 Un alimento en puré es un alimento que ha sido licuado, mesclado o procesado hasta crear una textura uniforme y suave. Los ejemplos de alimentos con una consistencia en puré incluyen la salsa de manzana, relleno de tarta de calabaza y humus. Los alimentos en puré pueden ser necesarios para personas con problemas al tragar y/o masticar. Para aquellos que requieren una dieta basada de purés, es muy importante proveer una variedad de alimentos. Casi todas las comidas se pueden preparar como puré. Sin embargo, algunas comidas pueden ser más aceptadas que otras. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl y Jamila R. Lepore, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
Un alimento en puré es un alimento que ha sido licuado, mesclado o procesado hasta crear una textura uniforme y suave. Los ejemplos de alimentos con una consistencia en puré incluyen la salsa de manzana, relleno de tarta de calabaza y humus. Los alimentos en puré pueden ser necesarios para personas con problemas al tragar y/o masticar. Para aquellos que requieren una dieta basada de purés, es muy importante proveer una variedad de alimentos. Casi todas las comidas se pueden preparar como puré. Sin embargo, algunas comidas pueden ser más aceptadas que otras. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl y Jamila R. Lepore, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs246
Category: Health & Nutrition
Alimentos en pure: Los pures altos en proteina
 La proteína es un nutriente esencial que nuestro cuerpo necesita para funcionar correctamente y de manera eficiente. Cada célula, tejido y órgano del cuerpo necesita una fuente constante de proteínas para mantener una buena salud y un buen funcionamiento. Para que estos procesos metabólicos ocurran, las proteínas se descomponen para que el cuerpo las pueda usar y se reemplazan por los alimentos que comemos. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
La proteína es un nutriente esencial que nuestro cuerpo necesita para funcionar correctamente y de manera eficiente. Cada célula, tejido y órgano del cuerpo necesita una fuente constante de proteínas para mantener una buena salud y un buen funcionamiento. Para que estos procesos metabólicos ocurran, las proteínas se descomponen para que el cuerpo las pueda usar y se reemplazan por los alimentos que comemos. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs245
Facts about Antioxidants
 Our bodies are made up of cells. Chemical reactions necessary for life are constantly occurring inside our cells, and sometimes they create free radicals — highly reactive molecules that can initiate damaging chain reactions known as oxidative stress.
Our bodies are made up of cells. Chemical reactions necessary for life are constantly occurring inside our cells, and sometimes they create free radicals — highly reactive molecules that can initiate damaging chain reactions known as oxidative stress.
Antioxidants can inactivate free radicals and protect our cells from oxidative stress and the damage it causes. Antioxidants also can help our immune system defend against bacteria, fungi, viruses, and some cancers. The body produces some of its own antioxidants, but eating a plant-based diet increases the level of antioxidants in our bodies. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Kaitlin G. Clark and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs242
Facts about Carbohydrate
 Carbohydrate, fat, and protein are the three nutrients that provide energy (calories). However, carbohydrate from starch and sugars is our main and most important source of energy. During digestion, starch is broken down to sugar (glucose). Carbohydrate in the form of glucose provides energy to cells, tissues, and organs to carry out daily activities. Some glucose is stored in the liver and muscle cells for later use when required. Children need carbohydrate for growth, and adults need carbohydrate to maintain their weight. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Nancy J. Gal, Amanda L. Ford, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
Carbohydrate, fat, and protein are the three nutrients that provide energy (calories). However, carbohydrate from starch and sugars is our main and most important source of energy. During digestion, starch is broken down to sugar (glucose). Carbohydrate in the form of glucose provides energy to cells, tissues, and organs to carry out daily activities. Some glucose is stored in the liver and muscle cells for later use when required. Children need carbohydrate for growth, and adults need carbohydrate to maintain their weight. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Nancy J. Gal, Amanda L. Ford, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs243
Facts about Flavonoids
 Flavonoids are organic compounds that occur naturally in plants. More than five thousand flavonoid compounds exist in nature, but those found in foods fall into six major categories: flavonols, anthocyanidins, isoflavones, flavan-3-ols, flavones, and flavonones. The compounds in these categories are of interest because of their potential health benefits. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Inbar Schapsis and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
Flavonoids are organic compounds that occur naturally in plants. More than five thousand flavonoid compounds exist in nature, but those found in foods fall into six major categories: flavonols, anthocyanidins, isoflavones, flavan-3-ols, flavones, and flavonones. The compounds in these categories are of interest because of their potential health benefits. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Inbar Schapsis and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs244
Los alimentos hechos en pure, las bebidas espesadas y las necesidades de agua
 El consumo adecuado del agua puede ser un problema para algunas personas con problemas de tragar, especialmente para aquellos que tienen dificultad para tragar los líquidos ligeros. Los ejemplos de líquidos ligeros son el agua, la leche, el café, el té, y la mayoría de los jugos de frutas. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2014.
El consumo adecuado del agua puede ser un problema para algunas personas con problemas de tragar, especialmente para aquellos que tienen dificultad para tragar los líquidos ligeros. Los ejemplos de líquidos ligeros son el agua, la leche, el café, el té, y la mayoría de los jugos de frutas. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs241
Frijoles, guisantes, y lentejas: Beneficios de la Salud
 Los frijoles, los guisantes y las lentejas son conocidos colectivamente como legumbres. Los frijoles son una gran fuente de muchos nutrientes, incluyendo proteína, fibra y potasio. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Lakshmi Mahan, Lauren Foster, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2014.
Los frijoles, los guisantes y las lentejas son conocidos colectivamente como legumbres. Los frijoles son una gran fuente de muchos nutrientes, incluyendo proteína, fibra y potasio. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Lakshmi Mahan, Lauren Foster, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs240
Facts about Vitamin D
 Vitamin D is needed for normal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. It helps put these minerals into bones and teeth. This makes bones stronger and reduces risk for bone fractures. Vitamin D also helps keep the immune system functioning normally, so our bodies can resist some types of disease. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff and Isabel Valentín-Oquendo, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2014.
Vitamin D is needed for normal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. It helps put these minerals into bones and teeth. This makes bones stronger and reduces risk for bone fractures. Vitamin D also helps keep the immune system functioning normally, so our bodies can resist some types of disease. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff and Isabel Valentín-Oquendo, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy207
Los alimentos en pure y la fibra
 La fibra es importante para la buena salud. El consumo inadecuado de fibra puede conducir al estreñimiento y a otros problemas gastrointestinales. Las dietas altas en fibra pueden ayudar a reducir el colesterol y la glucosa en la sangre, lo que reduce el riesgo de las enfermedades del corazón. Aunque la fibra se encuentra en todos los alimentos de origen vegetal como las frutas, los vegetales, los granos, las nueces y las semillas, la mayoría de las personas no consumen lo suficiente.The English version of this document is FSHN12-16/FS209 Puréed Foods and Fiber. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2013.
La fibra es importante para la buena salud. El consumo inadecuado de fibra puede conducir al estreñimiento y a otros problemas gastrointestinales. Las dietas altas en fibra pueden ayudar a reducir el colesterol y la glucosa en la sangre, lo que reduce el riesgo de las enfermedades del corazón. Aunque la fibra se encuentra en todos los alimentos de origen vegetal como las frutas, los vegetales, los granos, las nueces y las semillas, la mayoría de las personas no consumen lo suficiente.The English version of this document is FSHN12-16/FS209 Puréed Foods and Fiber. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs238
Facts about Fructose
 Fructose is a simple sugar found in many foods. Common table sugar is made of equal amounts fructose and glucose. Similarly, high-fructose corn syrup, commonly used to sweeten foods, contains a mixture of fructose and glucose. Fructose is sweeter than glucose, and for this reason it has been used in many sweetened foods. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Wendy Dahl, Lauren Foster, and Russel Owen, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, June 2013.
Fructose is a simple sugar found in many foods. Common table sugar is made of equal amounts fructose and glucose. Similarly, high-fructose corn syrup, commonly used to sweeten foods, contains a mixture of fructose and glucose. Fructose is sweeter than glucose, and for this reason it has been used in many sweetened foods. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Wendy Dahl, Lauren Foster, and Russel Owen, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, June 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs148
Facts about Phosphorus
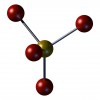 Phosphorus is a mineral found in every cell of the body, usually in the form of phosphate. It is the second most abundant mineral in the body after calcium. About 85% of phosphorus is stored in the bones and teeth. It is important for forming bones and teeth, as well as repairing bones. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Nancy J. Gal and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2014.
Phosphorus is a mineral found in every cell of the body, usually in the form of phosphate. It is the second most abundant mineral in the body after calcium. About 85% of phosphorus is stored in the bones and teeth. It is important for forming bones and teeth, as well as repairing bones. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Nancy J. Gal and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs237
Being Smart about Gluten and Gluten-free Issues, Part 2: What Retailers and Consumers Need to Know about Gluten and Gluten-free Product Labeling
 In 2011, gluten was recognized as having a specific link to celiac disease, and some consumers hoping to minimize the symptoms of celiac disease have opted to modify their diets. This is the second of a three-part series of publications called “Being Smart about Gluten and Gluten-Free Issues.” The purpose of this publication is to supply retailers and consumers with easy-to-understand information about labeling as related to gluten-free products. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Abigail Dicks, Amy Harder, and Amy Simonne, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2014.
In 2011, gluten was recognized as having a specific link to celiac disease, and some consumers hoping to minimize the symptoms of celiac disease have opted to modify their diets. This is the second of a three-part series of publications called “Being Smart about Gluten and Gluten-Free Issues.” The purpose of this publication is to supply retailers and consumers with easy-to-understand information about labeling as related to gluten-free products. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Abigail Dicks, Amy Harder, and Amy Simonne, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc153
Raising Healthy Children: Promoting a Positive Feeding Experience
 All parents have heard “I don’t like that!” or “I’m not hungry!” from their child at some point or another. It’s likely that your child will not like every food that is served, but that doesn’t mean mealtime can’t still be a pleasant experience for the family. Parents may think they have sole responsibility for their child’s food choices, but Ellyn Satter, a registered dietitian who specializes in feeding and eating, advises that young children also have responsibility in the eating process. If feeding your child is stressful, read this fact sheet to learn about the division of responsibility in feeding and how to make meal times more enjoyable for the whole family. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Tiffany N. Stodtko, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P.A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, December 2014.
All parents have heard “I don’t like that!” or “I’m not hungry!” from their child at some point or another. It’s likely that your child will not like every food that is served, but that doesn’t mean mealtime can’t still be a pleasant experience for the family. Parents may think they have sole responsibility for their child’s food choices, but Ellyn Satter, a registered dietitian who specializes in feeding and eating, advises that young children also have responsibility in the eating process. If feeding your child is stressful, read this fact sheet to learn about the division of responsibility in feeding and how to make meal times more enjoyable for the whole family. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Tiffany N. Stodtko, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P.A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, December 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1397
A Consumer's Guide to Eggs
 People have been eating eggs for centuries. Records as far back as 1400 BC show that the Chinese and Egyptians raised birds for their eggs. The first domesticated birds to reach the Americas arrived in 1493 on Christopher Columbus' second voyage to the New World. Most food stores in the United States offer many varieties of chicken eggs to choose from — white, brown, organic, cage free, vegetarian, omega-3 fatty acid enriched, and more. The bottom line is that buying eggs is not as simple as it used to be because more choices exist today. This 4-page fact sheet will help you understand the choices you have as a consumer, so you can determine which variety of egg suits you and your family best. Written by Jeanine Beatty, Karla Shelnutt, and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
People have been eating eggs for centuries. Records as far back as 1400 BC show that the Chinese and Egyptians raised birds for their eggs. The first domesticated birds to reach the Americas arrived in 1493 on Christopher Columbus' second voyage to the New World. Most food stores in the United States offer many varieties of chicken eggs to choose from — white, brown, organic, cage free, vegetarian, omega-3 fatty acid enriched, and more. The bottom line is that buying eggs is not as simple as it used to be because more choices exist today. This 4-page fact sheet will help you understand the choices you have as a consumer, so you can determine which variety of egg suits you and your family best. Written by Jeanine Beatty, Karla Shelnutt, and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1357
Eastern Bloodsucking Conenose, Triatoma sanguisuga (LeConte) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae)
 The eastern bloodsucking conenose belongs to the subfamily Triatominae, known as the kissing bugs. Despite their affectionate vernacular name, they are particularly threatening “assassin bugs” who require blood meals to survive and reproduce. They are a known vector of American trypanosomiasis (or Chagas Disease) in South America, a debilitating illness caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. This disease is a problem in South and Central America and has been detected in the United States, but has not been found in Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by John L. Capinera, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, November 2013.
The eastern bloodsucking conenose belongs to the subfamily Triatominae, known as the kissing bugs. Despite their affectionate vernacular name, they are particularly threatening “assassin bugs” who require blood meals to survive and reproduce. They are a known vector of American trypanosomiasis (or Chagas Disease) in South America, a debilitating illness caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. This disease is a problem in South and Central America and has been detected in the United States, but has not been found in Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by John L. Capinera, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1018
Shopping for Health: Foods with Added Fiber
 Fiber in foods consists of carbohydrates that cannot be digested. Although many foods naturally contain fiber, high-fiber ingredients are commonly added to foods to increase their fiber content. Fiber ingredients may be added to foods for health or functional reasons. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2013.
Fiber in foods consists of carbohydrates that cannot be digested. Although many foods naturally contain fiber, high-fiber ingredients are commonly added to foods to increase their fiber content. Fiber ingredients may be added to foods for health or functional reasons. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs235
Managing Stress During the Holidays
 When we think of the holidays, we often think about family, togetherness, giving, and celebrating. While the holiday season should be a time of enjoyment, there are many events associated with the season that can cause stress. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Heidi Radunovich, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
When we think of the holidays, we often think about family, togetherness, giving, and celebrating. While the holiday season should be a time of enjoyment, there are many events associated with the season that can cause stress. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Heidi Radunovich, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1404
Raising Healthy Children: Shellfish Allergies
 Learning that your child has a shellfish allergy can be scary. But having a plan and knowing how to treat and avoid a reaction to shellfish can ease this fear and keep your child safe. This publication explains shellfish allergies and provides information on the symptoms and how to respond if a reaction occurs. There are also tips to make it easier to manage your child’s shellfish allergy at home and away from home.This 4-page fact sheet was written by Kate Bennett, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
Learning that your child has a shellfish allergy can be scary. But having a plan and knowing how to treat and avoid a reaction to shellfish can ease this fear and keep your child safe. This publication explains shellfish allergies and provides information on the symptoms and how to respond if a reaction occurs. There are also tips to make it easier to manage your child’s shellfish allergy at home and away from home.This 4-page fact sheet was written by Kate Bennett, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1402
Choose MyPlate: Enjoy Your Food But Eat Less
 Americans tend to select and consume larger portions than they need, and they don’t always make the best choices either. Part of the secret to maintaining a healthy diet is to know which foods to select and how to balance your intake with the amount of energy your body uses. This publication provides information about which foods make the healthiest contributions to our diets and which to limit. It also provides tips for making it easier to adjust your portions and to enjoy foods while making adjustments to your plate. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Ashley Hamm, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
Americans tend to select and consume larger portions than they need, and they don’t always make the best choices either. Part of the secret to maintaining a healthy diet is to know which foods to select and how to balance your intake with the amount of energy your body uses. This publication provides information about which foods make the healthiest contributions to our diets and which to limit. It also provides tips for making it easier to adjust your portions and to enjoy foods while making adjustments to your plate. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Ashley Hamm, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1400
Healthy Eating: Food Storage Guide
 If you don’t shop for groceries often, you may want to buy food that will last until your next trip to the store. The following storage guidelines for perishable foods will help you decide how much food to buy when you visit the grocery. Keep in mind that safe storage times depend on the condition of the food when you purchase it and your refrigerator temperature and humidity. Check foods often for any signs of spoilage. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff and Jennifer Hillan, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, October 2013.
If you don’t shop for groceries often, you may want to buy food that will last until your next trip to the store. The following storage guidelines for perishable foods will help you decide how much food to buy when you visit the grocery. Keep in mind that safe storage times depend on the condition of the food when you purchase it and your refrigerator temperature and humidity. Check foods often for any signs of spoilage. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff and Jennifer Hillan, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy699