 La producción de olivo o aceitunas (Olea europea) en Florida ha aumentado en los últimos años. La disponibilidad de árboles en los viveros de plantas ha aumentado y muchos residentes los compran para plantarlos en su patio. Afortunadamente, los olivos son una especie relativamente resistente a muchas plagas, pero en ocasiones surgen invasores que pueden causar daños significativos. Algunos patógenos también pueden infectar los olivos y causar enfermedades, reducir los rendimientos o arruinar la apariencia estética de los árboles. Siguiendo las prácticas de cultivo apropiadas para olivos podemos reducir las probabilidades de perder árboles por plagas y enfermedades. Una encuesta realizada con productores de aceitunas en Florida durante el año 2014 identificó las plagas y enfermedades descritas en este documento.
La producción de olivo o aceitunas (Olea europea) en Florida ha aumentado en los últimos años. La disponibilidad de árboles en los viveros de plantas ha aumentado y muchos residentes los compran para plantarlos en su patio. Afortunadamente, los olivos son una especie relativamente resistente a muchas plagas, pero en ocasiones surgen invasores que pueden causar daños significativos. Algunos patógenos también pueden infectar los olivos y causar enfermedades, reducir los rendimientos o arruinar la apariencia estética de los árboles. Siguiendo las prácticas de cultivo apropiadas para olivos podemos reducir las probabilidades de perder árboles por plagas y enfermedades. Una encuesta realizada con productores de aceitunas en Florida durante el año 2014 identificó las plagas y enfermedades descritas en este documento.
This 6-page fact sheet was written by Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, Sandra A. Allan, Jonael H. Bosques-Méndez, and Lyle J. Buss; translated into Spanish by Jonael H. Bosques Méndez, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1052
Tag: J. Bosques
Budgets for Pasture Establishment: Seeded and Vegetative
 Budgets can be used to make rational decisions when establishing or renovating a pasture in Florida. This 3-page fact sheet is a guide for evaluating the costs of establishing a seeded-type pasture versus vegetatively propagated hybrid bermudagrasses. Written by Les Harrison, Jonael Bosques, and Yoana Newman, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014.
Budgets can be used to make rational decisions when establishing or renovating a pasture in Florida. This 3-page fact sheet is a guide for evaluating the costs of establishing a seeded-type pasture versus vegetatively propagated hybrid bermudagrasses. Written by Les Harrison, Jonael Bosques, and Yoana Newman, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag386
Pests and Fungal Organisms Identified on Olives (Olea europaea) in Florida
 Olive production in Florida has increased over the last few years. As trees become available in nurseries many homeowners are planting them in their landscapes. Fortunately, olives are a relatively pest-free species, but some occasional invaders can be a nuisance or cause lasting harm. A few plant pathogens that may infect olives also can lead to a decline in overall plant health, fruit yield, or the visual appearance of plants. Following correct cultural practices when growing olives can reduce your chances of tree loss from pests and diseases. A survey of olive production and interviews with Florida growers in 2014 identified the pests and diseases described in this 5-page fact sheet, written by Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, Sandra A. Allan, Jonael H. Bosques-Mendez, and Lyle J. Buss, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2014.
Olive production in Florida has increased over the last few years. As trees become available in nurseries many homeowners are planting them in their landscapes. Fortunately, olives are a relatively pest-free species, but some occasional invaders can be a nuisance or cause lasting harm. A few plant pathogens that may infect olives also can lead to a decline in overall plant health, fruit yield, or the visual appearance of plants. Following correct cultural practices when growing olives can reduce your chances of tree loss from pests and diseases. A survey of olive production and interviews with Florida growers in 2014 identified the pests and diseases described in this 5-page fact sheet, written by Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, Sandra A. Allan, Jonael H. Bosques-Mendez, and Lyle J. Buss, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1046
Bermudagrass Stem Maggot: A New Pest in Florida
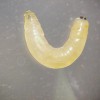 Bermudagrass is a dominant hay crop in Florida. Now, hay producers are facing a new emerging pest problem in bermudagrass and stargrass production fields. The bermudagrass stem maggot, is a new exotic invasive fly. It was first discovered damaging bermudagrass pasture and hay fields in Georgia. The identification of the fly was the first record of this species in North America, and it has the potential to become a serious pest of bermudagrass and stargrass in Florida. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Ann Blount, Tim Wilson, Jay Ferrell, Russ Mizell, and Jonael Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, June 2014.
Bermudagrass is a dominant hay crop in Florida. Now, hay producers are facing a new emerging pest problem in bermudagrass and stargrass production fields. The bermudagrass stem maggot, is a new exotic invasive fly. It was first discovered damaging bermudagrass pasture and hay fields in Georgia. The identification of the fly was the first record of this species in North America, and it has the potential to become a serious pest of bermudagrass and stargrass in Florida. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Ann Blount, Tim Wilson, Jay Ferrell, Russ Mizell, and Jonael Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, June 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag384
Estimando la Cantidad de Forraje en Campos de Heno y Potreros
 El forraje sirve como fuente primaria de nutrientes para la industria ganadera en Florida. El uso eficiente de esta fuente nutricional es crítico para la supervivencia de los agricultores y rancheros de dicho estado. El estimar la cantidad de forraje en potreros puede proveer información útil a la hora de tomar decisiones acerca del manejo de nuestros recursos. Debe de haber suficiente material en el predio para justificar el costo de utilizar el equipo para cosechar (por ejemplo, precio de compra del equipo, renta, costo del combustible a invertirse, y el costo de la mano de obra). Sin esta información, el predio debe ser sometido a pastoreo. Esta publicación contiene las instrucciones para la implementación de un método simple que nos permite determinar la cantidad aproximada de forraje en campos de heno y potreros.This 2-page fact sheet was written by T. Wilson, C. Sanders, J. Breman, y L. Sollenberger. Traducido por J. Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
El forraje sirve como fuente primaria de nutrientes para la industria ganadera en Florida. El uso eficiente de esta fuente nutricional es crítico para la supervivencia de los agricultores y rancheros de dicho estado. El estimar la cantidad de forraje en potreros puede proveer información útil a la hora de tomar decisiones acerca del manejo de nuestros recursos. Debe de haber suficiente material en el predio para justificar el costo de utilizar el equipo para cosechar (por ejemplo, precio de compra del equipo, renta, costo del combustible a invertirse, y el costo de la mano de obra). Sin esta información, el predio debe ser sometido a pastoreo. Esta publicación contiene las instrucciones para la implementación de un método simple que nos permite determinar la cantidad aproximada de forraje en campos de heno y potreros.This 2-page fact sheet was written by T. Wilson, C. Sanders, J. Breman, y L. Sollenberger. Traducido por J. Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag379
Construccion de Sistema Hidroponico Flotante (HS1210)
 Los aztecas maravillaron a los conquistadores españoles con sus huertos flotantes, y hoy, 500 años después, usted puede impresionar a sus amigos y vecinos con el suyo. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Horticultural Sciences, and published by the UF Department of J. Bosques, M. Sweat, R. Tyson, y R. Hochmuth, January 2013.
Los aztecas maravillaron a los conquistadores españoles con sus huertos flotantes, y hoy, 500 años después, usted puede impresionar a sus amigos y vecinos con el suyo. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Horticultural Sciences, and published by the UF Department of J. Bosques, M. Sweat, R. Tyson, y R. Hochmuth, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1210