Consumer demand for indoor foliage plants is decreasing. One strategy to counter decreasing demand is to align products with consumer needs. To explore this strategy, this 4-page fact sheet written by Hayk Khachatryan and Alicia Rihn and published by the Department of Food and Resource Economics examines purchasing barriers for indoor foliage plants so that breeders, growers, suppliers, and retailers may develop and promote products to overcome those barriers. This paper also investigates the potential of using novel plant attributes that are not readily apparent in retail outlets to generate consumer interest in indoor foliage plants.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe994
Category: Agriculture
Profitability of Citrus Tree Greenhouse Production Systems in Florida
Nurseries are a vital part of the citrus industry in Florida, providing growers with trees for replanting and expanding citrus groves. As part of the response to citrus greening and canker disease in the industry, nursery-aimed regulations were set in place to try to guarantee the production of trees “free of virus or other graft transmittable diseases” in plant nurseries. The new regulations resulted in an important shift for producers from traditional open field groves to greenhouses. This 4-page fact sheet describes an experiment performed at the UF/IFAS Mid-Florida REC in Apopka to test the profitability of different inputs in citrus-producing greenhouse nurseries and provides recommendations that will be useful for the whole citrus-tree-producing sector. Written by Hayk Khachatryan and Alicia Rihn and published by the Food and Resource Economics Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe999
Control Biologico Clasico de la Batata Aerea en la Florida

La batata aérea (Dioscorea bulbifera) es una enredadera herbácea y perenne que puede alcanzar longitudes de 20 metros o más, permitiéndole cubrir y ahogar a la vegetación nativa. En 1999, la batata aérea fue reconocida como un transformador de comunidades de plantas por el desplazamiento de especies nativas, cambios en la estructura de las comunidades y alteración de funciones ecológicas.
This is the Spanish language version of Classical Biological Control of Air Potato in Florida. Written by T. D. Center, W. A. Overholt, E. Rohrig and M. Rayamajhi and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, May 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1132
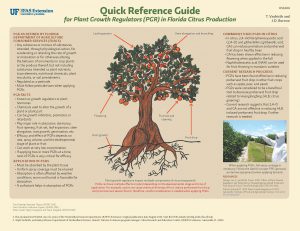
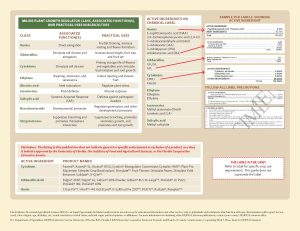
Quick Reference Guide: for Plant Growth Regulators (PGR) in Florida Citrus Production
A new two-page fact sheet explains Plant Growth Regulators (PGRS) and their application and use in Florida citrus production. Written by T. Vashisth and J.D. Burrow and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1284
Controlling Invasive Exotic Plants in North Florida Forests
Of the more than 4,000 known plant species growing in Florida, approximately 30% are not native to Florida or the Southeast, and in the US invasive exotic species cost an estimated $120 billion each year in damages. Early detection and removal of invasive plants is the key to successful management. This publication describes many of the current methods used in north Florida forest operations to manage invasive exotic plants. It also provides references for additional sources of information. Written by Chris Demers, Patrick Minogue, Michael Andreu, Alan Long, and Rick Williams.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr133
New World Screwworm topic page

New World Screwworm is the subject of a USDA alert October 3, 2016. A new EDIS topic page directs searchers to authoritative information sources or the IFAS home page (www.IFAS.ufl.edu) for additional information as it becomes available.
External Links
Preventing Escape of Non-Native Species from Aquaculture Facilities in Florida, Part 1: General Considerations and Regulations
Aquaculture is an important and diverse segment of the agricultural economy in Florida. Ornamental, live bait, food finfish, and other segments of this industry culture and trade in non-native species. Escape or release of these non-native cultured organisms is an environmental and legal concern in Florida and therefore a key consideration in aquaculture farm construction and operation. This 7-page fact sheet is the first in a four-part series devoted to educating industry and other stakeholders on the importance of preventing the escape of non-native species from aquaculture facilities as well as strategies for non-native species containment and regulatory compliance. Written by Quenton M. Tuckett, Carlos V. Martinez, Jared L. Ritch, Katelyn M. Lawson, and Jeffrey E. Hill and published by the School of Forest Resources and Conservation Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, it introduces the series, explains why non-native species containment is important, provides information on regulations, including the Florida Aquaculture Best Management Practices rule, describes the BMP inspection process, and provides advice on achieving compliance with these important regulations.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa195
Preventing Escape of Non-Native Species from Aquaculture Facilities in Florida, Part 2: Facility Evaluation Strategies
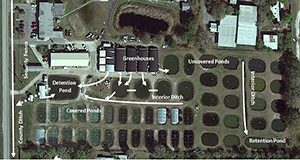
Understanding how non-native species escape or are accidentally released helps producers better design and operate aquaculture facilities to reduce or prevent escape. Active management of critical points where escape is possible will help achieve regulatory compliance. This 6-page fact sheet written by Jeffrey E. Hill, Quenton M. Tuckett, Carlos V. Martinez, Jared L. Ritch, and Katelyn M. Lawson and published by the School of Forest Resources and Conservation Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences is the second in a four-part series devoted to educating industry and other stakeholders on the importance of preventing the escape of non-native species from aquaculture facilities as well as strategies for non-native species containment and regulatory compliance. It describes farm layouts, explains how fish escape, and outlines a process that aquaculturists can complete to identify potential escape points on their farms.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa196
Preventing Escape of Non-Native Species from Aquaculture Facilities in Florida, Part 3: Structural Strategies
Non-native species sometimes escape from aquaculture facilities, but producers can prevent these potentially harmful escapes by placing barriers like screens, covers, control structures, and ponds at vulnerable points. Aquaculture producers use these structures to prevent release of non-native species in compliance with Florida Aquaculture Best Management Practices. Further, many of the structures discussed in this 9-page fact sheet are also effective in addressing and maintaining compliance with the discharge requirements of those Best Management Practices. Written by Quenton M. Tuckett, Carlos V. Martinez, Jared L. Ritch, Katelyn M. Lawson, and Jeffrey E. Hill and published by the School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, the fact sheet provides escape prevention strategies and advice for building structures and barriers that can keep potentially harmful non-native species safely contained on aquaculture facilities.
edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa197
Preventing Escape of Non-Native Species from Aquaculture Facilities in Florida, Part 4: Operational Strategies
Structural strategies to prevent the escape of non-native species from aquaculture facilities have numerous environmental benefits, and research at the UF/IFAS Tropical Aquaculture Laboratory has shown that structural strategies also reduce non-compliance with Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services Best Management Practices. Operational and management strategies, however, are also very important. The strategies discussed in this 6-page fact sheet, the management of water, facilities, and employees, must not be overlooked. Operational strategies are easy, inexpensive, and, when used alongside structural strategies, highly effective, offering an impressive return on a minimal investment in the overall effort to minimize the escape of non-native species.
Written by Quenton M. Tuckett, Carlos V. Martinez, Jared L. Ritch, Katelyn M. Lawson, and Jeffrey E. Hill and published by the School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, this fact sheet is the fourth in a four-part series devoted to educating industry and other stakeholders on the importance of preventing escape of non-native species from aquaculture facilities as well as strategies for non-native species containment and regulatory compliance.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa198
Biology and Management of Ragweed Parthenium (Parthenium hysterophorous L.) in Ornamental Crop Production
This six-page fact sheet provides an overview of Ragweed Parthenium, Parthenium hysterophorous L, including a species description and information on how to manage ragweed parthenium culturally, physically, and chemically. Written by Debalina Saha, Chris Marble, Robert H. Stamps, and Shawn Steed and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep531
Sequential Sampling for Wireworms (Coleoptera: Elateridae) at Sugarcane Planting
In the Everglades Agricultural Area of Florida, where sugarcane is planted on around 410,000 acres annually, wireworms are the most economically important insect pests of newly planted sugarcane. This 3-page fact sheet written by Matthew T. VanWeelden and Ron Cherry and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology provides a step-by-step plan to determine whether an application of soil insecticide may be needed to control wireworms. This publication is also a part of the Florida Sugarcane Handbook, an electronic publication of the Agronomy Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1143
Economic Contributions of Agriculture, Natural Resources, and Food Industries in Florida in 2014
Agriculture, natural resources, and food industries remain a significant force in the economy of Florida, and informed public policy demands recognition of the economic contributions of these industries. Economists at the University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (UF/IFAS) evaluated the economic contributions of the agriculture, natural resources, and food industries for calendar year 2014 to update previous reports and provide current information on economic trends.
Direct employment in agriculture, natural resources, and food industries in Florida grew from 1.252 million jobs in 2001 to a peak of 1.351 million jobs in 2008, before declining during the Great Recession of 2009/10, and then recovering to 1.565 million jobs in 2014, which was 24.9 percent higher than 2001, representing an average annual growth rate of 1.9 percent. Overall growth in industry contributions during this period reflected an increase in exports of Florida products to domestic and world markets.
This 5-page executive summary was written by Alan W. Hodges and Mohammad Rahmani and published by the Food and Resource Economics Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe993
Biology and Management of Goosegrass (Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn.) in Tomatoes, Peppers, Cucurbits, and Strawberries
This four-page fact sheet gives a brief description of the biology and management of goosegrass, a common annual turf and horticultural weed found throughout Florida that grows well in compact, wet soils and superficially resembles crabgrasses. Written by Nathan S. Boyd, Kiran Fnu, Chris Marble, Shawn Steed, and Andrew W. MacRae and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1178
Technically Speaking, What Is Sturgeon Caviar?
People all over the world eat fish and shellfish eggs. Seafood roes are among the most valuable of fishery commodities because they are considered a delicacy and sell for a high price. The eggs can be acquired as whole roe, (the eggs still attached to the ovary, as with mullet), or as individual eggs that may be collected directly from where the female deposits or spawns her eggs (for instance, “tobiko,” from flying fish), or by harvesting the female and separating the eggs from the ovary (as with salmon, lumpfish, and sturgeon “caviar”). The most sought-after and high-valued of all seafood roes are the eggs obtained from the sturgeon. Traditionally coveted by royalty and the aristocracy, sturgeon caviar today is prized by chefs and discerning food connoisseurs the world over for its delicate flavor and nutrient-rich health benefits. Learn what caviar is, find out how it’s collected, and discover more about the fascinating sturgeon fish in this 4-page fact sheet written by Frank A. Chapman and Joel P. Van Eenennaam and published by the School of Forest Resources Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa194
Pest Identification Guides, August 2016
Created to help growers and crop consultants, private homeowners, Master Gardeners, and the general public identify common arthropod pests and the damage they inflict, each field guide provides photos of the important life stages and crop damage associated with arthropod pests. The text highlights key general morphology and biology, distribution, and natural enemies. Written by Jeffrey Cluever and Hugh Smith, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology.
The following have been added to the existing series, http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_series_pest_identification_guides
Cob Flies, Megaselia spp. (Diptera: Phoridae), in Sweet Corn
Phorid flies (Diptera), also known as humpback flies or scuttle flies for their appearance and behavior, are an extremely diverse group of flies that are saprophagous (feed on decaying organic matter), parasitic, or phytophagous (feed on plants). Within the Phoridae family, the genus Megaselia is also extremely diverse, with more than 1400 described species, many very similar in appearance. The name “cob fly” was given to a Megaselia spp. that attacked corn in Texas. This 5-page fact sheet written by David Owens, Gregg S. Nuessly, Robert Beiriger, and Nicholas Larsen and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology describes the distribution of this pest, ways to distinguish it from other similar corn ear pests, its life cycle, the damage it causes, and some strategies for management.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1144
Managing Scale Insects on Ornamental Plants
Scale insects are a diverse group of piercing-sucking pests (Hemiptera) commonly found on ornamental plants in landscapes and nurseries. There are over 180 species of scale insects in Florida, but only a small percentage are important pests of ornamental plants. They damage plants and secrete a waxy covering that makes them difficult to control using most chemical control measures. This 7-page fact sheet written by Eileen A. Buss and Adam Dale and published by the Department of Entomology and Nematology differentiates between armored and soft-scale insect pests and lists common types of each, provides information about the biology of scale insects and how to identify them and the damage they cause, describes how to scout and monitor for scale insects, and lists several methods for prevention and control of scale insect invasions.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg005
Implications of Round Bale Dimensions on Hay Use
The dimensions of large round bales make a difference in many cases. Bale size determines the amount of hay in a purchased bale, the amount of nutrients in pounds, and the extent of spoilage during storage and feeding. Large round bales, the predominant form of hay made and fed to cattle, are under discussion. This 3-page fact sheet is a new document that examines the significance of bale dimensions, volume, density, and weight as well as the relationship of these factors to hay prices. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, June 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an326
Rhapis excelsa: Lady Palm
Rhapsis excelsa, the lady palm, is an outstanding, small clustering palm for shady landscape or interiorscape use. This two page fact sheet gives a brief overview of the Lady Palm. Written by Timothy K. Broschat and published by the Environmental Horticulture Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fp501