To perform a fetotomy means to dissect (to cut apart) a dead fetus in utero. Fetotomy is applicable particularly to cows because of the size of the uterus and the opportunity to introduce instruments to the full depth of the fetus. Fetotomy is an obstetric procedure that should only be performed by a trained veterinarian or under a trained veterinarian’s supervision. This 4-page fact sheet lists the circumstances when a fetotomy can be performed to save the life of the dam, the tools needed, fetotome preparation, the sequence of cuts for anterior presentation, and final comments. Written by Myriam Jimenez, Carlos Risco, and Klibs N. Galvão, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine-Large Animal Clinical Sciences, August 2015.
To perform a fetotomy means to dissect (to cut apart) a dead fetus in utero. Fetotomy is applicable particularly to cows because of the size of the uterus and the opportunity to introduce instruments to the full depth of the fetus. Fetotomy is an obstetric procedure that should only be performed by a trained veterinarian or under a trained veterinarian’s supervision. This 4-page fact sheet lists the circumstances when a fetotomy can be performed to save the life of the dam, the tools needed, fetotome preparation, the sequence of cuts for anterior presentation, and final comments. Written by Myriam Jimenez, Carlos Risco, and Klibs N. Galvão, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine-Large Animal Clinical Sciences, August 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm224
Category: Livestock
Implants for Cow-Calf and Stocker Beef Cattle

Getting cattle to put on a lot of muscle quickly is a crucial part of a beef cattle operation’s profitability. Growth promoting implants are one of the most cost-effective ways of increasing lean tissue in cattle and work by releasing hormones into the cow’s body that encourage muscle growth. This 4-page fact sheet explains implants’ mechanisms of action, how implants are administered and used, and concerns associated with implants. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, August 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an318
Can Calcium Propionate Help Maintain Calcium Concentrations and Prevent Metritis in Dairy Cows with Dystocia?
Studies have suggested that giving dairy cows supplemental calcium may reduce the incidence of metritis. This study tested this hypothesis with cows at the UF Dairy Unit and found that calcium supplements actually did not benefit postpartum health and are not recommended as means of metritis prevention. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Klibs N. Galvao, Mauricio Benzaquen, and Carlos A. Risco, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine—Large Animal Clinical Sciences, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm223
Getting Started in the 4-H Embryology Project: Tips for 4-H Agents and Teachers
 Usually considered an enrichment project for classrooms, the 4-H Embryology Project can also be modified for club or individual use. In it, young people use an incubator to grow avian embryos (inside fertile eggs) through the hatching process. Students learn basic biology and life science while they eagerly look forward to hatching chicks. This 5-page fact sheet describes the necessary equipment and other resources and provides tips and suggestions to increase the hatchability of fertile avian eggs. Written by Marcus Boston, Chris Decubellis, and Judith Levings, and published by the UF Department of 4-H Youth Development, April 2015. (Photo: Marcus Boston, UF/IFAS)
Usually considered an enrichment project for classrooms, the 4-H Embryology Project can also be modified for club or individual use. In it, young people use an incubator to grow avian embryos (inside fertile eggs) through the hatching process. Students learn basic biology and life science while they eagerly look forward to hatching chicks. This 5-page fact sheet describes the necessary equipment and other resources and provides tips and suggestions to increase the hatchability of fertile avian eggs. Written by Marcus Boston, Chris Decubellis, and Judith Levings, and published by the UF Department of 4-H Youth Development, April 2015. (Photo: Marcus Boston, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/4h367
Understanding Nitrogen Availability from Applications of Anaerobically Digested Beef-Cattle Manure in Florida Sandy Soil
 Anaerobic digestion of livestock manure is a microbe-mediated process carried out in vessels or tanks, where the livestock wastes are digested slowly in environment absent of oxygen. The main products are biogas, anaerobically digested liquid (ADL), and solid (ADS), which can be land-applied as an organic soil amendment or a source of plant nutrients. This 4-page fact sheet provides research-based information about using anaerobically digested beef-cattle manure as an organic source of nitrogen for supplementing crop nutrition in Florida sandy soils, including initial N concentration, application timing, rate of application, and method of application. Written by Rishi Prasad and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, April 2015. (Photo: George Hochmuth, UF/IFAS)
Anaerobic digestion of livestock manure is a microbe-mediated process carried out in vessels or tanks, where the livestock wastes are digested slowly in environment absent of oxygen. The main products are biogas, anaerobically digested liquid (ADL), and solid (ADS), which can be land-applied as an organic soil amendment or a source of plant nutrients. This 4-page fact sheet provides research-based information about using anaerobically digested beef-cattle manure as an organic source of nitrogen for supplementing crop nutrition in Florida sandy soils, including initial N concentration, application timing, rate of application, and method of application. Written by Rishi Prasad and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, April 2015. (Photo: George Hochmuth, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss637
Managing Nitrogen Inputs and Outputs on a Dairy Farm
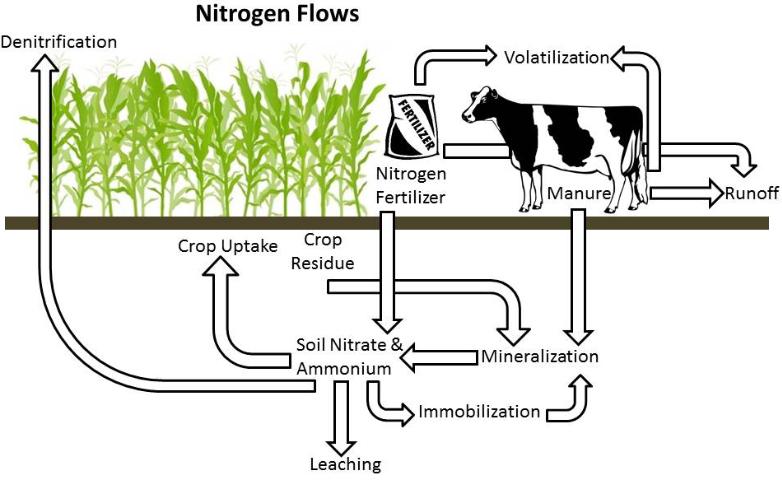
 In dairy production systems, nitrogen flows through both the forage crops and the dairy cows. Forage crops use nitrogen mineralized from manure for plant growth. Harvested crops are then fed to dairy cows that, in turn, use the nitrogen for their growth and milk production. When the cows excrete a portion of the consumed nitrogen as manure the cycle is renewed. This 5-page fact sheet focuses on the forage production aspect of the nitrogen cycle at a dairy farm. Written by Rebecca Hellmuth and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Image credit: R. Hellmuth)
In dairy production systems, nitrogen flows through both the forage crops and the dairy cows. Forage crops use nitrogen mineralized from manure for plant growth. Harvested crops are then fed to dairy cows that, in turn, use the nitrogen for their growth and milk production. When the cows excrete a portion of the consumed nitrogen as manure the cycle is renewed. This 5-page fact sheet focuses on the forage production aspect of the nitrogen cycle at a dairy farm. Written by Rebecca Hellmuth and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Image credit: R. Hellmuth)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss640
Chicken Mite (other common names: poultry red mite, roost mite) Dermanyssus gallinae (De Geer) (Arachnida: Acari: Dermanyssidae)
 The chicken mite affects egg-laying hens in many parts of the world, including Europe, Japan, China, and the United States. Although Dermanyssus gallinae affects birds in many regions, it is most prevalent in European countries, where egg industry losses are estimated at $177 million per year. It is a known vector for the St. Louis encephalitis virus, as well as other illnesses, such as fowl pox virus, Newcastle virus, and fowl cholera. In the United States, Dermanyssus gallinae is rarely found in caged-layer operations and is more commonly found in breeder farms. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ethan Carter and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2015. (Photo credit: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida)
The chicken mite affects egg-laying hens in many parts of the world, including Europe, Japan, China, and the United States. Although Dermanyssus gallinae affects birds in many regions, it is most prevalent in European countries, where egg industry losses are estimated at $177 million per year. It is a known vector for the St. Louis encephalitis virus, as well as other illnesses, such as fowl pox virus, Newcastle virus, and fowl cholera. In the United States, Dermanyssus gallinae is rarely found in caged-layer operations and is more commonly found in breeder farms. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ethan Carter and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2015. (Photo credit: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1070
Improving the Productivity of Beef Heifers in Florida
 Beef replacement heifers are a necessary but costly part of every cow-calf operation. A decision needs to be made to either purchase replacement heifers or raise them on the ranch. This is a long-term decision that will affect the ranch for many years through the genetics of the replacement heifers and through equipment and management inputs. This 9-page fact sheet provides an analysis of considerations for raising replacements; factors to consider in selection; and recommendations for nutritional management. Written by Phillip Lancaster, Chris Prevatt, and John Arthington, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, March 2015. (Photo: Beef Improvement Federation)
Beef replacement heifers are a necessary but costly part of every cow-calf operation. A decision needs to be made to either purchase replacement heifers or raise them on the ranch. This is a long-term decision that will affect the ranch for many years through the genetics of the replacement heifers and through equipment and management inputs. This 9-page fact sheet provides an analysis of considerations for raising replacements; factors to consider in selection; and recommendations for nutritional management. Written by Phillip Lancaster, Chris Prevatt, and John Arthington, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, March 2015. (Photo: Beef Improvement Federation)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an132
Smutgrass Control in Perennial Grass Pastures
 Smutgrass is a serious weed of improved perennial grass pastures, roadsides, natural areas, and waste areas in Florida. A 2003 survey found that smutgrass was second only to tropical soda apple as the most problematic weed species in Florida pastures, but now that practices to control tropical soda apple have been widely adopted in Florida, smutgrass is likely the most problematic weed species in Florida pastures today. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Brent Sellers, J. A. Ferrell, and N. Rana, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2015. (Photo Credit: B. Sellers, UF/IFAS)
Smutgrass is a serious weed of improved perennial grass pastures, roadsides, natural areas, and waste areas in Florida. A 2003 survey found that smutgrass was second only to tropical soda apple as the most problematic weed species in Florida pastures, but now that practices to control tropical soda apple have been widely adopted in Florida, smutgrass is likely the most problematic weed species in Florida pastures today. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Brent Sellers, J. A. Ferrell, and N. Rana, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2015. (Photo Credit: B. Sellers, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/aa261
How Do I Legally Sell Meat from Alligators, Wild Game, or My Farmed Game or Birds in Florida?
 Game meats provide wholesome and nutritious animal protein, but learning the regulations (and which agency has jurisdiction over which regulations) can be burdensome for those who want to be entrepreneurial. This 4-page fact sheet is a “one-stop-shop” for Florida residents who want to sell products from alligators, wild game, or their own farmed game or birds. Written by Chad Carr, Jason Scheffler, Larry Eubanks, Ron Webb, Lee Cornman, Scotland Talley, and Steve Stiegler, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
Game meats provide wholesome and nutritious animal protein, but learning the regulations (and which agency has jurisdiction over which regulations) can be burdensome for those who want to be entrepreneurial. This 4-page fact sheet is a “one-stop-shop” for Florida residents who want to sell products from alligators, wild game, or their own farmed game or birds. Written by Chad Carr, Jason Scheffler, Larry Eubanks, Ron Webb, Lee Cornman, Scotland Talley, and Steve Stiegler, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an315
Cull Cow Beef Quality Issues series
 Cull cattle are those that are sold from a herd for lack of performance, lack of resources, or genetic improvement The non-fed beef cattle market (cattle that are not managed through traditional feedlot finishing systems) is comprised primarily of cull cows and bulls. To address liability and food safety concerns, this series of articles discusses some quality defects identified in the non-fed beef market, how to prevent them, and how to address them when they appear in cattle.
Cull cattle are those that are sold from a herd for lack of performance, lack of resources, or genetic improvement The non-fed beef cattle market (cattle that are not managed through traditional feedlot finishing systems) is comprised primarily of cull cows and bulls. To address liability and food safety concerns, this series of articles discusses some quality defects identified in the non-fed beef market, how to prevent them, and how to address them when they appear in cattle.
- Overview of Cull Cow Beef Quality Issues
- Injection Sites and Abscesses
- Horns, Ocular Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Lumpy Jaw
- Bruising, Condemnation, and Foreign Objects
- Cow Condition and Muscling
- Hide Defects, Contamination, and Non-Ambulatory Cattle
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_series_cull_cow_beef_quality_issues
How Do I Legally Sell Meat from My Own Livestock and Poultry in Florida?
 There is much interest in locally produced foods, but the federal, state, and local regulations can be confusing. This 5-page fact sheet is a “one-stop-shop” for Florida residents who want to sell meat from their own livestock and poultry. Written by Chad Carr, Jason Scheffler, Larry Eubanks, Ron Webb, Lee Cornman, Scotland Talley, and Steve Stiegler, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
There is much interest in locally produced foods, but the federal, state, and local regulations can be confusing. This 5-page fact sheet is a “one-stop-shop” for Florida residents who want to sell meat from their own livestock and poultry. Written by Chad Carr, Jason Scheffler, Larry Eubanks, Ron Webb, Lee Cornman, Scotland Talley, and Steve Stiegler, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an316
Selective Antibiotic Treatment for Dairy Cow Mastitis
 Mastitis is the most common disease in dairy cattle and is estimated to cost dairy farmers $179 a case. When farmers detect clinical mastitis, they usually take immediate action with antibiotics; but many cases either do not need antimicrobial treatment, resolve without treatment, or are not effectively treated by the antimicrobial used. A selective treatment approach can be more effective. This two-step strategy involves first identifying the pathogen, then deciding on a treatment — this would decrease the use of antimicrobials as well as treatment-associated costs for the farmer. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Kathryn Merriman, Fiona Maunsell, Corwin Nelson, and Albert De Vries, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2014. (Photo: University of Minnesota Laboratory for Udder Health, 2004)
Mastitis is the most common disease in dairy cattle and is estimated to cost dairy farmers $179 a case. When farmers detect clinical mastitis, they usually take immediate action with antibiotics; but many cases either do not need antimicrobial treatment, resolve without treatment, or are not effectively treated by the antimicrobial used. A selective treatment approach can be more effective. This two-step strategy involves first identifying the pathogen, then deciding on a treatment — this would decrease the use of antimicrobials as well as treatment-associated costs for the farmer. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Kathryn Merriman, Fiona Maunsell, Corwin Nelson, and Albert De Vries, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2014. (Photo: University of Minnesota Laboratory for Udder Health, 2004)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an306
Environmental Impact of Beef Cattle Production Systems
 This 6-page fact sheet discusses beef demand in the context of a growing population, beef production’s greenhouse gases and their effect on the environment, the great advantage of ruminants, generating accurate greenhouse gas emissions estimates, greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector, and mitigation strategies. Written by Nicolas DiLorenzo, G. Cliff Lamb, Jose Dubeux, John Arthington, Joao Vendramini, and Phillip Lancaster and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo by Thomas Wright)
This 6-page fact sheet discusses beef demand in the context of a growing population, beef production’s greenhouse gases and their effect on the environment, the great advantage of ruminants, generating accurate greenhouse gas emissions estimates, greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector, and mitigation strategies. Written by Nicolas DiLorenzo, G. Cliff Lamb, Jose Dubeux, John Arthington, Joao Vendramini, and Phillip Lancaster and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo by Thomas Wright)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an302
Potential Bull Buyers Perceive Increased Value to their Operations When Purchasing Bulls from the Florida Bull Test
 Since its beginning in 2000, the Florida Bull Test has been under constant evolution to achieve its goal of helping producers select high-quality sires, thereby improving production and profitability of beef cattle producers in Florida and the Southeast United States. A survey of potential buyers before the 2014 sale succeeded in identifying which characteristics of bulls are most important to buyers purchasing bulls: purchasing bulls from the Florida Bull Test increases the value of calves sired by improving performance, genetics, and feed efficiency of their herds. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, Darren D. Henry, Francine M. Ciriaco, Paula M. Mercadante, Tessa Schulmeister, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
Since its beginning in 2000, the Florida Bull Test has been under constant evolution to achieve its goal of helping producers select high-quality sires, thereby improving production and profitability of beef cattle producers in Florida and the Southeast United States. A survey of potential buyers before the 2014 sale succeeded in identifying which characteristics of bulls are most important to buyers purchasing bulls: purchasing bulls from the Florida Bull Test increases the value of calves sired by improving performance, genetics, and feed efficiency of their herds. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Vitor R. G. Mercadante, Darren D. Henry, Francine M. Ciriaco, Paula M. Mercadante, Tessa Schulmeister, Nicolas DiLorenzo, and G. Cliff Lamb, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an313
Understanding Pregnancy Diagnosis in Beef Cattle
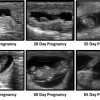 Because 55 to 70 percent of the input costs associated with a beef cattle operation are related to nutrition, culling open (non-pregnant) cows after the breeding season can save as much as $200 per head that can be diverted to the purchase or development of replacement females, sire selection, increased nutritional management, and other management-related costs. Pregnancy diagnosis can be performed simply during vaccination or at the time of weaning. There are three practical methods: rectal palpation, transrectal ultrasonography, or blood test. This 5-page fact sheet was written by G. Cliff Lamb, Darren D. Henry, Vitor R. G. Mercadante, and Doug E. Mayo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
Because 55 to 70 percent of the input costs associated with a beef cattle operation are related to nutrition, culling open (non-pregnant) cows after the breeding season can save as much as $200 per head that can be diverted to the purchase or development of replacement females, sire selection, increased nutritional management, and other management-related costs. Pregnancy diagnosis can be performed simply during vaccination or at the time of weaning. There are three practical methods: rectal palpation, transrectal ultrasonography, or blood test. This 5-page fact sheet was written by G. Cliff Lamb, Darren D. Henry, Vitor R. G. Mercadante, and Doug E. Mayo, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an314
Saddle and Tack Care in Hot and Humid Environments
 The South’s climate is appealing for equestrian activities. While riders enjoy the weather, it creates some challenges in caring for saddles and other tack. When the weather becomes hot and the humidity climbs and the rains are frequent, a tack room can become a breeding ground for mold and mildew. There are several things a rider can do, however, to lower the incidence of mildew on saddles and tack. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Joel McQuagge, Todd Thrift, and Ed Johnson, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014. (Photo credit: Joel McQuagge, UF/IFAS)
The South’s climate is appealing for equestrian activities. While riders enjoy the weather, it creates some challenges in caring for saddles and other tack. When the weather becomes hot and the humidity climbs and the rains are frequent, a tack room can become a breeding ground for mold and mildew. There are several things a rider can do, however, to lower the incidence of mildew on saddles and tack. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Joel McQuagge, Todd Thrift, and Ed Johnson, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, November 2014. (Photo credit: Joel McQuagge, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an303
2014 Cool-Season Forage Variety Recommendations for Florida
 This 4-page fact sheet provides the most up-to-date information on current adapted varieties of cool-season forages. The recommendation of varieties is based on multi-location, multi-year cultivar evaluation experiments that may include trials in Georgia and other states. Table 1 includes information about the planting dates, seeding rates, and other considerations. If you have questions about a particular variety, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension agent for additional information. Written by A. R. Blount, J. M. B. Vendramini, J. C. B. Dubeux, Md A. Babar, K. E. Kenworthy, P. R. Muñoz,and K. H. Quesenberry, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo: Josh Wickam)
This 4-page fact sheet provides the most up-to-date information on current adapted varieties of cool-season forages. The recommendation of varieties is based on multi-location, multi-year cultivar evaluation experiments that may include trials in Georgia and other states. Table 1 includes information about the planting dates, seeding rates, and other considerations. If you have questions about a particular variety, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension agent for additional information. Written by A. R. Blount, J. M. B. Vendramini, J. C. B. Dubeux, Md A. Babar, K. E. Kenworthy, P. R. Muñoz,and K. H. Quesenberry, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo: Josh Wickam)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/aa266
Effect of Anovulation and Subclinical Endometritis on Fertility of Lactating Dairy Cows: Why Are Dairy Cows Not Getting Pregnant: Lack of Cyclicity, Uterine Disease, or Both?
 Virtually all Holstein dairy cows have the first wave of follicle growth starting two weeks postpartum, with about 30% of these cows ovulating within 21 days in milk. This 3-page fact sheet presents the results of a recent paper that evaluated the individual and combined effects of anovulation and subclinical endometritis on reproductive performance of dairy cows. Written by Klibs N. Galvão and Achilles Vieira-Neto, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine-Large Animal Clinical Sciences, May 2014.
Virtually all Holstein dairy cows have the first wave of follicle growth starting two weeks postpartum, with about 30% of these cows ovulating within 21 days in milk. This 3-page fact sheet presents the results of a recent paper that evaluated the individual and combined effects of anovulation and subclinical endometritis on reproductive performance of dairy cows. Written by Klibs N. Galvão and Achilles Vieira-Neto, and published by the UF Department of Veterinary Medicine-Large Animal Clinical Sciences, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm222
Budgets for Pasture Establishment: Seeded and Vegetative
 Budgets can be used to make rational decisions when establishing or renovating a pasture in Florida. This 3-page fact sheet is a guide for evaluating the costs of establishing a seeded-type pasture versus vegetatively propagated hybrid bermudagrasses. Written by Les Harrison, Jonael Bosques, and Yoana Newman, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014.
Budgets can be used to make rational decisions when establishing or renovating a pasture in Florida. This 3-page fact sheet is a guide for evaluating the costs of establishing a seeded-type pasture versus vegetatively propagated hybrid bermudagrasses. Written by Les Harrison, Jonael Bosques, and Yoana Newman, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag386