 Animal manures have been used as natural crop fertilizers for centuries. Because of poultry manure’s high nitrogen content, it has long been recognized as one of the most desirable manures. Besides fertilizing crops, manures also supply other essential plant nutrients and serve as a soil amendment by adding organic matter, which helps improve the soil’s moisture and nutrient retention. Organic matter persistence will vary with temperature, drainage, rainfall, and other environmental factors. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Michael A. Davis, D.R. Sloan, Gerald Kidder, and R.D. Jacobs, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, November 2013.
Animal manures have been used as natural crop fertilizers for centuries. Because of poultry manure’s high nitrogen content, it has long been recognized as one of the most desirable manures. Besides fertilizing crops, manures also supply other essential plant nutrients and serve as a soil amendment by adding organic matter, which helps improve the soil’s moisture and nutrient retention. Organic matter persistence will vary with temperature, drainage, rainfall, and other environmental factors. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Michael A. Davis, D.R. Sloan, Gerald Kidder, and R.D. Jacobs, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/aa205
Author: dihagan
Eastern Bloodsucking Conenose, Triatoma sanguisuga (LeConte) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae)
 The eastern bloodsucking conenose belongs to the subfamily Triatominae, known as the kissing bugs. Despite their affectionate vernacular name, they are particularly threatening “assassin bugs” who require blood meals to survive and reproduce. They are a known vector of American trypanosomiasis (or Chagas Disease) in South America, a debilitating illness caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. This disease is a problem in South and Central America and has been detected in the United States, but has not been found in Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by John L. Capinera, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, November 2013.
The eastern bloodsucking conenose belongs to the subfamily Triatominae, known as the kissing bugs. Despite their affectionate vernacular name, they are particularly threatening “assassin bugs” who require blood meals to survive and reproduce. They are a known vector of American trypanosomiasis (or Chagas Disease) in South America, a debilitating illness caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. This disease is a problem in South and Central America and has been detected in the United States, but has not been found in Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by John L. Capinera, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1018
Why is your cup of coffee so expensive? Because of a tiny bark beetle!
 Sometimes an insect pest attacking crops in places as far away as Indonesia or Ethiopia can be very important to us here in Florida. One such insect is the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei Ferrari (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), a tiny (1.5 mm) bark beetle that originated in the highlands of central Africa. It would probably remain one of the many inconspicuous little beetles in the tropics, if not for the choice of its host: seeds of several Coffea species. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jiri Hulcr, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, October 2013.
Sometimes an insect pest attacking crops in places as far away as Indonesia or Ethiopia can be very important to us here in Florida. One such insect is the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei Ferrari (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), a tiny (1.5 mm) bark beetle that originated in the highlands of central Africa. It would probably remain one of the many inconspicuous little beetles in the tropics, if not for the choice of its host: seeds of several Coffea species. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jiri Hulcr, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr382
What is urea-triazone nitrogen?
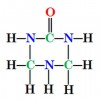 Foliar application of nitrogen and other nutrients essential for plant growth and development is an important practice for crop production. Most foliar nutrient N products contained the traditional N sources such as ammonium, nitrate and/or urea before urea-triazone N was available on the market. The traditional N sources have a greater salt index and leaf-burn potential than urea-triazone N. To avoid or minimize leaf burning, urea-triazone N fertilizers can be used instead of the traditional N sources. But growers have concerns about the safety of using triazone N fertilizers for commercial crop production because the fertilizers are still new to them. This 2-page fact sheet provides basic information on urea-triazone-based fertilizer for county faculty, crop consultants and advisors, growers, and students interested in commercial crop production. Written by Guodong Liu and Jeffrey Williamson, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2013.
Foliar application of nitrogen and other nutrients essential for plant growth and development is an important practice for crop production. Most foliar nutrient N products contained the traditional N sources such as ammonium, nitrate and/or urea before urea-triazone N was available on the market. The traditional N sources have a greater salt index and leaf-burn potential than urea-triazone N. To avoid or minimize leaf burning, urea-triazone N fertilizers can be used instead of the traditional N sources. But growers have concerns about the safety of using triazone N fertilizers for commercial crop production because the fertilizers are still new to them. This 2-page fact sheet provides basic information on urea-triazone-based fertilizer for county faculty, crop consultants and advisors, growers, and students interested in commercial crop production. Written by Guodong Liu and Jeffrey Williamson, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1233
Seed Sources for Florida Home-grown Vegetables
 The right vegetable varieties can make a big difference in the success of a home vegetable garden. Although a huge selection of seeds and transplants are available through garden centers, seed catalogs, and the internet, choosing what to buy can be confusing. Some of the best varieties for Florida gardens and seed suppliers that currently sell them are listed in this 6-page fact sheet written by Ed Thralls, Sydney Park Brown, and Ed Paulson, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, November 2013.
The right vegetable varieties can make a big difference in the success of a home vegetable garden. Although a huge selection of seeds and transplants are available through garden centers, seed catalogs, and the internet, choosing what to buy can be confusing. Some of the best varieties for Florida gardens and seed suppliers that currently sell them are listed in this 6-page fact sheet written by Ed Thralls, Sydney Park Brown, and Ed Paulson, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep486
Using Reclaimed Water to Irrigate Turfgrass: Lessons Learned from Research with Phosphorus
 Municipal wastes are treated at a wastewater treatment facility to produce biosolids and reclaimed water. Reclaimed water treated by filtration and chlorination is safe to use for designated purposes, such as residential landscape irrigation. Florida began using reclaimed water in 1966, and it is a leading state for using reclaimed water. Approximately 660 million gallons of reclaimed water are used every day in Florida, and the state encourages using reclaimed water as an alternative water source to reduce the pressure on potable water supplies. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of a recent research project and provides research-based information for improving nutrient and water management with reclaimed water irrigation of turfgrass. Written by George Hochmuth, Jinghua Fan, Jason Kruse, and Jerry Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2013.
Municipal wastes are treated at a wastewater treatment facility to produce biosolids and reclaimed water. Reclaimed water treated by filtration and chlorination is safe to use for designated purposes, such as residential landscape irrigation. Florida began using reclaimed water in 1966, and it is a leading state for using reclaimed water. Approximately 660 million gallons of reclaimed water are used every day in Florida, and the state encourages using reclaimed water as an alternative water source to reduce the pressure on potable water supplies. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of a recent research project and provides research-based information for improving nutrient and water management with reclaimed water irrigation of turfgrass. Written by George Hochmuth, Jinghua Fan, Jason Kruse, and Jerry Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss592
Using Reclaimed Water to Irrigate Turfgrass: Lessons Learned from Research with Nitrogen
 Municipal wastes are treated at a wastewater treatment facility to produce biosolids and reclaimed water. Reclaimed water treated by filtration and chlorination is safe to use for designated purposes, such as residential landscape irrigation. Florida began using reclaimed water in 1966, and it is a leading state for using reclaimed water. Approximately 660 million gallons of reclaimed water are used every day in Florida, and the state encourages using reclaimed water as an alternative water source to reduce the pressure on potable water supplies. This 5-page fact sheet summarizes the results of a recent research project and provides research-based information for improving nutrient and water management with reclaimed water irrigation of turfgrass. Written by George Hochmuth, Jinghua Fan, Jason Kruse, and Jerry Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2013.
Municipal wastes are treated at a wastewater treatment facility to produce biosolids and reclaimed water. Reclaimed water treated by filtration and chlorination is safe to use for designated purposes, such as residential landscape irrigation. Florida began using reclaimed water in 1966, and it is a leading state for using reclaimed water. Approximately 660 million gallons of reclaimed water are used every day in Florida, and the state encourages using reclaimed water as an alternative water source to reduce the pressure on potable water supplies. This 5-page fact sheet summarizes the results of a recent research project and provides research-based information for improving nutrient and water management with reclaimed water irrigation of turfgrass. Written by George Hochmuth, Jinghua Fan, Jason Kruse, and Jerry Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss591
Protected Culture for Vegetable and Small Fruit Crops: Southern Highbush Blueberry Cultivars under High Tunnels
 High tunnels have been proposed as an alternative for freeze protection and to increase fruit earliness of southern highbush blueberry. But there is no information about the effect of this type of structure on southern highbush blueberry fruit earliness under subtropical Florida conditions. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of 2-year study in a commercial southern highbush blueberry farm in North Central Florida to compare early fruit weight in high tunnels to that of open fields. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Bielinski M. Santos and Teresa P. Salame-Donoso, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2013.
High tunnels have been proposed as an alternative for freeze protection and to increase fruit earliness of southern highbush blueberry. But there is no information about the effect of this type of structure on southern highbush blueberry fruit earliness under subtropical Florida conditions. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of 2-year study in a commercial southern highbush blueberry farm in North Central Florida to compare early fruit weight in high tunnels to that of open fields. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Bielinski M. Santos and Teresa P. Salame-Donoso, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, July 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1226
Management Considerations for Wheat Production in Florida
 Higher wheat prices created the impetus for growing wheat in the southeastern United States. Since increasing amounts of corn have been diverted to ethanol production, there is a shortage of grain for America’s livestock industry. This shortage results in higher wheat and soybean prices. Wheat and soybean have been grown together as a double crop throughout the Southeast for many years, which generally increases profitability compared with growing only one of the crops. Planting wheat followed by cotton, peanut or grain sorghum has also become a common practice. The best management practices for high yields of wheat in the Southeast Coastal Plain are well established. This 3-page fact sheet lists production practices for small grains in Florida. Written by D.L. Wright, A.R. Blount, R.D. Barnett, C.L. Mackowiak, N. Dufault, and J. Marois, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2013.
Higher wheat prices created the impetus for growing wheat in the southeastern United States. Since increasing amounts of corn have been diverted to ethanol production, there is a shortage of grain for America’s livestock industry. This shortage results in higher wheat and soybean prices. Wheat and soybean have been grown together as a double crop throughout the Southeast for many years, which generally increases profitability compared with growing only one of the crops. Planting wheat followed by cotton, peanut or grain sorghum has also become a common practice. The best management practices for high yields of wheat in the Southeast Coastal Plain are well established. This 3-page fact sheet lists production practices for small grains in Florida. Written by D.L. Wright, A.R. Blount, R.D. Barnett, C.L. Mackowiak, N. Dufault, and J. Marois, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag293
Lettuce Cultivars Suitable for Use in Southern Florida
 Lettuce is an economically important winter vegetable crop in Florida, with approximately 11,000 acres in production and a farm gate value of $40–$50 million annually. Florida lettuce production occurs mainly in the Everglades Agricultural Area (EAA). In recent years, research scientists at the University of Florida conducted variety trials that included the major cultivars of romaine and iceberg types. These trials were conducted on organic soil in the Everglades Agricultural Area and the IFAS-recommended practice was followed. This 3-page fact sheet describes lettuce cultivars suitable for production on organic soils in the EAA of southern Florida. Written by Huangjun Lu, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2013.
Lettuce is an economically important winter vegetable crop in Florida, with approximately 11,000 acres in production and a farm gate value of $40–$50 million annually. Florida lettuce production occurs mainly in the Everglades Agricultural Area (EAA). In recent years, research scientists at the University of Florida conducted variety trials that included the major cultivars of romaine and iceberg types. These trials were conducted on organic soil in the Everglades Agricultural Area and the IFAS-recommended practice was followed. This 3-page fact sheet describes lettuce cultivars suitable for production on organic soils in the EAA of southern Florida. Written by Huangjun Lu, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1225
Identification and Control of Coral Ardisia (Ardisia crenata): A Potentially Poisonous Plant.
 Coral ardisia, also known as coral berry, spice berry, and scratchthroat, was introduced to Florida in the early 1900’s for ornamental purposes. Since then, it has escaped cultivation, and it is found in hardwood hammocks and other moist, natural-wooded areas and grazing lands. Although there is no published literature supporting the theory that coral ardisia is toxic, it is suspected that the berries and/or foliage are poisonous to livestock, pets, and humans. This 3-page fact sheet was written by B. A. Sellers, Sarah Lancaster, K. A. Langeland, J.A. Ferrell, Michael Meisenberg, and J. Walter, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, November 2013.
Coral ardisia, also known as coral berry, spice berry, and scratchthroat, was introduced to Florida in the early 1900’s for ornamental purposes. Since then, it has escaped cultivation, and it is found in hardwood hammocks and other moist, natural-wooded areas and grazing lands. Although there is no published literature supporting the theory that coral ardisia is toxic, it is suspected that the berries and/or foliage are poisonous to livestock, pets, and humans. This 3-page fact sheet was written by B. A. Sellers, Sarah Lancaster, K. A. Langeland, J.A. Ferrell, Michael Meisenberg, and J. Walter, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag281
The Use of Cost-Benefit Analysis in Environmental Policy
 When analyzing environmental problems, economists consider both the benefits and costs of actions. If benefits exceed costs then economic theory supports that action. For example, if the total benefits of conserving land exceed the costs then cost-benefit analysis would support conservation of the land. However, great care must be taken to accurately identify and quantify benefits and costs to determine whether an action is cost-benefit justified. Stakeholders may have an incentive to overstate costs or benefits, in order to influence decision-making. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Elizabeth F. Pienaar, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, September 2013.
When analyzing environmental problems, economists consider both the benefits and costs of actions. If benefits exceed costs then economic theory supports that action. For example, if the total benefits of conserving land exceed the costs then cost-benefit analysis would support conservation of the land. However, great care must be taken to accurately identify and quantify benefits and costs to determine whether an action is cost-benefit justified. Stakeholders may have an incentive to overstate costs or benefits, in order to influence decision-making. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Elizabeth F. Pienaar, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, September 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw383
Conversions of parts per million on soil test reports to pounds per acre
 Soil testing and the resulting fertilization recommendations are critical for appropriate nutrient management in commercial vegetable production, but growers and soil experts sometimes speak different languages. This 8-page fact sheet provides a simple conversion method for crop consultants, crop advisors, growers, students, and researchers who are interested in nutrient and water management of crop production. Written by Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, and Aparna Gazula, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, August 2013.
Soil testing and the resulting fertilization recommendations are critical for appropriate nutrient management in commercial vegetable production, but growers and soil experts sometimes speak different languages. This 8-page fact sheet provides a simple conversion method for crop consultants, crop advisors, growers, students, and researchers who are interested in nutrient and water management of crop production. Written by Guodong Liu, Yuncong Li, and Aparna Gazula, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, August 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1229
Alternatives to Invasive Plants Commonly Found in South Florida Landscapes
 Based on years of UF/IFAS research producing and trialing cultivars, this 5-page fact sheet lists native and non-invasive, non-native ornamentals as alternatives to invasive plants commonly used in Florida landscapes. Only plants considered to be generally available in the nursery trade are listed. Alternative plants are similar to respective invasive plants as much as possible in terms of size, habit, texture, and flower color. Written by Gary W. Knox, Sandra B. Wilson, Zhanao Deng, and Rosanna Freyre, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2013.
Based on years of UF/IFAS research producing and trialing cultivars, this 5-page fact sheet lists native and non-invasive, non-native ornamentals as alternatives to invasive plants commonly used in Florida landscapes. Only plants considered to be generally available in the nursery trade are listed. Alternative plants are similar to respective invasive plants as much as possible in terms of size, habit, texture, and flower color. Written by Gary W. Knox, Sandra B. Wilson, Zhanao Deng, and Rosanna Freyre, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep483
Shopping for Health: Foods with Added Fiber
 Fiber in foods consists of carbohydrates that cannot be digested. Although many foods naturally contain fiber, high-fiber ingredients are commonly added to foods to increase their fiber content. Fiber ingredients may be added to foods for health or functional reasons. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2013.
Fiber in foods consists of carbohydrates that cannot be digested. Although many foods naturally contain fiber, high-fiber ingredients are commonly added to foods to increase their fiber content. Fiber ingredients may be added to foods for health or functional reasons. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs235
Managing Stress During the Holidays
 When we think of the holidays, we often think about family, togetherness, giving, and celebrating. While the holiday season should be a time of enjoyment, there are many events associated with the season that can cause stress. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Heidi Radunovich, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
When we think of the holidays, we often think about family, togetherness, giving, and celebrating. While the holiday season should be a time of enjoyment, there are many events associated with the season that can cause stress. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Heidi Radunovich, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1404
Using Audience Commitment to Increase Behavior Changes in Sustainable Landscaping
 Participants in an Extension rain barrel workshop who said they would inspect their irrigation systems might begin to see themselves as people who use water wisely. Their perception of themselves as conservationists is strengthened with each new action. That makes them more likely to agree to an action that leads to an even bigger water savings. Research has shown that commitments can increase the percentage of people who will adopt a new behavior and give up an old one. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Laura A. Sanagorski and Paul Monaghan, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2013.
Participants in an Extension rain barrel workshop who said they would inspect their irrigation systems might begin to see themselves as people who use water wisely. Their perception of themselves as conservationists is strengthened with each new action. That makes them more likely to agree to an action that leads to an even bigger water savings. Research has shown that commitments can increase the percentage of people who will adopt a new behavior and give up an old one. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Laura A. Sanagorski and Paul Monaghan, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc154
The Savvy Survey #2: Using Surveys in Everyday Extension Programming
 This second publication in the Savvy Survey Series provides Extension faculty with additional information about using surveys in their everyday Extension programming. The publication suggests how surveys can be used in needs and assets assessments to inform program development, as formative and summative evaluations to support program improvement, and as customer service tools to capture satisfaction within programming efforts. This publication also introduces the concept of using logic models to guide questionnaire development, while also discussing general data types (demographics, factual information, attitudes and opinions, behaviors and events). This 5-page fact sheet was written by Glenn D. Israel and Jessica L. Gouldthorpe, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, October 2013.
This second publication in the Savvy Survey Series provides Extension faculty with additional information about using surveys in their everyday Extension programming. The publication suggests how surveys can be used in needs and assets assessments to inform program development, as formative and summative evaluations to support program improvement, and as customer service tools to capture satisfaction within programming efforts. This publication also introduces the concept of using logic models to guide questionnaire development, while also discussing general data types (demographics, factual information, attitudes and opinions, behaviors and events). This 5-page fact sheet was written by Glenn D. Israel and Jessica L. Gouldthorpe, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pd062
Incorporating Individual Teachings (aka Individual Contact Teaching Methods) into a Sustainable Landscaping Extension Plan of Work and Report of Accomplishment
 Many horticultural Extension professionals conduct numerous consulting phone calls, send e-mails, visit offices, conduct research, and visit landscapes to solve horticultural problems and concerns. Although many Extension faculty members are initially unaware that they are educating clients when providing these services, these activities shouldbe considered major educational methods. The activities should also be planned by Extension faculty and reported in an Extension plan of work and in their annual report of accomplishments. When planned thoughtfully, communicated clearly, and evaluated appropriately, these methods of individual contact teaching can become a substantial part of an Extension program. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Laura Sanagorski, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, November 2013.
Many horticultural Extension professionals conduct numerous consulting phone calls, send e-mails, visit offices, conduct research, and visit landscapes to solve horticultural problems and concerns. Although many Extension faculty members are initially unaware that they are educating clients when providing these services, these activities shouldbe considered major educational methods. The activities should also be planned by Extension faculty and reported in an Extension plan of work and in their annual report of accomplishments. When planned thoughtfully, communicated clearly, and evaluated appropriately, these methods of individual contact teaching can become a substantial part of an Extension program. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Laura Sanagorski, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc157
Spanish Moss, Ball Moss, and Lichens – Harmless Epiphytes
 Epiphytes are “air” plants that survive on moisture and nutrients in the atmosphere. Several epiphytic plants, like Spanish moss, ball moss, and lichen, are common to the Florida landscape and southeast United States. People unfamiliar with epiphytes sometimes worry that they may cause injuries to the plants they perch in. Epiphytes do attach themselves to plants, but they do not harm the plants, unlike mistletoe, a plant parasite. Without soil as a source of nutrients, epiphytic plants have evolved the capacity to obtain minerals dissolved in water that flows across leaves and down branches. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Joe Sewards and Sydney Park Brown, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2013.
Epiphytes are “air” plants that survive on moisture and nutrients in the atmosphere. Several epiphytic plants, like Spanish moss, ball moss, and lichen, are common to the Florida landscape and southeast United States. People unfamiliar with epiphytes sometimes worry that they may cause injuries to the plants they perch in. Epiphytes do attach themselves to plants, but they do not harm the plants, unlike mistletoe, a plant parasite. Without soil as a source of nutrients, epiphytic plants have evolved the capacity to obtain minerals dissolved in water that flows across leaves and down branches. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Joe Sewards and Sydney Park Brown, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, September 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep485