 Based on years of UF/IFAS research producing and trialing cultivars, this 3-page fact sheet lists native and non-invasive, non-native ornamentals as alternatives to invasive plants commonly used in Central Florida landscapes. Only plants considered to be generally available in the nursery trade are listed. Alternative plants are similar to respective invasive plants as much as possible in terms of size, habit, texture, and flower color. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Gary W. Knox, Sandra B. Wilson, Zhanao Deng, and Rosanna Freyre, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2013.
Based on years of UF/IFAS research producing and trialing cultivars, this 3-page fact sheet lists native and non-invasive, non-native ornamentals as alternatives to invasive plants commonly used in Central Florida landscapes. Only plants considered to be generally available in the nursery trade are listed. Alternative plants are similar to respective invasive plants as much as possible in terms of size, habit, texture, and flower color. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Gary W. Knox, Sandra B. Wilson, Zhanao Deng, and Rosanna Freyre, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep468
Author: dihagan
Directory of Certified Deciduous Fruit and Nut Crops in Florida
 This 8-page fact sheet written by experts at North Florida REC Peter C. Andersen, Robert C. Hochmuth, Sean R. McCoy, and Lei Lani L. Davis, assists farmers in locating recommended cultivars of fruit and nut crops from Florida nurseries. The nurseries listed in Table 1 offer fruit and nut trees and are listed as certified nurseries with the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Table 2 lists fruit and nut cultivars that UF/IFAS Extension specialists currently recommend or suggest on a trial basis. Published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2013.
This 8-page fact sheet written by experts at North Florida REC Peter C. Andersen, Robert C. Hochmuth, Sean R. McCoy, and Lei Lani L. Davis, assists farmers in locating recommended cultivars of fruit and nut crops from Florida nurseries. The nurseries listed in Table 1 offer fruit and nut trees and are listed as certified nurseries with the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Table 2 lists fruit and nut cultivars that UF/IFAS Extension specialists currently recommend or suggest on a trial basis. Published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1218
Healthy Eating: Calcium / Alimentación Saludable: Calcio
 Calcium is the major mineral found in your bones and teeth. Many older adults don’t get enough calcium from the foods they eat. This can lead to bone loss and the bone disease osteoporosis. Osteoporosis puts people at high risk for bone fractures. These 1-page, large print fact sheets were written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, June 2013.
Calcium is the major mineral found in your bones and teeth. Many older adults don’t get enough calcium from the foods they eat. This can lead to bone loss and the bone disease osteoporosis. Osteoporosis puts people at high risk for bone fractures. These 1-page, large print fact sheets were written by Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, June 2013.
English: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy057
Spanish: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy058
Economic Contributions of Agriculture, Natural Resources, and Related Food Industries in Florida in 2011
 Agriculture, natural resources, and related food industries remain a significant force in the economy of Florida, and it is important to recognize their economic contributions for informed public policy. We evaluated the economic contributions of these industries for calendar year 2011 to update previous reports and provide further information on economic trends in the wake of the historic global recession of 2007–2009. This 40-page report was written by Alan W. Hodges, Mohammad Rahmani, and Thomas J. Stevens, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, June 2013.
Agriculture, natural resources, and related food industries remain a significant force in the economy of Florida, and it is important to recognize their economic contributions for informed public policy. We evaluated the economic contributions of these industries for calendar year 2011 to update previous reports and provide further information on economic trends in the wake of the historic global recession of 2007–2009. This 40-page report was written by Alan W. Hodges, Mohammad Rahmani, and Thomas J. Stevens, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, June 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe935
US-Panama Free Trade Agreement: What Is in It for Florida Agriculture?
 On October 12, 2011, four years after it was agreed upon by both parties, the United States government signed into law the reciprocal US–Panama Free Trade Agreement (FTA)/Trade Promotion Agreement (TPA). The FTA provides US companies with better access to the Panamanian market and ensures that most US exports of consumer and industrial products to Panama will be accorded immediate duty-free privileges. The main elements of the US–Panama FTA as it relates to agricultural trade revolve around market access, agricultural export subsidies, safeguards, the sugar compensation mechanism, and sanitary and phytosanitary measures. This 11-page fact sheet was written by Edward A. Evans and Fredy H. Ballen, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2013.
On October 12, 2011, four years after it was agreed upon by both parties, the United States government signed into law the reciprocal US–Panama Free Trade Agreement (FTA)/Trade Promotion Agreement (TPA). The FTA provides US companies with better access to the Panamanian market and ensures that most US exports of consumer and industrial products to Panama will be accorded immediate duty-free privileges. The main elements of the US–Panama FTA as it relates to agricultural trade revolve around market access, agricultural export subsidies, safeguards, the sugar compensation mechanism, and sanitary and phytosanitary measures. This 11-page fact sheet was written by Edward A. Evans and Fredy H. Ballen, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe932
Palm Morphology and Anatomy
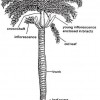 Palms differ greatly from broadleaf (dicot) and coniferous (Gymnosperm) trees in their overall form and external structure (morphology) and in their internal structure (anatomy). Morphology and anatomy determine how palms grow, function, and respond to external and internal stress factors. This publication provides a basic understanding of how palms are constructed. This 4-page fact sheet was written by T. K. Broschat, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, May2013.
Palms differ greatly from broadleaf (dicot) and coniferous (Gymnosperm) trees in their overall form and external structure (morphology) and in their internal structure (anatomy). Morphology and anatomy determine how palms grow, function, and respond to external and internal stress factors. This publication provides a basic understanding of how palms are constructed. This 4-page fact sheet was written by T. K. Broschat, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, May2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep473
Alternatives to Invasive Plants Commonly Found in North Florida Landscapes (ENH1206/EP467)
 Based on years of UF/IFAS research producing and trialing cultivars, this 3-page fact sheet lists native and non-invasive, non-native ornamentals as alternatives to invasive plants commonly used in Florida landscapes. Only plants considered to be generally available in the nursery trade are listed. Alternative plants are similar to respective invasive plants as much as possible in terms of size, habit, texture, and flower color.was written by Gary W. Knox, Sandra B. Wilson, Zhanao Deng, and Rosanna Freyre, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2013.
Based on years of UF/IFAS research producing and trialing cultivars, this 3-page fact sheet lists native and non-invasive, non-native ornamentals as alternatives to invasive plants commonly used in Florida landscapes. Only plants considered to be generally available in the nursery trade are listed. Alternative plants are similar to respective invasive plants as much as possible in terms of size, habit, texture, and flower color.was written by Gary W. Knox, Sandra B. Wilson, Zhanao Deng, and Rosanna Freyre, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, August 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep467
Eastern dobsonfly (adult), hellgrammite (larva) Corydalus cornutus (Linnaeus) (Insecta: Megaloptera: Corydalidae: Corydalinae) (EENY414/IN987)
 The eastern dobsonfly is one of our largest non-lepidopteran insects. Its larvae, known as hellgrammites, are the top invertebrate predators in rocky streams where they occur. Adult male dobsonflies are particularly spectacular because of their large sickle-shaped mandibles (jaws). This 4-page fact sheet was written by Donald W. Hall, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2013.
The eastern dobsonfly is one of our largest non-lepidopteran insects. Its larvae, known as hellgrammites, are the top invertebrate predators in rocky streams where they occur. Adult male dobsonflies are particularly spectacular because of their large sickle-shaped mandibles (jaws). This 4-page fact sheet was written by Donald W. Hall, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in987
Equine Lameness and Imaging Service series
The veterinarians of the University of Florida Equine Lameness & Imaging Service specialize in the treatment and rehabilitation of poor performance in sport horses. This series of one-page full color fact sheets describes various diagnostic and imaging services available for diagnosing and treating lameness issues in horses. Computed Tomography (CT) for the Horse
Digital Ultrasonography for the Horse
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for the Horse
Lameness Locator™ for the Horse
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for the Horse
Nuclear Scintigraphy (Bone Scan) for the Horse
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_series_equine_lameness_and_imaging_service
Conservation Subdivision: Post-construction Phase–Engaging Residents (WEC334/UW379)
 As urban communities grow, design and management strategies for new developments become critical factors that determine impacts on natural resources. How can we accommodate growth yet conserve natural resources, such as biodiversity, water, and energy? In this document, we focus on conserving biodiversity when land is subdivided, constructed, and occupied. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Daniel Feinberg and Mark Hostetler, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, June 2013.
As urban communities grow, design and management strategies for new developments become critical factors that determine impacts on natural resources. How can we accommodate growth yet conserve natural resources, such as biodiversity, water, and energy? In this document, we focus on conserving biodiversity when land is subdivided, constructed, and occupied. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Daniel Feinberg and Mark Hostetler, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, June 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw379
Infant Botulism and Honey (ENY128/AA142)
 Since honey is a potential and avoidable source of Clostridium botulinum spores, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, the American Academy of Pediatricsm and the National Honey Board recommend that honey not be given to infants younger than 12 months of age. Honey should not be added to water, food, or formula fed to infants under 12 months of age. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Malcolm T. Sanford, Eddie Atkinson, Jeanette Klopchin, and Jamie Ellis, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, June 2013.
Since honey is a potential and avoidable source of Clostridium botulinum spores, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, the American Academy of Pediatricsm and the National Honey Board recommend that honey not be given to infants younger than 12 months of age. Honey should not be added to water, food, or formula fed to infants under 12 months of age. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Malcolm T. Sanford, Eddie Atkinson, Jeanette Klopchin, and Jamie Ellis, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, June 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/aa142
Disease Control for Florida Tomatoes (PPP35/VH056)
 Successful disease management has always been vital in Florida tomato production, given the generally ideal environmental conditions for most plant diseases. An integrated disease management program is a successful approach. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Mathews Paret, Ken Pernezny, and Pam Roberts, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, August 2013.
Successful disease management has always been vital in Florida tomato production, given the generally ideal environmental conditions for most plant diseases. An integrated disease management program is a successful approach. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Mathews Paret, Ken Pernezny, and Pam Roberts, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, August 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vh056
Watering Your Florida Lawn (ENH9/LH025)
 Irrigation is one of the most important cultural practices that we do for our lawns. Since water is a limited resource and is vital to the health of your lawn, it is very important that watering be done correctly. This 3-page fact sheet was written by L. E. Trenholm, J. B. Unruh, and J. L. Cisar, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, April 2013.
Irrigation is one of the most important cultural practices that we do for our lawns. Since water is a limited resource and is vital to the health of your lawn, it is very important that watering be done correctly. This 3-page fact sheet was written by L. E. Trenholm, J. B. Unruh, and J. L. Cisar, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/lh025
Calibration of Chemical Applicators Used in Vegetables (HS1220)
 Calibration is the process used to determine the amount of chemical material applied per unit area. Equipment for applying liquid and dry materials must be accurately calibrated for pesticides to work efficiently and to avoid crop injury or death. The pesticide label is a legal document and must be followed. Properly calibrating equipment ensures the product is being applied as specified on the label and that environmental contamination will be minimized. This 6-page fact sheet discusses some methods for calibration of sprayers and dry material spreaders and includes information about calibration to help growers properly apply pesticides. written by M. R. Miller and P. J. Dittmar, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, May 2013.
Calibration is the process used to determine the amount of chemical material applied per unit area. Equipment for applying liquid and dry materials must be accurately calibrated for pesticides to work efficiently and to avoid crop injury or death. The pesticide label is a legal document and must be followed. Properly calibrating equipment ensures the product is being applied as specified on the label and that environmental contamination will be minimized. This 6-page fact sheet discusses some methods for calibration of sprayers and dry material spreaders and includes information about calibration to help growers properly apply pesticides. written by M. R. Miller and P. J. Dittmar, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1220
Factors Affecting Herbicide Use in Fruits and Vegetables (HS1219)
 Proper herbicide application is critical for fruit and vegetable growers to effectively manage weeds. Improper herbicide application may lead to herbicide loss from the targeted area, increased crop injury, and reduced weed control. Growers need to take into account a number of factors before and during application in any crop to ensure the herbicide is effective. Herbicide efficacy is greatly affected by timing and environmental conditions. Although complete weed control is not always possible, even slight reductions in weed populations can greatly enhance productivity in fruit and vegetable crops. This 4-page fact sheet reviews techniques and processes to help growers properly apply herbicides. Understanding the processes and applying the following techniques will help to increase the overall efficacy of herbicides in fruit and vegetable production. Written by C. E. Rouse and P. J. Dittmar, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, May 2013.
Proper herbicide application is critical for fruit and vegetable growers to effectively manage weeds. Improper herbicide application may lead to herbicide loss from the targeted area, increased crop injury, and reduced weed control. Growers need to take into account a number of factors before and during application in any crop to ensure the herbicide is effective. Herbicide efficacy is greatly affected by timing and environmental conditions. Although complete weed control is not always possible, even slight reductions in weed populations can greatly enhance productivity in fruit and vegetable crops. This 4-page fact sheet reviews techniques and processes to help growers properly apply herbicides. Understanding the processes and applying the following techniques will help to increase the overall efficacy of herbicides in fruit and vegetable production. Written by C. E. Rouse and P. J. Dittmar, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1219
La Seguridad en la Produccion de Alimentos en la Granja – Resumen de Buenas Practicas Agricolas (FSHN0601S/FS230)
 Las Buenas Prácticas Agrícolas (BPA) y Buenas Prácticas de Manejo (BPM) cubren los procedimientos generales que los productores, empacadores y procesadores de frutas y verduras frescas deben seguir para garantizar la seguridad de sus productos. Las BPA son usadas antes de la cosecha (es decir, en el campo), mientras que las BPM se utilizan luego de la cosecha, incluyendo el embalaje y envío. El objetivo de este panfleto es revisar los principios generalmente reconocidos como BPA en la producción de frutas y verduras frescas, sobre todo a nivel de fincas o granjas. Otros panfletos de la Extensián Cooperativa de la Florida sobre la Inocuidad de los Alimentos cubren los principios individuales en detalle, con énfasis especial en los cultivos y el manejo apropiado de los mismos en la Florida.
Las Buenas Prácticas Agrícolas (BPA) y Buenas Prácticas de Manejo (BPM) cubren los procedimientos generales que los productores, empacadores y procesadores de frutas y verduras frescas deben seguir para garantizar la seguridad de sus productos. Las BPA son usadas antes de la cosecha (es decir, en el campo), mientras que las BPM se utilizan luego de la cosecha, incluyendo el embalaje y envío. El objetivo de este panfleto es revisar los principios generalmente reconocidos como BPA en la producción de frutas y verduras frescas, sobre todo a nivel de fincas o granjas. Otros panfletos de la Extensián Cooperativa de la Florida sobre la Inocuidad de los Alimentos cubren los principios individuales en detalle, con énfasis especial en los cultivos y el manejo apropiado de los mismos en la Florida.
This 3-page fact sheet was written by Federico G. Caro, Renee Goodrich Schneider, Keith R. Schneider, y Douglas L. Archer, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs230
Powdery Mildew of Strawberries (PP208/PP129)
 Powdery mildew occurs in most areas of the world where strawberries are grown, infecting leaves, flowers, and fruit. Infected transplants are normally the primary source of inoculum for fruiting fields in Florida, but even disease-free fields can become infected by conidia blown in from neighboring fields. Fields with susceptible cultivars should be surveyed regularly for powdery mildew, especially early in the season. Usually, controlling foliar infection helps to prevent fruit infection. This 4-page fact sheet was written by N. A. Peres and J. C. Mertely, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, May 2013.
Powdery mildew occurs in most areas of the world where strawberries are grown, infecting leaves, flowers, and fruit. Infected transplants are normally the primary source of inoculum for fruiting fields in Florida, but even disease-free fields can become infected by conidia blown in from neighboring fields. Fields with susceptible cultivars should be surveyed regularly for powdery mildew, especially early in the season. Usually, controlling foliar infection helps to prevent fruit infection. This 4-page fact sheet was written by N. A. Peres and J. C. Mertely, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp129
Koi Herpesvirus Disease (KHVD) (VM149/VM113)
 Koi herpesvirus (KHV) is a highly contagious virus that causes significant morbidity and mortality in common carp varieties. Common carp is raised as a foodfish in many countries and has also been selectively bred for the ornamental fish industry where it is known as koi. The first recognized case of KHV occurred in the United Kingdom in 1996. Since then other cases have been confirmed in almost all countries that culture koi and/or common carp with the exception of Australia. This 9-page fact sheet is intended to inform veterinarians, biologists, fish producers and hobbyists about KHV disease. Written by Kathleen H. Hartman, Roy P.E. Yanong, Deborah B. Pouder, B. Denise Petty, Ruth Francis-Floyd, Allen C. Riggs, and Thomas B. Waltzek, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, April 2013.
Koi herpesvirus (KHV) is a highly contagious virus that causes significant morbidity and mortality in common carp varieties. Common carp is raised as a foodfish in many countries and has also been selectively bred for the ornamental fish industry where it is known as koi. The first recognized case of KHV occurred in the United Kingdom in 1996. Since then other cases have been confirmed in almost all countries that culture koi and/or common carp with the exception of Australia. This 9-page fact sheet is intended to inform veterinarians, biologists, fish producers and hobbyists about KHV disease. Written by Kathleen H. Hartman, Roy P.E. Yanong, Deborah B. Pouder, B. Denise Petty, Ruth Francis-Floyd, Allen C. Riggs, and Thomas B. Waltzek, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm113
Measuring Productivity of Citrus Hand Harvesters and Assessing Implications on Harvest Costs and Mechanical Harvesting Developments (FE933)
 Existing mechanical harvesters recover 70 to 95 percent of the available fruit crop. While changes can be made to increase fruit recovery percentages, mechanical systems will never equal the fruit recovery percentages from hand-harvesting crews, much less capture 100 percent of the available fruit. Whether or not to glean (to use manual labor to collect fruit not harvested by the machine) will remain an important question that growers will have to face with every block they choose to mechanically harvest. This study incorporated field harvesting data and developed a model that predicted the extent to which labor productivity would be affected by decreasing the number of oranges available for harvesting by manual labor. Given current market prices of fruit, recovery percentage of crops harvested using mechanical harvesting equipment can improve up to 99 percent and gleaning will remain a profitable activity.
Existing mechanical harvesters recover 70 to 95 percent of the available fruit crop. While changes can be made to increase fruit recovery percentages, mechanical systems will never equal the fruit recovery percentages from hand-harvesting crews, much less capture 100 percent of the available fruit. Whether or not to glean (to use manual labor to collect fruit not harvested by the machine) will remain an important question that growers will have to face with every block they choose to mechanically harvest. This study incorporated field harvesting data and developed a model that predicted the extent to which labor productivity would be affected by decreasing the number of oranges available for harvesting by manual labor. Given current market prices of fruit, recovery percentage of crops harvested using mechanical harvesting equipment can improve up to 99 percent and gleaning will remain a profitable activity.
This 6-page fact sheet was written by Fritz M. Roka and Barbara R. Hyman, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe933
Bacterial Blight of Ficus elastica Caused by Xanthomonas (PP305)
 In the summer of 2010, leaf blight cases were reported on several Ficus elastica cultivars in Homestead nurseries. Symptoms somewhat resembled those caused by Xanthomonas campestris p.v. fici, but this pathogen has never been reported to occur on Ficus elastica. The outbreak was severe, and the majority of commercial producers in the southern portion of the state were affected. The widespread outbreak from 2010 to date has caused many nurseries to lose entire Ficus elastica crops. This 3-page fact sheet describes the symptoms and disease management recommendations. Written by E. V. Campoverde and A. J. Palmateer, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, April 2013.
In the summer of 2010, leaf blight cases were reported on several Ficus elastica cultivars in Homestead nurseries. Symptoms somewhat resembled those caused by Xanthomonas campestris p.v. fici, but this pathogen has never been reported to occur on Ficus elastica. The outbreak was severe, and the majority of commercial producers in the southern portion of the state were affected. The widespread outbreak from 2010 to date has caused many nurseries to lose entire Ficus elastica crops. This 3-page fact sheet describes the symptoms and disease management recommendations. Written by E. V. Campoverde and A. J. Palmateer, and published by the UF Department of Plant Pathology, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pp305