As society confronts the consequences of global warming, deteriorating water quality, and impoverished biodiversity, there is a growing urgency to develop and expand water buffers' multifunctional ecosystem services. However, limited information is available on other potential co-benefits associated with the use of buffers, particularly VFSs. This 5-page fact sheet provides information on buffers' multiple ecosystem benefits, such as niche products production, carbon sequestration, and flood risk mitigation, as well as recommendations on future research needs necessary to enhance multiple ecosystem services and benefits of buffers. Written by Lei Wu, Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2015.
As society confronts the consequences of global warming, deteriorating water quality, and impoverished biodiversity, there is a growing urgency to develop and expand water buffers' multifunctional ecosystem services. However, limited information is available on other potential co-benefits associated with the use of buffers, particularly VFSs. This 5-page fact sheet provides information on buffers' multiple ecosystem benefits, such as niche products production, carbon sequestration, and flood risk mitigation, as well as recommendations on future research needs necessary to enhance multiple ecosystem services and benefits of buffers. Written by Lei Wu, Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss647
Category: Water
Vegetative Filter Strips: A Best Management Practice for Controlling Nonpoint Source Pollution
 Increasing numbers of pollutants have been observed in natural water systems. As awareness of agricultural sources of water pollution has grown, Best Management Practices (BMPs) have been specifically designed to address agricultural water pollutants and protect water quality. This 4-page fact sheet introduces one of the BMPs, Vegetative Filter Strips (VFSs), which efficiently control nonpoint pollution such as sediments, nutrients, and pesticides. The publication covers primary functions, key design factors, and maintenance of VFSs. Written by Lei Wu, Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2015.
Increasing numbers of pollutants have been observed in natural water systems. As awareness of agricultural sources of water pollution has grown, Best Management Practices (BMPs) have been specifically designed to address agricultural water pollutants and protect water quality. This 4-page fact sheet introduces one of the BMPs, Vegetative Filter Strips (VFSs), which efficiently control nonpoint pollution such as sediments, nutrients, and pesticides. The publication covers primary functions, key design factors, and maintenance of VFSs. Written by Lei Wu, Rafael Muñoz-Carpena, and Yuncong Li, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss646
Frequently Asked Questions about Soil Moisture Sensor Irrigation Controllers (SMS)
![]()
A soil moisture sensor (SMS) is a device that detects how much moisture is in the soil and prevents an irrigation system from running when it is not needed. This 4-page fact sheet written by Paul Monaghan, Ondine Wells, Michael Dukes, Maria Morera, and Laura Warner and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communications explains how the technology functions as well as how to install, program, operate, and maintain an SMS for a money- and water-wise sustainable home landscape that’s lush and beautiful.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc238
Frequently Asked Questions about Evapotranspiration (ET) Irrigation Controllers
Evapotranspiration is the amount of water that is released into the atmosphere through evaporation and plant transpiration. An evapotranspiration irrigation controller is a device that uses data about the landscape, the type of irrigation system, and local weather conditions to determine when and how much to irrigate. This 5-page fact sheet written by Paul Monaghan, Ondine Wells, Michael Dukes, Maria Morera, and Laura Warner and published by the Department of Agricultural Education and Communications explains how the technology functions as well as how to install, program, operate, and maintain an ET controller for a money- and water-wise sustainable home landscape that’s lush and beautiful.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc237
Sand-Clay Mix in Phosphate Mine Reclamation: Characteristics and Land Use

Phosphate rock is a key component in producing fertilizer and many other economically important products. Getting phosphate rock out of the ground produces a by-produce called phosphate clay, which mining operations must return to the landscape. However, phosphate clay retains large amounts of water, making them unsuitable for use as farmland or wildlife habitat. This 6-page fact sheet explains how using a sand-clay mix can more efficiently restore the landscape and put it to beneficial use. Written by Casey Beavers, Edward A. Hanlon, Matt Wilson, James “Bud” Cates, and George J. Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Sciences, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss636
Strategies to Encourage Adoption of Stormwater Pond Best Management Practices (BMPs) by Homeowners
Man-made ponds can be a useful way to collect, store, and treat stormwater runoff in residential areas. However, these ponds can become polluted when runoff contains fertilizers, pesticides, and pet waste from the neighborhood. This 8-page fact sheet outlines several best management practices (BMPs) for reducing stormwater pond pollution. Based on a survey of residents who live near stormwater ponds, the authors recommend strategies Extension educators can use to encourage residents to adopt these BMPs. Written by Emily Ott, Paul Monaghan, Ondine Wells, Gail Hansen, Laura Warner, and Michelle Atkinson, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc214
Estimated Water Savings Potential of Florida-Friendly Landscaping™ Activities

To help homeowners predict the impact of implementing some of the water conservation measures listed on Florida-Friendly Landscaping™ checklist, this 5-page fact sheet offers a table of estimated water savings. Homeowners can select activities which are the best fit for their landscape and can also see which have the most conservation potential. The water savings is compared to a baseline case of typical irrigation behavior. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Mackenzie Boyer and Michael Dukes, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, August 2015. (Photo credit: Michael Gutierrez, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae515
Basics of the National Flood Insurance Program

Established by Congress in 1968 because the private market stopped offering flood insurance, the NFIP provides federally backed flood insurance to property owners in participating communities. This 10-page fact sheet covers topics such as: why buy flood insurance, recent changes, flood zones and insurance rate maps, ways to reduce premiums, rate increases for pre-1974 structures, and actions communities can take to lower citizen premiums related to climate change and sea-level rise. Written by Thomas Ruppert and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg139
Encouraging Landscape Water-Conservation Behaviors #3: Developing Extension and Outreach Messages That Encourage Landscape Water Conservation Practice Adoption
Message framing can be an effective tool for crafting messages for a target audience. This 5-page fact sheet explains how Extension can use gain and loss message framing to encourage Florida residents who irrigate their home landscape to adopt water-conservation practices. Part three of the series Encouraging Landscape Water-Conservation Behaviors and written by Courtney Owens, Laura Warner, Joy Rumble, Alexa Lamm, and Randall Cantrell, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc201
Using the Decision-Ade(TM) Segmentation Strategy to Better Understand Extension Audiences

Decision-Ade™ is a tool Extension can use to better understand how residents with a range of household budgets feel about their utility bills. Analyzing households in terms of both income and utility bill “botheredness” creates a more comprehensive picture of that household’s utility use and its willingness to modify utility consumption relative to other households. This 5-page fact sheet uses survey data of Florida residents to demonstrate the insights Decision Ade™ can provide and how those insights can inform Extension programming. Written by Randall Cantrell, Laura Warner, Joy Rumble, and Alexa Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, July 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1461
Contaminantes en el Medio Ambiente Urbano: Los Perfluoroalquilos
 Los perfluoroalquilos–los perfluorocarbonos (PFC) o, en inglés, perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs)–son los productos químicos artificiales más comunes y persistentes en el planeta. Algunos de los productos más comunes que contienen perfluoroalquilos son sartenes de teflón, utensilios de cocina antiadherente, chaquetas impermeables (como Gore-Tex), espumas de extinción de incendios, envases de alimentos, alfombras y telas para muebles. Los perfluoroalquilos poseen un largo tiempo de residencia en el medio ambiente, lo que significa que los perfluoroalquilos pueden acumularse en los organismos en niveles que causan efectos nocivos.
Los perfluoroalquilos–los perfluorocarbonos (PFC) o, en inglés, perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs)–son los productos químicos artificiales más comunes y persistentes en el planeta. Algunos de los productos más comunes que contienen perfluoroalquilos son sartenes de teflón, utensilios de cocina antiadherente, chaquetas impermeables (como Gore-Tex), espumas de extinción de incendios, envases de alimentos, alfombras y telas para muebles. Los perfluoroalquilos poseen un largo tiempo de residencia en el medio ambiente, lo que significa que los perfluoroalquilos pueden acumularse en los organismos en niveles que causan efectos nocivos.
This 6-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Contaminants in the Urban Environment: Perfluoroalkyl Substances, written by Ignacio A. Rodriguez-Jorquera and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss644
Feature image credit: iStock/Thinkstock.com (non-stick pan, waterproof fabric, and fire fighting foam)/Digital Vision/Thinkstock.com (fast food)
Climate Change and the Occurrence of Harmful Microorganisms in Florida’s Ocean and Coastal Waters
Climate change is expected to result in increased temperatures of nearshore ocean water, and this could lead to increased growth of harmful microorganisms. These include algae that form noxious or toxic blooms, including red tides, and bacteria and other pathogens. This situation could have negative consequences in regard to human health and also Florida’s ocean-related economy. A 6-page fact sheet written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg136
Lionfish: Is It Safe to Eat?

Lionfish is not a traditional or likely seafood selection, but growing interest in response to the invasive and increasing abundance has stirred recreational and commercial interest. This prolific, invasive fish is threatening reefs and coastal fisheries in ocean waters throughout the Caribbean Seas and neighboring regions, and eating lionfish is being encouraged as one of the best options to mitigate the its harmful impact. This 4-page fact sheet discusses the risks in handling and consuming lionfish, and offers recommendations for avoiding risk, for both recreational and commercial harvesters. Written by Steve Otwell, and published by Florida Sea Grant, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg135
Climate Change: Effects on Salinity in Florida's Estuaries and Responses of Oysters, Seagrass, and Other Biota
 Florida’s economically important estuaries could be heavily impacted by sea-level rise and altered river flow, both caused by climate change. The resulting higher salinity, or saltiness of the water, could harm plants and animals, alter fish and bird habitat, and reduce the capacity of estuaries to provide such important services as seafood production and the protection of shorelines from erosion. This 6-page fact sheet explains the importance of estuaries, salinity in estuaries, and provides examples of stress from extreme high salinity. Then it explores the projected change in climate that could affect salinity in estuaries, how plants and animals would be affected, mitigating effects, and other impacts of climate change on estuaries. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
Florida’s economically important estuaries could be heavily impacted by sea-level rise and altered river flow, both caused by climate change. The resulting higher salinity, or saltiness of the water, could harm plants and animals, alter fish and bird habitat, and reduce the capacity of estuaries to provide such important services as seafood production and the protection of shorelines from erosion. This 6-page fact sheet explains the importance of estuaries, salinity in estuaries, and provides examples of stress from extreme high salinity. Then it explores the projected change in climate that could affect salinity in estuaries, how plants and animals would be affected, mitigating effects, and other impacts of climate change on estuaries. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg138
Climate Change and Ecosystem Services of Florida's Largest Water Body: Lake Okeechobee
 Future climate change could result in higher temperatures and greater evaporative water loss in Florida. If these changes are not compensated for by more rainfall, the state’s largest water body, Lake Okeechobee, could experience prolonged periods of very low water levels and catastrophic loss of its ecosystem services, which are the benefits that people receive from ecosystems. This 6-page fact sheet provides background, optimal and actual water levels, projected changes in South Florida climate & their effects on water levels in Lake Okeechobee, their effects on ecosystem services, and possible remedies. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
Future climate change could result in higher temperatures and greater evaporative water loss in Florida. If these changes are not compensated for by more rainfall, the state’s largest water body, Lake Okeechobee, could experience prolonged periods of very low water levels and catastrophic loss of its ecosystem services, which are the benefits that people receive from ecosystems. This 6-page fact sheet provides background, optimal and actual water levels, projected changes in South Florida climate & their effects on water levels in Lake Okeechobee, their effects on ecosystem services, and possible remedies. Written by Karl Havens, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg137
Climate Change and the Occurrence of Harmful Microorganisms in Florida's Ocean and Coastal Waters
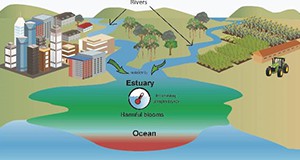 Climate change is expected to result in increased temperatures of nearshore ocean water, and this could lead to increased growth of harmful microorganisms. These include algae that form noxious or toxic blooms, including red tides, and bacteria and other pathogens. This situation could have negative consequences in regard to human health and also Florida’s ocean-related economy. This 6-page fact sheet discusses projected ocean temperatures, how harmful microorganisms living in the ocean might respond, and how this might affect people, and identifies actions that could be taken to reduce these impacts. Written by Karl Havens, and published by Florida Sea Grant, June 2015.
Climate change is expected to result in increased temperatures of nearshore ocean water, and this could lead to increased growth of harmful microorganisms. These include algae that form noxious or toxic blooms, including red tides, and bacteria and other pathogens. This situation could have negative consequences in regard to human health and also Florida’s ocean-related economy. This 6-page fact sheet discusses projected ocean temperatures, how harmful microorganisms living in the ocean might respond, and how this might affect people, and identifies actions that could be taken to reduce these impacts. Written by Karl Havens, and published by Florida Sea Grant, June 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg136
Encouraging Landscape Water-Conservation Behaviors #1: Tailoring Programs To Florida Residents Who Use Irrigation in the Home Landscape
To better promote water-conservation practices among homeowners who irrigate their landscaping, Extension professionals must first have a clear understanding of this target audience’s habits, beliefs, and needs. This 10-page fact sheet recommends that Extension professionals analyze their audiences through several factors, including their interest in water conservation and knowledge of water issues and laws. Written by Laura A. Warner, Emmett Martin, Alexa Lamm, Joy Rumble, and Randall Cantrell, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, May 2015. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc199
Contaminants in the Urban Environment: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs), Parts 1 and 2
 Pharmaceuticals and personal care products contain a variety of chemical substances that enter household wastewater from bath and shower, sinks, and washers and ultimately find their way into the environment. Continuous discharge of wastewater contributes to the accumulation of these substances in the environment — where they can be harmful to organisms. These fact sheets were written by Yun-Ya Yang and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
Pharmaceuticals and personal care products contain a variety of chemical substances that enter household wastewater from bath and shower, sinks, and washers and ultimately find their way into the environment. Continuous discharge of wastewater contributes to the accumulation of these substances in the environment — where they can be harmful to organisms. These fact sheets were written by Yun-Ya Yang and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
Part 1 provides an overview of the use and sale of PPCPs in the United States and the world: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss632
Part 2 discusses the sources and impacts of PPCPs and offers common-sense ways we can protect our environment from PPCPs.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss633
Nutrient Management of Vegetable and Agronomic Row Crops Handbook
 Through the implementation of a series of targeted cultural practices discussed in this production guide, growers should be able to reconcile economic profitability and responsible use of water and fertilizer. Topics include: proper sampling practices and test interpretations; irrigation management methods and automation; use of alternate fertilizer materials to retain nutrients in the soil but allow adequate supply for crop uptake. Use of these BMPs ensures that adequate fertilizer rates may be achieved by combinations of UF/IFAS recommended base rates and supplemental fertilizer applications. This 199-page handbook was edited by Kelly T. Morgan, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, February 2015.
Through the implementation of a series of targeted cultural practices discussed in this production guide, growers should be able to reconcile economic profitability and responsible use of water and fertilizer. Topics include: proper sampling practices and test interpretations; irrigation management methods and automation; use of alternate fertilizer materials to retain nutrients in the soil but allow adequate supply for crop uptake. Use of these BMPs ensures that adequate fertilizer rates may be achieved by combinations of UF/IFAS recommended base rates and supplemental fertilizer applications. This 199-page handbook was edited by Kelly T. Morgan, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, February 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss639
Ecosystem Services Valuation for Estuarine and Coastal Restoration in Florida
 Throughout Florida’s history, humans have altered the coastlines, leading to large-scale degradation of coastal ecosystems. This has led to the loss of associated ecosystem services, including products such as food and timber and processes like coastal protection and disease control. Unfortunately, ecosystem restoration efforts have not always been a priority for coastal management. This 10-page literature review surveys the available ecosystem-service valuation literature for five of Florida’s coastal natural communities–oyster reefs, beach dunes, mangrove forests, seagrass beds, and salt marshes–to facilitate the quantification of ecosystem services to provide a better measure of the full impact of restoration efforts. Written by Susanna Blair, Carrie Adams, Tom Ankersen, Maia McGuire, and David Kaplan, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, November 2014. (UF/IFAS photo by Tyler Jones)
Throughout Florida’s history, humans have altered the coastlines, leading to large-scale degradation of coastal ecosystems. This has led to the loss of associated ecosystem services, including products such as food and timber and processes like coastal protection and disease control. Unfortunately, ecosystem restoration efforts have not always been a priority for coastal management. This 10-page literature review surveys the available ecosystem-service valuation literature for five of Florida’s coastal natural communities–oyster reefs, beach dunes, mangrove forests, seagrass beds, and salt marshes–to facilitate the quantification of ecosystem services to provide a better measure of the full impact of restoration efforts. Written by Susanna Blair, Carrie Adams, Tom Ankersen, Maia McGuire, and David Kaplan, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, November 2014. (UF/IFAS photo by Tyler Jones)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg134