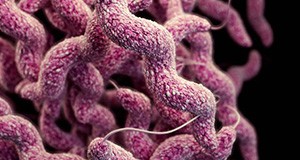
Campylobacteriosis is a gastrointestinal infection caused by bacteria of the genus Campylobacter. These bacteria require low levels of oxygen to survive and have been found in wild birds, poultry, pigs, cattle, domesticated animals, unpasteurized milk, produce, and contaminated water. A part of a series on preventing foodborne illness, this five-page fact sheet describes the Campylobacter bacteria, the causes and symptoms of campylobacteriosis disease, and how to prevent the disease through good sanitation methods and practices for receiving, handling, processing, and storing food products. Written by Soohyoun Ahn, Renée M. Goodrich-Schneider, Rachael Silverberg, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs098
Tag: Food Science and Human Nutrition Department
Shopping for Health: Breakfast Cereals
It is no secret that breakfast is an important meal. Eating breakfast provides you with physical and mental energy to start the day, along with vitamins and minerals. Cereal is a quick, versatile, and budget-friendly breakfast choice. The benefits of eating a healthy cereal include increased fiber intake and lower body weight. But navigating the cereal aisle at your local grocery store can be an overwhelming experience. Continue reading this three-page fact sheet to learn more about cereal and how to find your new go-to breakfast choices. Written by Jenna Sechar and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs274
Food Safety within the Household: Risk Reduction

Food poisoning is common in the United States. The CDC estimates that 48 million Americans acquire foodborne illness every year, many of which were attributed to food preparation occurring in private homes. In 2013, the top five identified bacterial and viral causes of food poisoning attributed to home food preparation were Salmonella, norovirus, shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, and Campylobacter. This six page fact sheet outlines the most common food-safety handling mistakes, which are improper food storage, inadequate cooking or reheating temperatures, cross-contamination, and infected food handlers. Written by Lucianna Grasso, Rachael Silverberg, George L. Baker, Renée M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs195
Preventing Foodborne and Non-foodborne Illness: Vibrio parahaemolyticus
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a naturally occurring bacterium that inhabits coastal brackish marine waters throughout the world and is commonly found in the United States and Canada. If ingested in sufficient numbers, this bacterium can cause illness such as gastroenteritis with symptoms such as cramps, vomiting, and nausea. Illnesses linked with this organism are usually associated with the consumption of raw or improperly cooked seafood, particularly raw oysters. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses Vibrio parahaemolyticus, illness caused by the bacterium, factors that increase risk of infection, methods of infection, seafood and shellfish handling recommendations, and prevention. Written by Anita C. Wright, Renée M. Goodrich, Michael A. Hubbard, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition. Original publication date: July 2009. Revised October 2015.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a naturally occurring bacterium that inhabits coastal brackish marine waters throughout the world and is commonly found in the United States and Canada. If ingested in sufficient numbers, this bacterium can cause illness such as gastroenteritis with symptoms such as cramps, vomiting, and nausea. Illnesses linked with this organism are usually associated with the consumption of raw or improperly cooked seafood, particularly raw oysters. This 3-page fact sheet is a major revision that discusses Vibrio parahaemolyticus, illness caused by the bacterium, factors that increase risk of infection, methods of infection, seafood and shellfish handling recommendations, and prevention. Written by Anita C. Wright, Renée M. Goodrich, Michael A. Hubbard, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition. Original publication date: July 2009. Revised October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs146
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Bacillus cereus

Ingesting foods contaminated with Bacillus cereus bacteria can lead to nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Though B. cereus is commonly found in many types of fresh and processed foods, proper cooking, handling, and storage can minimize the risk of contamination. This 5-page fact sheet explains how B. cereus is transmitted, what foods it is commonly associated with, the methods used to prevent contamination, and good practices for receiving, handling, processing, and storing food. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée Goodrich Schneider, and Rachael Silverberg, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, August 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs269
Value-Added Products for Fresh Highbush Blueberries

Blueberries are one of the most popular fruits worldwide. Blueberries’ health benefits have fueled this popularity, and today, blueberries can be found in products ranging from nutritional supplements to pet food. This 4-page fact sheet covers the processing methods such as freezing or drying that transform fresh blueberries into ingredients that can be used in other products. Written by Ruiqi Li and Liwei Gu, and published by the UF Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs268
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Norovirus
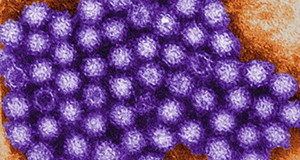
If you have ever had the stomach flu, norovirus was likely the culprit. Norovirus is the most common cause of foodborne illness in the United States and is transmitted through direct person-to-person contact or contaminated objects and food. This 5-page fact sheet covers how norovirus is spread, foods associated with norovirus, symptoms of infection, who is at risk, as well proper sanitation methods for preventing the spread of norovirus. Written by Rachael Silverberg, Melissa K. Jones, Renée Goodrich Schneider, Aswathy Sreedharan and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs129
Health Benefits and Medicinal Value of Honey
 Honey has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. It is rich in sugars such as glucose and fructose, but it also contains small amounts of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and antioxidants such as phenolic acids and flavonoids. These nutrients help to make honey a unique, natural health product. Its market niche as a health product is growing, and current research supports the potential of honey as a medicinal product. This 3-page fact sheet describes health aspects of honey deriving from the floral source and color, beneficial compounds, anti-microbial properties and anti-inflammatory properties. Written by Sara Marshall, Liwei Gu, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2015.
Honey has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. It is rich in sugars such as glucose and fructose, but it also contains small amounts of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and antioxidants such as phenolic acids and flavonoids. These nutrients help to make honey a unique, natural health product. Its market niche as a health product is growing, and current research supports the potential of honey as a medicinal product. This 3-page fact sheet describes health aspects of honey deriving from the floral source and color, beneficial compounds, anti-microbial properties and anti-inflammatory properties. Written by Sara Marshall, Liwei Gu, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs267
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Cyclospora cayetanensis
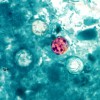 Cyclospora cayetanensis is a microscopic, spore-forming, intestinal protozoan parasite and a known cause of the gastrointestinal infection cyclosporiasis, often referred to as “traveler’s diarrhea” for its prevalence among visitors to regions where the species is endemic. These organisms have a protective covering that makes them resistant to disinfectants and that gives Cyclospora the ability to survive outside of hosts for extended periods. The incidence of cyclosporiasis has been increasing worldwide, with several documented cases in the United States and Canada. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Keith R. Schneider, Rachael Silverberg, Susie Richardson, and Renée Goodrich Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2015. (Photo: CDC/DPDx – Melanie Moser)
Cyclospora cayetanensis is a microscopic, spore-forming, intestinal protozoan parasite and a known cause of the gastrointestinal infection cyclosporiasis, often referred to as “traveler’s diarrhea” for its prevalence among visitors to regions where the species is endemic. These organisms have a protective covering that makes them resistant to disinfectants and that gives Cyclospora the ability to survive outside of hosts for extended periods. The incidence of cyclosporiasis has been increasing worldwide, with several documented cases in the United States and Canada. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Keith R. Schneider, Rachael Silverberg, Susie Richardson, and Renée Goodrich Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2015. (Photo: CDC/DPDx – Melanie Moser)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs130
Women's Nutrition: Folate/Folic Acid
 To decrease a baby’s chances of having certain types of births defects, mothers need to have already been consuming enough of the vitamin called folate, or folic acid, before they become pregnant. This article provides information about the folate/folic acid needs of women who are capable of becoming pregnant, including its role in preventing birth defects, sources, and strategies for meeting the recommended intake. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Caroline Dunn and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2015. (Photo Credit: Mike Watson Images/moodboard/Thinkstock.com)
To decrease a baby’s chances of having certain types of births defects, mothers need to have already been consuming enough of the vitamin called folate, or folic acid, before they become pregnant. This article provides information about the folate/folic acid needs of women who are capable of becoming pregnant, including its role in preventing birth defects, sources, and strategies for meeting the recommended intake. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Caroline Dunn and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2015. (Photo Credit: Mike Watson Images/moodboard/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs265
De compras para la salud: Comidas para una persona
 En el mundo ajetreado de hoy, muchos estadounidenses se encuentran cocinando para ellos mismos. Los adultos mayores y estudiantes universitarios por igual, se enfrentan al desafío de preparar la comida como una prioridad, cuando nadie más se encarga de ellos para crear una comida balanceada. Ya sea que usted coloque una comida en el microondas después de un día muy ocupado, o pase tiempo cocinando una comida especial para usted, comprar y preparar comidas saludables para uno mismo a bajo costo puede ser agradable, simplemente con un poco de planificación. This 5-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of FSHN13-02/FS224: Shopping for Health: A Menu for One. It was written by Morgan Denhard and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2015. (Photo: Thinkstock.com)
En el mundo ajetreado de hoy, muchos estadounidenses se encuentran cocinando para ellos mismos. Los adultos mayores y estudiantes universitarios por igual, se enfrentan al desafío de preparar la comida como una prioridad, cuando nadie más se encarga de ellos para crear una comida balanceada. Ya sea que usted coloque una comida en el microondas después de un día muy ocupado, o pase tiempo cocinando una comida especial para usted, comprar y preparar comidas saludables para uno mismo a bajo costo puede ser agradable, simplemente con un poco de planificación. This 5-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of FSHN13-02/FS224: Shopping for Health: A Menu for One. It was written by Morgan Denhard and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2015. (Photo: Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs266
