 Biochar can potentially provide better conditions in the soil to increase plant growth. However, research has shown that weed species show minimal changes in germination and emergence patterns with the addition of biochar. Regardless, if biochar is used in the field it is important to monitor for changes in weed populations. This is especially important because biochar can decrease herbicide efficacy. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Neeta Soni, Ramon G. Leon, John E. Erickson, and Jason A. Ferrell, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2015. (Photo: Neeta Soni)
Biochar can potentially provide better conditions in the soil to increase plant growth. However, research has shown that weed species show minimal changes in germination and emergence patterns with the addition of biochar. Regardless, if biochar is used in the field it is important to monitor for changes in weed populations. This is especially important because biochar can decrease herbicide efficacy. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Neeta Soni, Ramon G. Leon, John E. Erickson, and Jason A. Ferrell, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2015. (Photo: Neeta Soni)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag390
Tag: Agronomy Department
Sugarcane Mosaic
 Mosaic’s most distinctive symptom is a pattern of contrasting shades of green, often islands of normal green on a background of paler green or yellowish chlorotic areas on the leaf blade. It had not been a problem in Florida until 1996, when it was observed on CP72-2086, a major commercial cultivar, near the intersection of Hatton Highway and US 98. Presently, because of the limited acreage of CP72-2086, the disease is only a potential threat. This 3-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, J. C. Comstock, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, February 2015. (Photo: Philippe Rott, UF/IFAS)
Mosaic’s most distinctive symptom is a pattern of contrasting shades of green, often islands of normal green on a background of paler green or yellowish chlorotic areas on the leaf blade. It had not been a problem in Florida until 1996, when it was observed on CP72-2086, a major commercial cultivar, near the intersection of Hatton Highway and US 98. Presently, because of the limited acreage of CP72-2086, the disease is only a potential threat. This 3-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, J. C. Comstock, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, February 2015. (Photo: Philippe Rott, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc009
Hairy Indigo Control in Peanut
 Hairy indigo is an annual legume that was introduced to Florida as a forage crop. It has since escaped cultivation and can be a troublesome weed in some crop settings, particularly in peanut production, since we are attempting to control a legume weed in a legume crop. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Jason Ferrell, Blaire Colvin, and Ramon Leon, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2015. (Photo by Blaire Colvin, UF/IFAS)
Hairy indigo is an annual legume that was introduced to Florida as a forage crop. It has since escaped cultivation and can be a troublesome weed in some crop settings, particularly in peanut production, since we are attempting to control a legume weed in a legume crop. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Jason Ferrell, Blaire Colvin, and Ramon Leon, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2015. (Photo by Blaire Colvin, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag391
Carinata Production in Florida
 Brassica carinata is a promising oilseed crop with great potential for profitable cultivation in Florida. Its high oil content and favorable fatty acid profile make it suitable for the biofuel industry, especially as a biojet fuel. The UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC) in Quincy, Florida, has been working to identify advanced carinata genotypes that are high yielding (seed and oil), disease resistant, early maturing, and adapted to Florida. The work at NFREC is being done in conjunction with Agrisoma Biosciences Inc., a crop company that has the world’s largest collection of carinata germplasm. This 6-page fact sheet’s “Agronomic Management” section provides recommendations resulting from NFREC’s research. was written by C. M. Bliss, R. Seepaul, D. L. Wright, J. J. Marois, R. Leon, N. Dufault, S. George, and S. M. Olson, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, December 2014.
Brassica carinata is a promising oilseed crop with great potential for profitable cultivation in Florida. Its high oil content and favorable fatty acid profile make it suitable for the biofuel industry, especially as a biojet fuel. The UF/IFAS North Florida Research and Education Center (NFREC) in Quincy, Florida, has been working to identify advanced carinata genotypes that are high yielding (seed and oil), disease resistant, early maturing, and adapted to Florida. The work at NFREC is being done in conjunction with Agrisoma Biosciences Inc., a crop company that has the world’s largest collection of carinata germplasm. This 6-page fact sheet’s “Agronomic Management” section provides recommendations resulting from NFREC’s research. was written by C. M. Bliss, R. Seepaul, D. L. Wright, J. J. Marois, R. Leon, N. Dufault, S. George, and S. M. Olson, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, December 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag389
Weed Management in Rice
 Successful weed control is essential for economical rice production in the Everglades Agricultural Area. Weeds reduce rice yields by competing for moisture, nutrients, and light during the growing season. Weed infestations can also interfere with combine operation at harvest and can significantly increase harvesting and drying costs. Weed seed contamination of rice grain lowers grain quality and may lower the cash value of the crop. As with any biological system, an effective weed management program must consider many factors that vary from crop to crop and year to year. The most important of these factors include planting date, climatic conditions, seedbed preparation, seed quality, stand establishment, and water management. This 5-page fact sheet was written by D.C. Odero and C. Rainbolt, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2014. (Photo: C. Odero, UF/IFAS)
Successful weed control is essential for economical rice production in the Everglades Agricultural Area. Weeds reduce rice yields by competing for moisture, nutrients, and light during the growing season. Weed infestations can also interfere with combine operation at harvest and can significantly increase harvesting and drying costs. Weed seed contamination of rice grain lowers grain quality and may lower the cash value of the crop. As with any biological system, an effective weed management program must consider many factors that vary from crop to crop and year to year. The most important of these factors include planting date, climatic conditions, seedbed preparation, seed quality, stand establishment, and water management. This 5-page fact sheet was written by D.C. Odero and C. Rainbolt, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2014. (Photo: C. Odero, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wg001
Sugarcane Ratoon Stunting
 Ratoon stunting, also known as ratoon stunting disease (RSD), is considered by many sugarcane pathologists to be the most important disease affecting sugarcane production worldwide, because it can cause 5% to 15% crop yield losses without growers even realizing their fields are infected. This 3-page fact sheet describes the symptoms, causal agent, and prevention and control. Written by P. Rott, S. Sood, J. C. Comstock, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014. (Photo credit: Sushma Sood, USDA)
Ratoon stunting, also known as ratoon stunting disease (RSD), is considered by many sugarcane pathologists to be the most important disease affecting sugarcane production worldwide, because it can cause 5% to 15% crop yield losses without growers even realizing their fields are infected. This 3-page fact sheet describes the symptoms, causal agent, and prevention and control. Written by P. Rott, S. Sood, J. C. Comstock, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014. (Photo credit: Sushma Sood, USDA)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc002
Managing Against the Development of Herbicide-Resistant Weeds: Sugarcane
 Profitable sugarcane production in Florida requires effective weed management. Herbicides provide an efficient and cost-effective means of weed control, but excessive use of a single herbicide or group of herbicides with the same mechanism of action has resulted in the development of herbicide-resistant weeds. In crops such as sugarcane where a limited number of herbicides are registered, the loss of a single effective herbicide can be very costly. Thus, it is critical to manage herbicides in order to prevent or delay the development of herbicide-resistant weed populations. This 4-page fact sheet lists herbicides by group number, mechanism of action, chemical family, common name, and trade name. Written by D.C. Odero, B.A. Sellers, J.A. Ferrell, and G.E. MacDonald, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2014.
Profitable sugarcane production in Florida requires effective weed management. Herbicides provide an efficient and cost-effective means of weed control, but excessive use of a single herbicide or group of herbicides with the same mechanism of action has resulted in the development of herbicide-resistant weeds. In crops such as sugarcane where a limited number of herbicides are registered, the loss of a single effective herbicide can be very costly. Thus, it is critical to manage herbicides in order to prevent or delay the development of herbicide-resistant weed populations. This 4-page fact sheet lists herbicides by group number, mechanism of action, chemical family, common name, and trade name. Written by D.C. Odero, B.A. Sellers, J.A. Ferrell, and G.E. MacDonald, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, October 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc077
2014 Cool-Season Forage Variety Recommendations for Florida
 This 4-page fact sheet provides the most up-to-date information on current adapted varieties of cool-season forages. The recommendation of varieties is based on multi-location, multi-year cultivar evaluation experiments that may include trials in Georgia and other states. Table 1 includes information about the planting dates, seeding rates, and other considerations. If you have questions about a particular variety, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension agent for additional information. Written by A. R. Blount, J. M. B. Vendramini, J. C. B. Dubeux, Md A. Babar, K. E. Kenworthy, P. R. Muñoz,and K. H. Quesenberry, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo: Josh Wickam)
This 4-page fact sheet provides the most up-to-date information on current adapted varieties of cool-season forages. The recommendation of varieties is based on multi-location, multi-year cultivar evaluation experiments that may include trials in Georgia and other states. Table 1 includes information about the planting dates, seeding rates, and other considerations. If you have questions about a particular variety, contact your local UF/IFAS Extension agent for additional information. Written by A. R. Blount, J. M. B. Vendramini, J. C. B. Dubeux, Md A. Babar, K. E. Kenworthy, P. R. Muñoz,and K. H. Quesenberry, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo: Josh Wickam)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/aa266
Pool Chemicals and Personal Safety
 Pool chemicals are among the most common household substances and are used to protect health in recreational waters. Pool chemicals containing chlorine safeguard against recreational-water illnesses caused by disease-causing pathogens, such as the diarrhea-causing Cryptosporidium. They also enhance disinfection by regulating water pH. But even though these materials are regularly handled by homeowners, most don’t ever realize that they are handling pesticides. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Fred Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
Pool chemicals are among the most common household substances and are used to protect health in recreational waters. Pool chemicals containing chlorine safeguard against recreational-water illnesses caused by disease-causing pathogens, such as the diarrhea-causing Cryptosporidium. They also enhance disinfection by regulating water pH. But even though these materials are regularly handled by homeowners, most don’t ever realize that they are handling pesticides. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Fred Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi253
Sugarcane Orange Rust
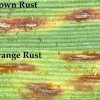 In June 2007, rust symptoms were observed on sugarcane cultivar CP80-1743 about six miles east of Belle Glade, Florida. The disease was confirmed as orange rust of sugarcane. It is hypothesized that rust spores were blown into the region as a disperse spore cloud from an unknown source rather than spread from a single or several small focal points. This 7-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, S. Sood, J. C. Comstock, R. N. Raid, N. C. Glynn, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2014.
In June 2007, rust symptoms were observed on sugarcane cultivar CP80-1743 about six miles east of Belle Glade, Florida. The disease was confirmed as orange rust of sugarcane. It is hypothesized that rust spores were blown into the region as a disperse spore cloud from an unknown source rather than spread from a single or several small focal points. This 7-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, S. Sood, J. C. Comstock, R. N. Raid, N. C. Glynn, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc099
Waterhyacinth: Florida's Worst Floating Weed
 Waterhyacinth is one of the world’s worst aquatic weeds and is Florida’s most intensively managed floating plant. Dense mats formed by this species interfere with human uses of water bodies and disrupt ecosystems by preventing penetration of light and oxygen into the water column. This attractive, free-floating aquatic plant grows throughout the year in southern Florida but often dies back during the winter in the northern parts of the state. Waterhyacinth is cultivated as a water garden and pond plant, but cultivation, sale, and possession of this noxious weed is prohibited in Florida. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Lyn A. Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
Waterhyacinth is one of the world’s worst aquatic weeds and is Florida’s most intensively managed floating plant. Dense mats formed by this species interfere with human uses of water bodies and disrupt ecosystems by preventing penetration of light and oxygen into the water column. This attractive, free-floating aquatic plant grows throughout the year in southern Florida but often dies back during the winter in the northern parts of the state. Waterhyacinth is cultivated as a water garden and pond plant, but cultivation, sale, and possession of this noxious weed is prohibited in Florida. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Lyn A. Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag385
Budgets for Pasture Establishment: Seeded and Vegetative
 Budgets can be used to make rational decisions when establishing or renovating a pasture in Florida. This 3-page fact sheet is a guide for evaluating the costs of establishing a seeded-type pasture versus vegetatively propagated hybrid bermudagrasses. Written by Les Harrison, Jonael Bosques, and Yoana Newman, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014.
Budgets can be used to make rational decisions when establishing or renovating a pasture in Florida. This 3-page fact sheet is a guide for evaluating the costs of establishing a seeded-type pasture versus vegetatively propagated hybrid bermudagrasses. Written by Les Harrison, Jonael Bosques, and Yoana Newman, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, August 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag386
Peanut Variety Performance in Florida, 2010–2013
 Variety choice is a critical management decision in producing a peanut crop. Since several good peanut varieties are available, it is essential to know each variety’s attributes and how different varieties might fit into a farm plan. This 7-page fact sheet provides data conducted from trials in Florida at UF/IFAS research centers located in Gainesville (Citra), Marianna, and Jay from 2010–2013. Written by Barry Tillman, Mark Gomillion, Justin McKinney, and George Person, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2014.
Variety choice is a critical management decision in producing a peanut crop. Since several good peanut varieties are available, it is essential to know each variety’s attributes and how different varieties might fit into a farm plan. This 7-page fact sheet provides data conducted from trials in Florida at UF/IFAS research centers located in Gainesville (Citra), Marianna, and Jay from 2010–2013. Written by Barry Tillman, Mark Gomillion, Justin McKinney, and George Person, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag382
Bermudagrass Stem Maggot: A New Pest in Florida
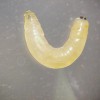 Bermudagrass is a dominant hay crop in Florida. Now, hay producers are facing a new emerging pest problem in bermudagrass and stargrass production fields. The bermudagrass stem maggot, is a new exotic invasive fly. It was first discovered damaging bermudagrass pasture and hay fields in Georgia. The identification of the fly was the first record of this species in North America, and it has the potential to become a serious pest of bermudagrass and stargrass in Florida. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Ann Blount, Tim Wilson, Jay Ferrell, Russ Mizell, and Jonael Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, June 2014.
Bermudagrass is a dominant hay crop in Florida. Now, hay producers are facing a new emerging pest problem in bermudagrass and stargrass production fields. The bermudagrass stem maggot, is a new exotic invasive fly. It was first discovered damaging bermudagrass pasture and hay fields in Georgia. The identification of the fly was the first record of this species in North America, and it has the potential to become a serious pest of bermudagrass and stargrass in Florida. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Ann Blount, Tim Wilson, Jay Ferrell, Russ Mizell, and Jonael Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, June 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag384
Clasificacion de las licencias para aplicadores dictadas por el Departamento de Agricultura y Servicios al Consumidor del estado de la Florida (FDACS), relacionadas con agricultura y control de plagas
 Esta guía ofrece una explicación de las licencias para aplicadores de pesticidas privados, públicos y comerciales emitidos por FDACS en el Capítulo 487 de los Estatutos de la Florida. This 4-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Agricultural and Related Pest Control Applicator License Classifications under the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS). Written by Frederick M. Fishel and Tatiana Sanchez, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, February 2014.
Esta guía ofrece una explicación de las licencias para aplicadores de pesticidas privados, públicos y comerciales emitidos por FDACS en el Capítulo 487 de los Estatutos de la Florida. This 4-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Agricultural and Related Pest Control Applicator License Classifications under the Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (FDACS). Written by Frederick M. Fishel and Tatiana Sanchez, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, February 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi249
American Lotus, Yellow Lotus: Nelumbo lutea
 American lotus is an ideal native plant for constructed or restored wetland areas, where it provides shelter, habitat, and food for wildlife. It is an herbaceous aquatic perennial native plant that tolerates a wide range of conditions. The fragrant yellow flowers, huge round leaves, and persistent seed pods borne on stiff stalks high above the water make it both distinctive and visually striking. Native American tribes treated the American lotus as a sacred plant with mystical powers, and many tribes ate the large rhizomes and used parts of the plant for medicinal purposes. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Warner Orozco-Obando and Lyn Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2014.
American lotus is an ideal native plant for constructed or restored wetland areas, where it provides shelter, habitat, and food for wildlife. It is an herbaceous aquatic perennial native plant that tolerates a wide range of conditions. The fragrant yellow flowers, huge round leaves, and persistent seed pods borne on stiff stalks high above the water make it both distinctive and visually striking. Native American tribes treated the American lotus as a sacred plant with mystical powers, and many tribes ate the large rhizomes and used parts of the plant for medicinal purposes. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Warner Orozco-Obando and Lyn Gettys, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag380
Rotala: A New Canal Invader in Southern Florida
 Rotala is a relative newcomer to Florida. Since it was first found in Coral Springs in 1996, it has established large, but mostly isolated, populations throughout the southern regions of Florida. It is especially problematic in Lee and Collier Counties and along the west coast. Extremely dense submersed populations and large thick mats dominate the surface of the water, greatly reducing ecosystem services, because oxygen level and light penetration are hampered. Because the rapid and vigorous growth of rotala inhibits water flow, the ability of infested canals to function properly in flood control systems is greatly hindered. Management of this aquatic weed is a major concern for resource managers. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Lyn A. Gettys and Carl J. Della Torre II, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, April 2014.
Rotala is a relative newcomer to Florida. Since it was first found in Coral Springs in 1996, it has established large, but mostly isolated, populations throughout the southern regions of Florida. It is especially problematic in Lee and Collier Counties and along the west coast. Extremely dense submersed populations and large thick mats dominate the surface of the water, greatly reducing ecosystem services, because oxygen level and light penetration are hampered. Because the rapid and vigorous growth of rotala inhibits water flow, the ability of infested canals to function properly in flood control systems is greatly hindered. Management of this aquatic weed is a major concern for resource managers. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Lyn A. Gettys and Carl J. Della Torre II, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, April 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag381
2013 Evaluation of Non-Irrigated Early-Maturing Cotton Varieties in Jay, Florida
 This report includes a summary of the 2013 early-season cotton Official Variety Trial in Jay, Florida. It shows the performance of 11 cotton varieties. This data represents only one year and one location, and readers are cautioned that test results should be considered over several locations and years before final conclusions are valid. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Darcy Telenko and Michael Donahoe , and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
This report includes a summary of the 2013 early-season cotton Official Variety Trial in Jay, Florida. It shows the performance of 11 cotton varieties. This data represents only one year and one location, and readers are cautioned that test results should be considered over several locations and years before final conclusions are valid. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Darcy Telenko and Michael Donahoe , and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag378
Estimando la Cantidad de Forraje en Campos de Heno y Potreros
 El forraje sirve como fuente primaria de nutrientes para la industria ganadera en Florida. El uso eficiente de esta fuente nutricional es crítico para la supervivencia de los agricultores y rancheros de dicho estado. El estimar la cantidad de forraje en potreros puede proveer información útil a la hora de tomar decisiones acerca del manejo de nuestros recursos. Debe de haber suficiente material en el predio para justificar el costo de utilizar el equipo para cosechar (por ejemplo, precio de compra del equipo, renta, costo del combustible a invertirse, y el costo de la mano de obra). Sin esta información, el predio debe ser sometido a pastoreo. Esta publicación contiene las instrucciones para la implementación de un método simple que nos permite determinar la cantidad aproximada de forraje en campos de heno y potreros.This 2-page fact sheet was written by T. Wilson, C. Sanders, J. Breman, y L. Sollenberger. Traducido por J. Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
El forraje sirve como fuente primaria de nutrientes para la industria ganadera en Florida. El uso eficiente de esta fuente nutricional es crítico para la supervivencia de los agricultores y rancheros de dicho estado. El estimar la cantidad de forraje en potreros puede proveer información útil a la hora de tomar decisiones acerca del manejo de nuestros recursos. Debe de haber suficiente material en el predio para justificar el costo de utilizar el equipo para cosechar (por ejemplo, precio de compra del equipo, renta, costo del combustible a invertirse, y el costo de la mano de obra). Sin esta información, el predio debe ser sometido a pastoreo. Esta publicación contiene las instrucciones para la implementación de un método simple que nos permite determinar la cantidad aproximada de forraje en campos de heno y potreros.This 2-page fact sheet was written by T. Wilson, C. Sanders, J. Breman, y L. Sollenberger. Traducido por J. Bosques, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag379
2013 Evaluation of Non-Irrigated Mid- to Full-Season Maturing Cotton Varieties in Jay, Florida
 This report includes a summary of the 2013 mid- to full-season cotton Official Variety Trial in Jay, Florida. It shows the performance of 16 cotton varieties. This data represents only one year and one location, and readers are cautioned that test results should be considered over several locations and years before final conclusions are valid. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Darcy E. P. Telenko and Michael Donahoe, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
This report includes a summary of the 2013 mid- to full-season cotton Official Variety Trial in Jay, Florida. It shows the performance of 16 cotton varieties. This data represents only one year and one location, and readers are cautioned that test results should be considered over several locations and years before final conclusions are valid. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Darcy E. P. Telenko and Michael Donahoe, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, January 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag377