This guide is for Extension personnel who may encounter questions from growers about the functioning and accuracy of soil moisture sensors (SMSs) for fruit tree production. The 4-page publication focuses on two types of handheld sensors currently used in Florida for irrigation management of citrus and other trees: the transmission line oscillator (TLO) and time-domain transmissometer (TDT). Written by Eric Herrera, Sandra M. Guzmán, and Eduart Murcia, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, February 2021.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae551
Tag: Citrus
Computer Tools for Diagnosing Citrus Leaf Symptoms (Part 2): Smartphone Apps for Expert Diagnosis of Citrus Leaf Symptoms
Visual identification of nutrient deficiencies in foliage is an important diagnostic tool for fine-tuning nutrient management of citrus. This new 2-page article describes a new smartphone app that uses a trained neural network to identify disease and pest symptoms on citrus leaves through your phone’s camera. Written by Arnold Schumann, Laura Waldo, Perseveranca Mungofa, and Chris Oswalt, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss691
Computer Tools for Diagnosing Citrus Leaf Symptoms (Part 1): Diagnosis and Recommendation Integrated System (DRIS)
This new 2-page article provides instructions for using the Diagnosis and Recommendation Integrated System, or DRIS, a web tool designed for analyzing leaf nutrient concentrations of Florida citrus. Written by Arnold Schumann and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss683
Soil Sampling Procedures
To achieve optimal grove nutrition, citrus growers must test grove soil before beginning any fertilization program. Standard procedures for sampling, preparing, and analyzing soil should be followed for meaningful interpretations of the test results and accurate recommendations. This new two-page fact sheet, published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences, provides illustrated soil sampling procedures and tables to aid in basic interpretation of lab results. Written by Davie Kadyampakeni, Kelly Morgan, Arnold Schumann, and Rhuanito S. Ferrarezi.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss667
Identification and Management of Clustered Pellitory (Parietaria praetermissa) in Citrus Groves
In Florida, clustered pellitory is becoming a troublesome weed for citrus, especially from the winter through early summer. Inadequate management of this weed can result in its heavy infestation in tree rows and can interrupt the spray pattern of low-volume drip irrigation systems. This new 3-page publication of the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department will assist Florida citrus growers with proper identification of clustered pellitory and with adoption of adequate and timely strategies to manage this weed in their groves. Written by Ramdas Kanissery, Biwek Gairhe, Brent Sellers, and Steve Futch.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1341
Citrus Rootstock Propagation: Traditional Techniques and Recent Advances
Commercially grown citrus trees are usually composed of two parts: 1) the scion, which is the aboveground portion of the tree that produces the fruit, and 2) the rootstock, which comprises the root system and the lower portion of the trunk. This new 4-page publication, chapter 6 of the forthcoming Citrus Nursery Production Guide, discusses three kinds of rootstock propagation: seed, cuttings, and tissue culture. Written by Ute Albrecht, Lorenzo Rossi, and Mongi Zekri and published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department.
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1329
Children’s Citrus Activity: Citrus Counting
Florida is well known for its citrus industry, valued at over eight billion dollars, and is one of the top citrus-producing states in the United States. This new one-page children’s activity sheet about Florida citrus includes an activity for students learning to count and match. Written by Jamie D. Burrow and Ariel Singerman and published by the UF/IFAS Extension 4-H Youth Development Program.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/4h402
Irrigation Management of HLB-Affected Trees
Water is a limiting factor in Florida citrus production due to non-uniform rainfall distribution and the low water-holding capacity of our sandy soils. Because periods of low rainfall coincide with critical stages of citrus production, additional irrigation is necessary to reduce the negative effects of water stress. This 6-page document covers recent findings on water use of trees affected by citrus greening and the impact this would have on irrigation management considerations. Written by Davie Kadyampakeni, Kelly Morgan, Mongi Zekri, Rhuanito Ferrarezi, Arnold Schumann, and Thomas A. Obreza and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences, October 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss659
Citrus Propagation
Plant propagation is the art and science of reproducing plants while preserving their unique characteristics from one generation to the next. This 6-page document, written by Ute Albrecht, Mongi Zekri, and Jeffrey Williamson, describes the propagation process for commercial citrus. Published by the UF/IFAS Horticultural Sciences Department, October 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1309
2017-2018 Florida Citrus Production Guide: Fresh Fruit Pesticide Residue Limits
Current citrus production practices often include the use of various chemicals, many of which are pesticides. Chemical residues on the fruit after harvest are a concern to regulators and the public alike because of their potential negative health effects. Therefore, the US and other countries set maximum residue limits (MRLs) on fresh produce for various chemicals. This five-page document is part of the 2017-2018 Florida Citrus Production Guide and discusses the MRLs for various chemicals used on Florida citrus. Written by Mark Ritenour and published by UF’s Horticultural Sciences Department, October 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1301
Citrus Fruit Blemishes and Decay Caused by Fungi and Bacteria
This new one-page citrus identification fact sheet illustrates different blemishes from fungi and bacteria that affect citrus. Written by Mark A. Ritenour, Jamie D. Burrow, Megan M. Dewdney, and John Zhang and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1291
Citrus Disorders and Physical/Chemical Injuries
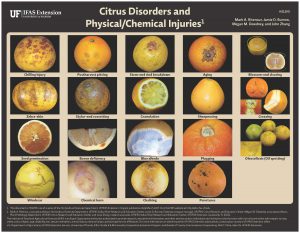
This new one-page Citrus Identification fact sheet illustrates different disorders and injuries that affect citrus. Written by Mark A. Ritenour, Jamie D. Burrow, Megan M. Dewdney, and John Zhang and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1290
Florida Citrus Activity Book
The Florida Citrus Activity Book is a basic introduction to Florida citrus trees, diseases, and pests. This 20-page booklet is for elementary students. Written by J.D. Burrow, M.M. Dewdney, M.E. Rogers, and T. Vashisth and published by the Plant Pathology Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp331
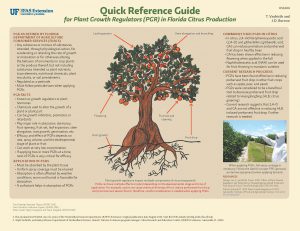
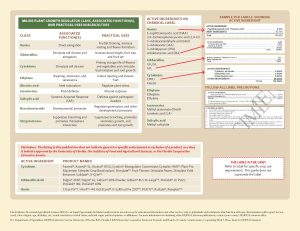
Quick Reference Guide: for Plant Growth Regulators (PGR) in Florida Citrus Production
A new two-page fact sheet explains Plant Growth Regulators (PGRS) and their application and use in Florida citrus production. Written by T. Vashisth and J.D. Burrow and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1284
Freeze Damage Symptoms and Recovery for Citrus

Citrus trees are evergreen, never become fully dormant, and cannot withstand temperatures as low as those tolerated by deciduous trees. But citrus trees can become preconditioned or acclimated to cool air temperatures that occur in late fall and winter. One of the best ways to lessen cold injury and to hasten recovery from cold damage is to maintain healthy trees. This five-page fact sheet discusses the symptoms of freeze damage and ways to help recover trees that have been damaged. Written by Mongi Zekri, Chris Oswalt, Steve Futch, Gary England, Camilly McAvoy, Laurie Hurner, and Parker Platts, and published by the Horticultural Sciences Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1250
Phytophtora Management in Citrus Nurseries

Check out the new fact sheet about Phytopthora Management in Citrus Nurseries. A great on-hand resource, this fact sheet covers sanitation practices, tools, and potting media for citrus nurseries. It also illustrates correct and incorrect practices and provides information about disinfectants and chemicals to use. Written by Megan M. Dewdney and Jamie D. Burrow, and published by the Plant Pathology Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp322
PP270 Foliar Fungal Disease Management for Commercial Citrus Groves
PP270, a 2-page illustrated fact sheet by Megan M. Dewdney and Jamie D. Yates, highlights symptoms and management for greasy spot, melanose, alternaria brown spot, and citrus scab for commercial citrus groves. Published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, August 2009.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/PP270