Shopping for Health: Snack Foods
 At first glance, you might think that snacking should be avoided because of the extra calories they can add to your diet. However, studies have shown there may be benefits when healthy snack choices are made. Read this 4-page fact sheet to learn about the benefits of healthy snacks and to learn healthy snack shopping tips. Includes recipes for homemade crispy kale chips and peanut butter and jelly yogurt. Written by Carley Rusch and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
At first glance, you might think that snacking should be avoided because of the extra calories they can add to your diet. However, studies have shown there may be benefits when healthy snack choices are made. Read this 4-page fact sheet to learn about the benefits of healthy snacks and to learn healthy snack shopping tips. Includes recipes for homemade crispy kale chips and peanut butter and jelly yogurt. Written by Carley Rusch and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs262
Shopping for Health: Seafood
 Seafood is part of the protein foods group of MyPlate and also provides other nutrients needed for good health. Because of the many health benefits, adults should consume at least eight ounces of a variety of seafood every week. Still, it is important to consider your budget when shopping for seafood. This 4-page fact sheet explains the health benefits of seafood and offers some money-saving strategies for making seafood more affordable. Written by Michelle Brown and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2014. (Photo: Elena Gaak/iStock/Thinkstock)
Seafood is part of the protein foods group of MyPlate and also provides other nutrients needed for good health. Because of the many health benefits, adults should consume at least eight ounces of a variety of seafood every week. Still, it is important to consider your budget when shopping for seafood. This 4-page fact sheet explains the health benefits of seafood and offers some money-saving strategies for making seafood more affordable. Written by Michelle Brown and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2014. (Photo: Elena Gaak/iStock/Thinkstock)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs247
Facts about Protein
 There are many sources of dietary protein. This 3-page fact sheet covers protein basics, the role of proteins in the body, recommended intake, sources of protein and how to make healthier choices. Written by Nicole C. Agro and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2015.
There are many sources of dietary protein. This 3-page fact sheet covers protein basics, the role of proteins in the body, recommended intake, sources of protein and how to make healthier choices. Written by Nicole C. Agro and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs261
Food Safety for the Holiday Season
 Food is always an important part of holiday festivities, but holiday meals can take a turn for the worse if food safety is not properly practiced when preparing and cooking the food. The food you serve your family and friends can be very harmful if your turkey, ham, or home-prepared meat products are not appropriately handled. The good news is that by practicing four basic food safety measures you can help prevent foodborne illness over the holiday season. This 6-page fact sheet provides information about safe food practices for the holidays. Written by Soohyoun Ahn and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2014. (Photo: Stockbyte/Thinkstock)
Food is always an important part of holiday festivities, but holiday meals can take a turn for the worse if food safety is not properly practiced when preparing and cooking the food. The food you serve your family and friends can be very harmful if your turkey, ham, or home-prepared meat products are not appropriately handled. The good news is that by practicing four basic food safety measures you can help prevent foodborne illness over the holiday season. This 6-page fact sheet provides information about safe food practices for the holidays. Written by Soohyoun Ahn and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2014. (Photo: Stockbyte/Thinkstock)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs260
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Clostridium botulinum
 Clostridium botulinum is ubiquitous in nature, often found in soil and water. The bacteria and spores alone do not cause disease, but they produce the botulinum toxin that causes botulism, a serious paralytic condition that can lead to death. Although it is one of the least common of the foodborne diseases, anyone is susceptible even with the ingestion of only a small amount of toxin present in contaminated food. Immunocompromised individuals, young children, and elderly individuals may suffer from more serious symptoms. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Keith R. Schneider, Rachael Silverberg, Alexandra Chang and Renée Goodrich Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2014.
Clostridium botulinum is ubiquitous in nature, often found in soil and water. The bacteria and spores alone do not cause disease, but they produce the botulinum toxin that causes botulism, a serious paralytic condition that can lead to death. Although it is one of the least common of the foodborne diseases, anyone is susceptible even with the ingestion of only a small amount of toxin present in contaminated food. Immunocompromised individuals, young children, and elderly individuals may suffer from more serious symptoms. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Keith R. Schneider, Rachael Silverberg, Alexandra Chang and Renée Goodrich Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs104
How to Start a Food Business: Writing a Business Plan
 Before starting a new food business, you should set a goal and have detailed plans to accomplish that goal. But writing a good business plan is often a challenge and it requires a great amount of effort. This 3-page fact sheet provides guidance on how to write a good food-business plan. Written by Soohyoun Ahn, Lisa House, and Renée Goodrich-Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock)
Before starting a new food business, you should set a goal and have detailed plans to accomplish that goal. But writing a good business plan is often a challenge and it requires a great amount of effort. This 3-page fact sheet provides guidance on how to write a good food-business plan. Written by Soohyoun Ahn, Lisa House, and Renée Goodrich-Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs259
Prueba de la cuchara para alimentos en pure
 Los alimentos en puré preparados para personas con problemas al tragar deben satisfacer las guías de textura recomendadas. La textura apropiada es la prioridad cuando se crean purés. Un puré debe tener textura uniforme que es un “espesor en la cuchara” y no requiere masticar. No debe ser seco, pegajoso, grumoso o delgado. Los ajustes de espesor pueden hacerse de acuerdo a las necesidades específicas del individuo.This 1-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Spoon Test for Puréed Food. Written by Wendy Dahl and Jamila Frazier, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014.
Los alimentos en puré preparados para personas con problemas al tragar deben satisfacer las guías de textura recomendadas. La textura apropiada es la prioridad cuando se crean purés. Un puré debe tener textura uniforme que es un “espesor en la cuchara” y no requiere masticar. No debe ser seco, pegajoso, grumoso o delgado. Los ajustes de espesor pueden hacerse de acuerdo a las necesidades específicas del individuo.This 1-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Spoon Test for Puréed Food. Written by Wendy Dahl and Jamila Frazier, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs257
Genetically Modified Food
 A food is considered genetically modified when its genetic makeup is altered in some way as a result of the use of recombinant DNA biotechnological procedures. These changes result in the expression of attributes not found in the original. Examples include delayed-ripening tomatoes and pest-resistant or herbicide-tolerant crops. Genetic modification can be used to improve crop yields, reduce insecticide use, or increase the nutritional value of foods. This 5-page fact sheet answers questions consumers might have about genetically modified food. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée Goodrich Schneider, and Susanna Richardson, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
A food is considered genetically modified when its genetic makeup is altered in some way as a result of the use of recombinant DNA biotechnological procedures. These changes result in the expression of attributes not found in the original. Examples include delayed-ripening tomatoes and pest-resistant or herbicide-tolerant crops. Genetic modification can be used to improve crop yields, reduce insecticide use, or increase the nutritional value of foods. This 5-page fact sheet answers questions consumers might have about genetically modified food. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée Goodrich Schneider, and Susanna Richardson, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs084
Outbreaks of Foodborne Illness Associated with Melons
 Despite the manner in which they are prepared, melons are commonly consumed raw without a processing step which would eliminate pathogenic bacteria. For those concerned about the safety of melons, including cantaloupe, honeydew, and watermelon, this 6-page fact sheet lists outbreaks associated with melons in the United States, Canada, and Europe, along with information about the location, pathogen, and incidence of illness. Written by Michelle D. Danyluk, Rachel McEgan, Ashley N. Turner, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo by Thomas Wright)
Despite the manner in which they are prepared, melons are commonly consumed raw without a processing step which would eliminate pathogenic bacteria. For those concerned about the safety of melons, including cantaloupe, honeydew, and watermelon, this 6-page fact sheet lists outbreaks associated with melons in the United States, Canada, and Europe, along with information about the location, pathogen, and incidence of illness. Written by Michelle D. Danyluk, Rachel McEgan, Ashley N. Turner, and Keith R. Schneider, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo by Thomas Wright)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs258