 Although many homeowners enjoy wildlife in their yards, there are situations where wildlife can become a nuisance. In some circumstances, wild animals can cause extensive damage to lawns and gardens. Learning to identify which species is responsible for this damage is the first step in finding a solution to the problem. This 6-page fact sheet provides images of wildlife damage in residential settings to help you determine which species may be causing similar problems in your yard. Written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
Although many homeowners enjoy wildlife in their yards, there are situations where wildlife can become a nuisance. In some circumstances, wild animals can cause extensive damage to lawns and gardens. Learning to identify which species is responsible for this damage is the first step in finding a solution to the problem. This 6-page fact sheet provides images of wildlife damage in residential settings to help you determine which species may be causing similar problems in your yard. Written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw369
Author: dihagan
Family Relationships in an Aging Society (FCS2210/FY625)
 Never in the history of America or the world has the population had more older adults than children. This 5-page fact sheet discusses some issues that happen as a result of having a greater number of older adults than children. It also looks at the roles of the family and intergenerational relationships supporting our aging society. Written by Martie Gillen, Terry Mills, and Jenny Jump, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
Never in the history of America or the world has the population had more older adults than children. This 5-page fact sheet discusses some issues that happen as a result of having a greater number of older adults than children. It also looks at the roles of the family and intergenerational relationships supporting our aging society. Written by Martie Gillen, Terry Mills, and Jenny Jump, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy625
The Food Groups of MyPlate (FCS8873/FY1077)
 Plan your food group choices wisely. Choose nutrient-rich foods that are fat-free or low-fat and low in added sugars. This 3-page fact sheet gives an overview of the MyPlate food groups. Written by Glenda L. Warren and Jennifer Walsh, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, Novemeber 2012.
Plan your food group choices wisely. Choose nutrient-rich foods that are fat-free or low-fat and low in added sugars. This 3-page fact sheet gives an overview of the MyPlate food groups. Written by Glenda L. Warren and Jennifer Walsh, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, Novemeber 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1077
Overview of How to Stop Damage Caused by Nuisance Wildlife in Your Yard (WEC323/UW368)
 In Florida, we are fortunate to have a wide variety of wildlife to watch and enjoy. Indeed, many homeowners attempt to attract particular types of wildlife to their yards to watch. However, wild animals can become a nuisance in some situations. This 4-page fact sheet is the first in a five-part series describing tactics you can use to cope with wildlife that have become a nuisance. Here we suggest a sequence of steps you can implement when wildlife are causing damage in your yard. These suggestions should help reduce wildlife damage in a practical, humane, and environmentally responsible manner. Written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
In Florida, we are fortunate to have a wide variety of wildlife to watch and enjoy. Indeed, many homeowners attempt to attract particular types of wildlife to their yards to watch. However, wild animals can become a nuisance in some situations. This 4-page fact sheet is the first in a five-part series describing tactics you can use to cope with wildlife that have become a nuisance. Here we suggest a sequence of steps you can implement when wildlife are causing damage in your yard. These suggestions should help reduce wildlife damage in a practical, humane, and environmentally responsible manner. Written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw368
Diseases of Bitter Melon in South Florida (PP300)
 Bitter melon, a tropical and subtropical cucurbit, is widely grown in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean for its edible fruit. Rich in vitamins A and C, iron, and phosphorus, it contains a compound (charantin) that has been used to lower blood sugar levels to treat diabetes. Two major types of bitter melon, Chinese and Indian, are grown in South Florida year-round. This publication describes common diseases and provides recommendations for their control. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Shouan Zhang, Mary Lamberts, and Gene McAvoy, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, October 2012.
Bitter melon, a tropical and subtropical cucurbit, is widely grown in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean for its edible fruit. Rich in vitamins A and C, iron, and phosphorus, it contains a compound (charantin) that has been used to lower blood sugar levels to treat diabetes. Two major types of bitter melon, Chinese and Indian, are grown in South Florida year-round. This publication describes common diseases and provides recommendations for their control. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Shouan Zhang, Mary Lamberts, and Gene McAvoy, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp300
Snack Attacks: Be Prepared (FCS8865/FY1020)
 Children may feel hungry or have a “snack attack” right after school each day. Plan ahead and have ready-to-eat healthful foods available for children to enjoy. Use the MyPlate food groups as a guide to prepare snacks that will help children meet their nutritional needs. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Glenda L. Warren and Jennifer Walsh, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
Children may feel hungry or have a “snack attack” right after school each day. Plan ahead and have ready-to-eat healthful foods available for children to enjoy. Use the MyPlate food groups as a guide to prepare snacks that will help children meet their nutritional needs. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Glenda L. Warren and Jennifer Walsh, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1020
Soil pH Range for Optimum Commercial Vegetable Production (HS1207)
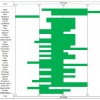 Soil pH affects nutrient bioavailability by controlling the chemical forms of nutrients. This 11-page fact sheet provides information about soil pH basics to commercial growers, county Extension agents, and college students specializing in vegetable production. Written by Guodong Liu and Edward Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2012.
Soil pH affects nutrient bioavailability by controlling the chemical forms of nutrients. This 11-page fact sheet provides information about soil pH basics to commercial growers, county Extension agents, and college students specializing in vegetable production. Written by Guodong Liu and Edward Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1207
How to Modify Habitat to Discourage Nuisance Wildlife in Your Yard (WEC325/UW370)
 Although often overlooked, habitat modification is the cheapest and most effective long-term solution to nuisance wildlife problems in residential landscapes. Removing the resources wildlife are seeking when they visit your yard can be a much more cost-effective solution than restricting access to those resources with physical barriers, scaring wildlife with hazing tactics, deterring wildlife with repellents, or removing wildlife by trapping or killing nuisance animals. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
Although often overlooked, habitat modification is the cheapest and most effective long-term solution to nuisance wildlife problems in residential landscapes. Removing the resources wildlife are seeking when they visit your yard can be a much more cost-effective solution than restricting access to those resources with physical barriers, scaring wildlife with hazing tactics, deterring wildlife with repellents, or removing wildlife by trapping or killing nuisance animals. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw370
How to Use Traps to Catch Nuisance Wildlife in Your Yard (WEC327/UW372)
 When wildlife become a nuisance in your yard, there are three general approaches you can take: make habitat modifications, use deterrents, or trap animals. In most residential settings, making habitat modifications or using deterrents will be both simpler and more effective than trapping. But trapping is warranted in certain situations when trying to solve conflicts between people and wildlife. This 6-page fact sheet provides information on stopping wildlife damage through the use of trapping. Written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
When wildlife become a nuisance in your yard, there are three general approaches you can take: make habitat modifications, use deterrents, or trap animals. In most residential settings, making habitat modifications or using deterrents will be both simpler and more effective than trapping. But trapping is warranted in certain situations when trying to solve conflicts between people and wildlife. This 6-page fact sheet provides information on stopping wildlife damage through the use of trapping. Written by Holly K. Ober and Arlo Kane, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw372
Evolution of Citrus Disease Management Programs and Their Economic Implications: The Case of Florida's Citrus Industry (FE915)
 Managing new exotic endemic diseases is very costly, and it is imperative that state and federal governments focus on preventing the introduction of other diseases such as citrus variegataed cholorosis and citrus leprosis virus. This 6-page fact sheet focuses on the expanded costs of managing exotic citrus diseases as they become endemic or established within a citrus industry. Written by Ronald P. Muraro, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, October 2012.
Managing new exotic endemic diseases is very costly, and it is imperative that state and federal governments focus on preventing the introduction of other diseases such as citrus variegataed cholorosis and citrus leprosis virus. This 6-page fact sheet focuses on the expanded costs of managing exotic citrus diseases as they become endemic or established within a citrus industry. Written by Ronald P. Muraro, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe915
Pesticidas y Colinesterasa (PI242)
 Esta publicación describe la colinesterasa, cómo varios pesticidas de diferentes familias pueden afectar los niveles de colinesterasa en los seres humanos; y la importancia del control oportuno de los niveles de colinesterasa de las personas que manejan pesticidas organofosforados o carbamatos que inhiben la colinesterasa. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Frederick M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2012.
Esta publicación describe la colinesterasa, cómo varios pesticidas de diferentes familias pueden afectar los niveles de colinesterasa en los seres humanos; y la importancia del control oportuno de los niveles de colinesterasa de las personas que manejan pesticidas organofosforados o carbamatos que inhiben la colinesterasa. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Frederick M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi242
Multiple-Use Landscapes: Reclaimed Phosphate Mined Lands (SL374/SS575)
 Phosphate mining is a temporary land use. The jobs and economic activity associated with mining depart an area once the resource is exhausted — but the landscape created as a result of mining and reclamation will exist in perpetuity. Communities affected by mining activities need to have reclamation result in lands with high potential to provide sustainable economic opportunities while maintaining ecosystem services and ecological functions. This 8-page fact sheet provides a brief overview of the landscapes being created as a result of phosphate mining and reclamation activities in Florida. Written by M. Wilson and E.A. Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
Phosphate mining is a temporary land use. The jobs and economic activity associated with mining depart an area once the resource is exhausted — but the landscape created as a result of mining and reclamation will exist in perpetuity. Communities affected by mining activities need to have reclamation result in lands with high potential to provide sustainable economic opportunities while maintaining ecosystem services and ecological functions. This 8-page fact sheet provides a brief overview of the landscapes being created as a result of phosphate mining and reclamation activities in Florida. Written by M. Wilson and E.A. Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss575
Una mirada a la produccion, el comercio y el consumo de papaya a nivel mundial (FE917)
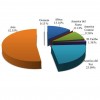 Este artículo provee información referente a las tendencias globales en cuanto a producción, comercio mundial y los países exportadores e importadores de papaya. Written by Edward A. Evans and Fredy H. Ballen, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, October 2012.
Este artículo provee información referente a las tendencias globales en cuanto a producción, comercio mundial y los países exportadores e importadores de papaya. Written by Edward A. Evans and Fredy H. Ballen, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe917
Production Systems: Florida Greenhouse Vegetable Production Handbook, Vol 3 (HS785/CV263)
 Worldwide, commercial greenhouse vegetable producers currently use numerous production systems. Among the more prevalent include lay-flat bag or upright container culture, trough culture, rockwool, vertical culture, nutrient film technique (NFT), and ground (in-soil) culture. Many modifications of these basic production systems are presently in use, and most are appropriate for Florida, except for unamended ground culture. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Dan Fenneman, Michael Sweat, George Hochmuth, and Robert Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2012.
Worldwide, commercial greenhouse vegetable producers currently use numerous production systems. Among the more prevalent include lay-flat bag or upright container culture, trough culture, rockwool, vertical culture, nutrient film technique (NFT), and ground (in-soil) culture. Many modifications of these basic production systems are presently in use, and most are appropriate for Florida, except for unamended ground culture. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Dan Fenneman, Michael Sweat, George Hochmuth, and Robert Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/cv263
Saying Goodbye: Military Deployments (FAR0013/FM072)
 “Those last few hugs, the last few kisses, the last few goodbyes are what many military families across the United States have experienced when seeing a loved one leave for deployment. An estimated 1.4 million servicemen and women serve as active duty members in the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, or Air Force. Deployments are nothing new in the military community. However, during these times of separation, family members of those serving, especially the children, undergo many hardships. Studies show children’s reactions to separation can even lead to depression.” This 2-page Family Album Radio transcript was written by Alexandra Ulrich and Suzanna Smith, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
“Those last few hugs, the last few kisses, the last few goodbyes are what many military families across the United States have experienced when seeing a loved one leave for deployment. An estimated 1.4 million servicemen and women serve as active duty members in the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, or Air Force. Deployments are nothing new in the military community. However, during these times of separation, family members of those serving, especially the children, undergo many hardships. Studies show children’s reactions to separation can even lead to depression.” This 2-page Family Album Radio transcript was written by Alexandra Ulrich and Suzanna Smith, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fm072
Ayude a su sistema digestivo: Entendiendo los probioticos (FSHN1111S/FS203)
 Los probióticos son conocidos como “bacterias buenas.” Frecuentemente cuando pensamos en las bacterias, pensamos en las que causan enfermedades. Aunque hay muchas bacterias que causan enfermedades, hay muchas otras que son benéficas para nuestra salud. Los probióticos son microorganismos vivos, los cuales cuando son administrados en cantidades adecuadas, proveen un beneficio para la salud. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Volker Mai, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs203
Los probióticos son conocidos como “bacterias buenas.” Frecuentemente cuando pensamos en las bacterias, pensamos en las que causan enfermedades. Aunque hay muchas bacterias que causan enfermedades, hay muchas otras que son benéficas para nuestra salud. Los probióticos son microorganismos vivos, los cuales cuando son administrados en cantidades adecuadas, proveen un beneficio para la salud. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Volker Mai, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs203
Ayude a su sistema digestivo: Entendiendo la microbiota y los prebioticos (FSHN1110S/FS202)
 Todos nosotros tenemos bacterias buenas por todo nuestro cuerpo. Una población grande de bacterias vive en nuestro tracto gastrointestinal, mayormente en el colon (intestino grueso). Esto se conoce como nuestra flora intestinal. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Volker Mai, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
Todos nosotros tenemos bacterias buenas por todo nuestro cuerpo. Una población grande de bacterias vive en nuestro tracto gastrointestinal, mayormente en el colon (intestino grueso). Esto se conoce como nuestra flora intestinal. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Volker Mai, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs202
De compras para la salud: Frijoles, guisantes y lentejas (FSHN1105S/FS201)
 Las legumbres son unos de los alimentos más completos en la naturaleza que proveen una gran variedad de beneficios para la salud. Las legumbres tienen mucha proteína, fibra y vitaminas. También son bajas en grasa, no tienen colesterol y son muy bajas en grasa saturada. Los frijoles oscuros tienen alto contenido de antioxidantes. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Lakshmi Mahan, Lauren Foster y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
Las legumbres son unos de los alimentos más completos en la naturaleza que proveen una gran variedad de beneficios para la salud. Las legumbres tienen mucha proteína, fibra y vitaminas. También son bajas en grasa, no tienen colesterol y son muy bajas en grasa saturada. Los frijoles oscuros tienen alto contenido de antioxidantes. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Lakshmi Mahan, Lauren Foster y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs201
De compras para la salud: Leche (FSHN1109S/FS200)
 La leche ofrece una variedad de nutrientes esenciales que el cuerpo necesita para mantenerse saludable. Estos nutrientes incluyen el calcio, la vitamina D, la vitamina A y el potasio. La leche también contiene proteína de alta calidad que ayuda a satisfacer las necesidades de su cuerpo. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Lauren Foster, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
La leche ofrece una variedad de nutrientes esenciales que el cuerpo necesita para mantenerse saludable. Estos nutrientes incluyen el calcio, la vitamina D, la vitamina A y el potasio. La leche también contiene proteína de alta calidad que ayuda a satisfacer las necesidades de su cuerpo. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Lauren Foster, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs200
De compras para la salud: Yogurt (FSHN1201S/FS198)
 El yogur se ha convertido en un producto muy popular en la dieta de los Estadounidenses y se ha apoderado de la mayoría de la sección de los productos lácteos en muchas tiendas. ¿Alguna vez se ha preguntado qué es el yogur, cuáles son los beneficios para la salud o cuál es la diferencia entre los tipos de yogures? Continúe leyendo para encontrar las respuestas a estas preguntas y para aprender más sobre el yogur.This 3-page fact sheet was written by Stephanie B. Meyer, Ada Medina-Solórzano y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
El yogur se ha convertido en un producto muy popular en la dieta de los Estadounidenses y se ha apoderado de la mayoría de la sección de los productos lácteos en muchas tiendas. ¿Alguna vez se ha preguntado qué es el yogur, cuáles son los beneficios para la salud o cuál es la diferencia entre los tipos de yogures? Continúe leyendo para encontrar las respuestas a estas preguntas y para aprender más sobre el yogur.This 3-page fact sheet was written by Stephanie B. Meyer, Ada Medina-Solórzano y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs198