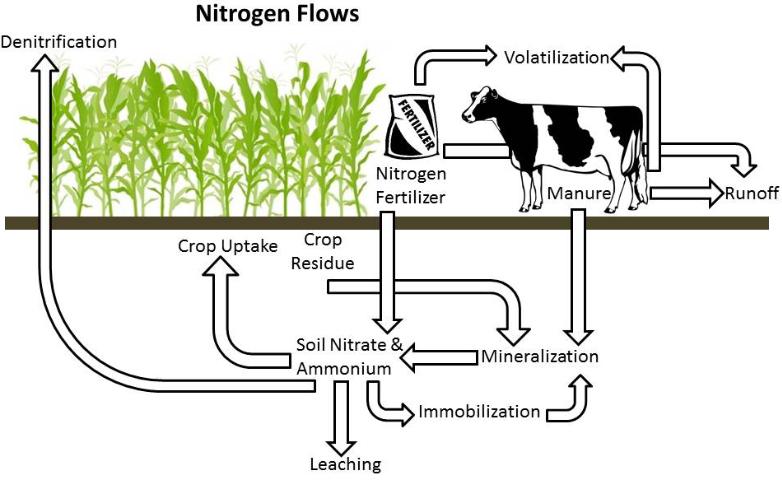
 In dairy production systems, nitrogen flows through both the forage crops and the dairy cows. Forage crops use nitrogen mineralized from manure for plant growth. Harvested crops are then fed to dairy cows that, in turn, use the nitrogen for their growth and milk production. When the cows excrete a portion of the consumed nitrogen as manure the cycle is renewed. This 5-page fact sheet focuses on the forage production aspect of the nitrogen cycle at a dairy farm. Written by Rebecca Hellmuth and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Image credit: R. Hellmuth)
In dairy production systems, nitrogen flows through both the forage crops and the dairy cows. Forage crops use nitrogen mineralized from manure for plant growth. Harvested crops are then fed to dairy cows that, in turn, use the nitrogen for their growth and milk production. When the cows excrete a portion of the consumed nitrogen as manure the cycle is renewed. This 5-page fact sheet focuses on the forage production aspect of the nitrogen cycle at a dairy farm. Written by Rebecca Hellmuth and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Image credit: R. Hellmuth)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss640
Author: dihagan
Contaminants in the Urban Environment: Perfluoroalkyl Substances
 Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) or perfluorochemicals (PFCs) are the most widespread and persistent manmade chemicals on earth. Common products that contain PFASs are Teflon pans, non-stick cookware, rain/waterproof jackets (like Gore-Tex), fire-fighting foams, food packaging, carpets, and furniture fabrics. PFASs stay in the environment for a long period of time, which means they can accumulate in organisms to levels that cause harmful effects. This 9-page fact sheet discusses the occurrence, use, exposure, and potential harmful effects of PFASs to humans and the environment, and suggests ways to reduce your exposure to PFSAs. Written by Ignacio A. Rodriguez-Jorquera and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Photos: Thinkstock.com)
Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) or perfluorochemicals (PFCs) are the most widespread and persistent manmade chemicals on earth. Common products that contain PFASs are Teflon pans, non-stick cookware, rain/waterproof jackets (like Gore-Tex), fire-fighting foams, food packaging, carpets, and furniture fabrics. PFASs stay in the environment for a long period of time, which means they can accumulate in organisms to levels that cause harmful effects. This 9-page fact sheet discusses the occurrence, use, exposure, and potential harmful effects of PFASs to humans and the environment, and suggests ways to reduce your exposure to PFSAs. Written by Ignacio A. Rodriguez-Jorquera and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Photos: Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss631
Contaminants in the Urban Environment: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs), Parts 1 and 2
 Pharmaceuticals and personal care products contain a variety of chemical substances that enter household wastewater from bath and shower, sinks, and washers and ultimately find their way into the environment. Continuous discharge of wastewater contributes to the accumulation of these substances in the environment — where they can be harmful to organisms. These fact sheets were written by Yun-Ya Yang and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
Pharmaceuticals and personal care products contain a variety of chemical substances that enter household wastewater from bath and shower, sinks, and washers and ultimately find their way into the environment. Continuous discharge of wastewater contributes to the accumulation of these substances in the environment — where they can be harmful to organisms. These fact sheets were written by Yun-Ya Yang and Gurpal S. Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
Part 1 provides an overview of the use and sale of PPCPs in the United States and the world: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss632
Part 2 discusses the sources and impacts of PPCPs and offers common-sense ways we can protect our environment from PPCPs.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss633
Floridian Consumer Perceptions of Local versus Organic Ornamental Plants
 Horticultural consumers in Florida are interested in local and organically produced plants. But these terms can mean different things in different regions. UF/IFAS researchers conducted a survey last summer which suggests that consumers in central Florida define local as plants that are grown near where they are sold and identify the most important local benefits as product safety, quality, and community support. Organic plants are perceived as requiring fewer chemical additives and being healthier for the environment. The importance of these traits varies by plant type. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Hayk Khachatryan and Alicia Rihn, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, February 2015.
Horticultural consumers in Florida are interested in local and organically produced plants. But these terms can mean different things in different regions. UF/IFAS researchers conducted a survey last summer which suggests that consumers in central Florida define local as plants that are grown near where they are sold and identify the most important local benefits as product safety, quality, and community support. Organic plants are perceived as requiring fewer chemical additives and being healthier for the environment. The importance of these traits varies by plant type. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Hayk Khachatryan and Alicia Rihn, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, February 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe964
Congratulations to CALS Award Recipients
Congratulations to the following EDIS authors who were recognized with awards at this year’s UF/IFAS College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Scholarship and Leadership Awards Banquet:
- Rebecca Baldwin, Entomology and Nematology – Undergraduate Adviser of the Year
- Andrea Lucky, Entomology and Nematology – Undergraduate Teacher of the Year
- Martha Monroe, Forest Resources and Conservation – Graduate Teacher/Adviser of the Year
- Amanda Ford, Nutritional Sciences – Jimmy G. Cheek Graduate Student Medal of Excellence
Chicken Mite (other common names: poultry red mite, roost mite) Dermanyssus gallinae (De Geer) (Arachnida: Acari: Dermanyssidae)
 The chicken mite affects egg-laying hens in many parts of the world, including Europe, Japan, China, and the United States. Although Dermanyssus gallinae affects birds in many regions, it is most prevalent in European countries, where egg industry losses are estimated at $177 million per year. It is a known vector for the St. Louis encephalitis virus, as well as other illnesses, such as fowl pox virus, Newcastle virus, and fowl cholera. In the United States, Dermanyssus gallinae is rarely found in caged-layer operations and is more commonly found in breeder farms. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ethan Carter and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2015. (Photo credit: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida)
The chicken mite affects egg-laying hens in many parts of the world, including Europe, Japan, China, and the United States. Although Dermanyssus gallinae affects birds in many regions, it is most prevalent in European countries, where egg industry losses are estimated at $177 million per year. It is a known vector for the St. Louis encephalitis virus, as well as other illnesses, such as fowl pox virus, Newcastle virus, and fowl cholera. In the United States, Dermanyssus gallinae is rarely found in caged-layer operations and is more commonly found in breeder farms. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ethan Carter and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2015. (Photo credit: Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1070
Women's Nutrition: Folate/Folic Acid
 To decrease a baby’s chances of having certain types of births defects, mothers need to have already been consuming enough of the vitamin called folate, or folic acid, before they become pregnant. This article provides information about the folate/folic acid needs of women who are capable of becoming pregnant, including its role in preventing birth defects, sources, and strategies for meeting the recommended intake. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Caroline Dunn and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2015. (Photo Credit: Mike Watson Images/moodboard/Thinkstock.com)
To decrease a baby’s chances of having certain types of births defects, mothers need to have already been consuming enough of the vitamin called folate, or folic acid, before they become pregnant. This article provides information about the folate/folic acid needs of women who are capable of becoming pregnant, including its role in preventing birth defects, sources, and strategies for meeting the recommended intake. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Caroline Dunn and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2015. (Photo Credit: Mike Watson Images/moodboard/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs265
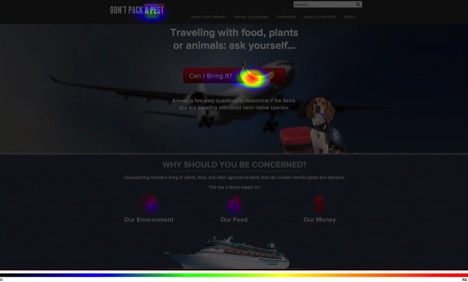
Using Heat Maps to Determine the Usability of Extension Communication Materials
 This heat map from a website usability test shows that more people click on the banana image than anywhere else on the computer screen, followed by the button at the top of the screenshot. This tool allows Extension faculty to determine the ease of respondent use of the communication material. This 6-page fact sheet explains how to use heat maps and how to develop heat map questions in Qualtrics. Written by Laura M. Gorham, Shuyang Qu, Ricky Telg, and Alexa Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, February 2015.
This heat map from a website usability test shows that more people click on the banana image than anywhere else on the computer screen, followed by the button at the top of the screenshot. This tool allows Extension faculty to determine the ease of respondent use of the communication material. This 6-page fact sheet explains how to use heat maps and how to develop heat map questions in Qualtrics. Written by Laura M. Gorham, Shuyang Qu, Ricky Telg, and Alexa Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, February 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc198
Biochar Effects on Weed Management
 Biochar can potentially provide better conditions in the soil to increase plant growth. However, research has shown that weed species show minimal changes in germination and emergence patterns with the addition of biochar. Regardless, if biochar is used in the field it is important to monitor for changes in weed populations. This is especially important because biochar can decrease herbicide efficacy. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Neeta Soni, Ramon G. Leon, John E. Erickson, and Jason A. Ferrell, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2015. (Photo: Neeta Soni)
Biochar can potentially provide better conditions in the soil to increase plant growth. However, research has shown that weed species show minimal changes in germination and emergence patterns with the addition of biochar. Regardless, if biochar is used in the field it is important to monitor for changes in weed populations. This is especially important because biochar can decrease herbicide efficacy. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Neeta Soni, Ramon G. Leon, John E. Erickson, and Jason A. Ferrell, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2015. (Photo: Neeta Soni)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag390
Improving the Productivity of Beef Heifers in Florida
 Beef replacement heifers are a necessary but costly part of every cow-calf operation. A decision needs to be made to either purchase replacement heifers or raise them on the ranch. This is a long-term decision that will affect the ranch for many years through the genetics of the replacement heifers and through equipment and management inputs. This 9-page fact sheet provides an analysis of considerations for raising replacements; factors to consider in selection; and recommendations for nutritional management. Written by Phillip Lancaster, Chris Prevatt, and John Arthington, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, March 2015. (Photo: Beef Improvement Federation)
Beef replacement heifers are a necessary but costly part of every cow-calf operation. A decision needs to be made to either purchase replacement heifers or raise them on the ranch. This is a long-term decision that will affect the ranch for many years through the genetics of the replacement heifers and through equipment and management inputs. This 9-page fact sheet provides an analysis of considerations for raising replacements; factors to consider in selection; and recommendations for nutritional management. Written by Phillip Lancaster, Chris Prevatt, and John Arthington, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, March 2015. (Photo: Beef Improvement Federation)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an132
Sugarcane Mosaic
 Mosaic’s most distinctive symptom is a pattern of contrasting shades of green, often islands of normal green on a background of paler green or yellowish chlorotic areas on the leaf blade. It had not been a problem in Florida until 1996, when it was observed on CP72-2086, a major commercial cultivar, near the intersection of Hatton Highway and US 98. Presently, because of the limited acreage of CP72-2086, the disease is only a potential threat. This 3-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, J. C. Comstock, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, February 2015. (Photo: Philippe Rott, UF/IFAS)
Mosaic’s most distinctive symptom is a pattern of contrasting shades of green, often islands of normal green on a background of paler green or yellowish chlorotic areas on the leaf blade. It had not been a problem in Florida until 1996, when it was observed on CP72-2086, a major commercial cultivar, near the intersection of Hatton Highway and US 98. Presently, because of the limited acreage of CP72-2086, the disease is only a potential threat. This 3-page fact sheet was written by P. Rott, J. C. Comstock, R. A. Gilbert, and H. S. Sandhu, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, February 2015. (Photo: Philippe Rott, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sc009
Biology and Management of Oxalis (Oxalis stricta) in Ornamental Crop Production
 Oxalis grows throughout the year in Florida. It can be found growing in sidewalk cracks, alongside trails, in lawns, flower beds, cultivated fields, and in container nursery stock. In greenhouse studies, oxalis populations have been shown to negatively impact the growth rates of ornamental crops. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Matt Lollar and Chris Marble, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, February 2015. (Photo: Chris Marble)
Oxalis grows throughout the year in Florida. It can be found growing in sidewalk cracks, alongside trails, in lawns, flower beds, cultivated fields, and in container nursery stock. In greenhouse studies, oxalis populations have been shown to negatively impact the growth rates of ornamental crops. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Matt Lollar and Chris Marble, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, February 2015. (Photo: Chris Marble)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep514
Vida Saludable: Examinando el nivel de glucosa en la sangre
 Examinar el nivel de glucosa en su sangre es una parte importante en el manejo de la diabetes. El conocer los valores de glucosa en su sangre le indica que tan eficiente está funcionando su plan de cuidado y si debe hacer algún cambio. ¡Continúe leyendo para aprender más!
Examinar el nivel de glucosa en su sangre es una parte importante en el manejo de la diabetes. El conocer los valores de glucosa en su sangre le indica que tan eficiente está funcionando su plan de cuidado y si debe hacer algún cambio. ¡Continúe leyendo para aprender más!
This 4-page fact sheet is the Spanish language version of Healthy Living: Checking Blood Glucose. Written by Jennifer Hillan and Linda B. Bobroff, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, January 2015. (Photo: iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy908
Healthy Eating: Nutrition and Diabetes
 A healthy diet, along with exercise and medication, can help control diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. A healthy lifestyle also helps reduce the chances of developing diabetes for those who are at high risk. For a healthy diet, follow these tips. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff, Jennifer Hillan, and Emily Minton, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2015. (Photo:iStock/Thinkstock.com)
A healthy diet, along with exercise and medication, can help control diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. A healthy lifestyle also helps reduce the chances of developing diabetes for those who are at high risk. For a healthy diet, follow these tips. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Linda B. Bobroff, Jennifer Hillan, and Emily Minton, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2015. (Photo:iStock/Thinkstock.com)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy685
Economic Contributions and Ecosystem Services of Springs in the Lower Suwannee and Santa Fe River Basins of North-Central Florida
 This study examined the economic contributions, consumer surplus, and ecosystem services provided by recreational use of fifteen major springs sites in north central Florida. The estimated annual economic contributions of springs-related recreational spending in north-central Florida for FY 2012/13 are summarized. Among the findings, there was $84.2 million in total visitor spending for springs recreation, and 1,160 full- and part-time jobs. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Tatiana Borisova, Alan W. Hodges, and Thomas J. Stevens, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, April 2015.
This study examined the economic contributions, consumer surplus, and ecosystem services provided by recreational use of fifteen major springs sites in north central Florida. The estimated annual economic contributions of springs-related recreational spending in north-central Florida for FY 2012/13 are summarized. Among the findings, there was $84.2 million in total visitor spending for springs recreation, and 1,160 full- and part-time jobs. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Tatiana Borisova, Alan W. Hodges, and Thomas J. Stevens, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, April 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe958
Managing Conflicts with Wildlife: Living with Snakes
 Snakes provide numerous benefits to people and to the environment, by controlling rat and mice populations in the environment, for example. Or in the laboratory, where pygmy rattlesnake venom research helped develop medicine to thin the blood of heart attack patients. Most snakes are secretive and rarely bother people, but there are situations where some snakes can become dangerous. In this 4-page fact sheet, we present some facts about snakes, describe dangers they may cause, and provide suggestions on how to cope with these dangers. Written by Holly K. Ober, Steve Johnson, and William M. Giuliano, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, November 2014. (Photo: Steve Johnson)
Snakes provide numerous benefits to people and to the environment, by controlling rat and mice populations in the environment, for example. Or in the laboratory, where pygmy rattlesnake venom research helped develop medicine to thin the blood of heart attack patients. Most snakes are secretive and rarely bother people, but there are situations where some snakes can become dangerous. In this 4-page fact sheet, we present some facts about snakes, describe dangers they may cause, and provide suggestions on how to cope with these dangers. Written by Holly K. Ober, Steve Johnson, and William M. Giuliano, and published by the UF Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, November 2014. (Photo: Steve Johnson)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/uw395
Tawny Crazy Ant (previously known as Caribbean crazy ant) Nylanderia (formerly Paratrechina) fulva (Mayr) (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Formicinae)
 Nylanderia fulva is part of a group of ants referred to as “crazy ants” due to their quick and erratic movements. It has been reported from 27 counties of Florida and 27 counties of Texas, as well as from Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Georgia. Huge number of workers in infested areas can make human activities uncomfortable and difficult. They can infest sidewalks, buildings and gardens, and damage phone lines, air conditioning units and computers. They have killed honey bee larvae and used the hives as their nests, and are even displacing red imported fire ants where the two populations overlap in Texas. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Shweta Sharma, John Warner, and Rudolph H. Scheffrahn, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2014. (Photo: Lyle Buss, UF/IFAS)
Nylanderia fulva is part of a group of ants referred to as “crazy ants” due to their quick and erratic movements. It has been reported from 27 counties of Florida and 27 counties of Texas, as well as from Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Georgia. Huge number of workers in infested areas can make human activities uncomfortable and difficult. They can infest sidewalks, buildings and gardens, and damage phone lines, air conditioning units and computers. They have killed honey bee larvae and used the hives as their nests, and are even displacing red imported fire ants where the two populations overlap in Texas. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Shweta Sharma, John Warner, and Rudolph H. Scheffrahn, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2014. (Photo: Lyle Buss, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1071
Fiddlewood leafroller, seagrape moth (suggested common names) Epicorsia oedipodalis (Guenée, 1854) (Lepidoptera: Ditrysia: Pyraloidea: Pyralidae: Pyraustinae)
 These caterpillars roll up leaves of the host plants and use the rolled leaves as larval retreats and locations for pupal cocoons. Although these leaf-eating pests do no permanent damage, they can completely defoliate fiddlewood, a Florida native that can form a large shrub or small tree. The shrub simply puts out a new flush of leaves. The larvae themselves are valuable food source for baby birds during the spring dry season in Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by William H. Kern, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, February 2015. (Photo:W.H. Kern, Jr., UF/IFAS/FLREC)
These caterpillars roll up leaves of the host plants and use the rolled leaves as larval retreats and locations for pupal cocoons. Although these leaf-eating pests do no permanent damage, they can completely defoliate fiddlewood, a Florida native that can form a large shrub or small tree. The shrub simply puts out a new flush of leaves. The larvae themselves are valuable food source for baby birds during the spring dry season in Florida. This 4-page fact sheet was written by William H. Kern, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, February 2015. (Photo:W.H. Kern, Jr., UF/IFAS/FLREC)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1079
Squash Vine Borer Melittia cucurbitae (Harris) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Sesiidae)
 Squash vine borer is a moth species that is active during the day (diurnal). The larvae complete their growth and development on wild and domesticated species of the genus Cucurbita. Once only considered a nuisance to commercial growers, with the expansion of cucurbit production in the United States over the last decade, the squash vine borer has become a pest of economic importance. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Eutychus Kariuki and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2014. (Photo: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS)
Squash vine borer is a moth species that is active during the day (diurnal). The larvae complete their growth and development on wild and domesticated species of the genus Cucurbita. Once only considered a nuisance to commercial growers, with the expansion of cucurbit production in the United States over the last decade, the squash vine borer has become a pest of economic importance. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Eutychus Kariuki and Jennifer L. Gillett-Kaufman, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2014. (Photo: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1068
Rice Bug (suggested common name) Leptocorisa acuta (Thunberg) (Insecta: Hemiptera: Alydidae)
 Broad-headed bugs belong to a well-known but relatively small family of plant-feeding true bugs, usually seen feeding on the foliage and flowers of leguminous and graminaceous crops. Leptocorisa acuta (Thunberg) can be found on many crop plants in the family Poaceae (grasses), especially rice, and is a reported pest of economic significance in rice-producing countries like India, Australia, and China. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Amelio Chi Serrano, Russell F. Mizell, III, and Morgan A. Byron, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2014. (Photo: Lary E. Reeves, UF/IFAS)
Broad-headed bugs belong to a well-known but relatively small family of plant-feeding true bugs, usually seen feeding on the foliage and flowers of leguminous and graminaceous crops. Leptocorisa acuta (Thunberg) can be found on many crop plants in the family Poaceae (grasses), especially rice, and is a reported pest of economic significance in rice-producing countries like India, Australia, and China. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Amelio Chi Serrano, Russell F. Mizell, III, and Morgan A. Byron, and published by the UF Department of Entomology and Nematology, December 2014. (Photo: Lary E. Reeves, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/in1067