plant grows throughout the year in southern Florida but often dies back during the winter in the northern parts of the state. Waterhyacinth is cultivated as a water garden and pond plant, but cultivation, sale, and possession of this noxious weed is prohibited in Florida. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Lyn A. Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag385
Eye-Tracking Methodology and Applications in Consumer Research
 Eye-tracking technology is a means of exploring the relationship between visual attention and consumer behavior. In the past, eye-tracking technology has been used to conduct research on consumer decision-making, marketing, and advertising. This 5-page fact sheet serves as an introduction to eye-tracking technology and methodology. Written by Hayk Khachatryan and Alicia L. Rihn, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, July 2014.
Eye-tracking technology is a means of exploring the relationship between visual attention and consumer behavior. In the past, eye-tracking technology has been used to conduct research on consumer decision-making, marketing, and advertising. This 5-page fact sheet serves as an introduction to eye-tracking technology and methodology. Written by Hayk Khachatryan and Alicia L. Rihn, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe947
Survival of Foodborne Pathogens on Berries
 Fresh and frozen berries are popular foods. When berries are picked for fresh consumption, they are usually packed directly without washing because they are highly perishable. There is typically no “kill step” that would eliminate pathogens on fresh or frozen berries. Foodborne illness outbreaks have been associated with the consumption of fresh or frozen berries that were contaminated with pathogenic viruses, parasites, or bacteria. Contamination can occur before or during harvest or during final preparation. This 11-page fact sheet was written by Mary Palumbo, Linda J. Harris, and Michelle D. Danyluk, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014.
Fresh and frozen berries are popular foods. When berries are picked for fresh consumption, they are usually packed directly without washing because they are highly perishable. There is typically no “kill step” that would eliminate pathogens on fresh or frozen berries. Foodborne illness outbreaks have been associated with the consumption of fresh or frozen berries that were contaminated with pathogenic viruses, parasites, or bacteria. Contamination can occur before or during harvest or during final preparation. This 11-page fact sheet was written by Mary Palumbo, Linda J. Harris, and Michelle D. Danyluk, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs236