 There are many fertilizer sources available for commercial crop production. The characteristics of each fertilizer type determine whether its use poses an advantage or a disadvantage to a farmer. This 6-page fact sheet focuses on how to select the right fertilizer to enhance profitability and satisfy best management practices (BMPs). Written by Guodong Liu, Lincoln Zotarelli, Yuncong Li, David Dinkins, Qingren Wang, and Monica Ozores-Hampton, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo by Thomas Wright)
There are many fertilizer sources available for commercial crop production. The characteristics of each fertilizer type determine whether its use poses an advantage or a disadvantage to a farmer. This 6-page fact sheet focuses on how to select the right fertilizer to enhance profitability and satisfy best management practices (BMPs). Written by Guodong Liu, Lincoln Zotarelli, Yuncong Li, David Dinkins, Qingren Wang, and Monica Ozores-Hampton, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2014. (UF/IFAS Photo by Thomas Wright)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1255
Category: Water
Engaging Consumers in At-Home Water Conservation: A Guide for Extension
 With a growing urban population and increased demands on water for recreational and agricultural purposes, Florida will have to identify a solution to its water quality and quantity issues. Although all Florida residents will play a part in conserving water in the future, the ability of Extension faculty to work with consumers and encourage new water conservation behaviors at home will be vital. This 4-page fact sheet provides information to Extension faculty about the water conservation behaviors in which Florida residents currently engage, water conservation product ownership, and public interest in water-related topics. Written by Caroline G. Roper and Alexa J. Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2014.
With a growing urban population and increased demands on water for recreational and agricultural purposes, Florida will have to identify a solution to its water quality and quantity issues. Although all Florida residents will play a part in conserving water in the future, the ability of Extension faculty to work with consumers and encourage new water conservation behaviors at home will be vital. This 4-page fact sheet provides information to Extension faculty about the water conservation behaviors in which Florida residents currently engage, water conservation product ownership, and public interest in water-related topics. Written by Caroline G. Roper and Alexa J. Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc169
Extension and the Environment: Understanding Florida Residents' Perceptions of Environmental Water-Related Topics
 By understanding Florida residents’ perceptions of water quality and quantity issues, Extension faculty can better communicate with them about water quantity and quality issues. This 4-page fact sheet explores Florida residents’ perceptions of water topics related to environmental issues. Written by Caroline G. Roper and Alexa J. Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2014.
By understanding Florida residents’ perceptions of water quality and quantity issues, Extension faculty can better communicate with them about water quantity and quality issues. This 4-page fact sheet explores Florida residents’ perceptions of water topics related to environmental issues. Written by Caroline G. Roper and Alexa J. Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, September 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc167
Incorporating Woody Ornamentals into Residential Landscapes to Reduce Nutrient Leaching
 Urban landscapes in Florida are typically dominated by turfgrass monoculture, with ornamental landscape plants comprising only a small portion of the landscape. Incorporating more woody ornamentals into your landscape can reduce fertilization and irrigation demand and help reduce nutrient leaching losses from your yard—a combination that will help protect Florida’s water resources. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Drew C. McLean, Andrew K. Koeser, Amy L Shober, Zhixuan Qin, Gitta Hasing, and Richard C. Beeson, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, July 2014.
Urban landscapes in Florida are typically dominated by turfgrass monoculture, with ornamental landscape plants comprising only a small portion of the landscape. Incorporating more woody ornamentals into your landscape can reduce fertilization and irrigation demand and help reduce nutrient leaching losses from your yard—a combination that will help protect Florida’s water resources. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Drew C. McLean, Andrew K. Koeser, Amy L Shober, Zhixuan Qin, Gitta Hasing, and Richard C. Beeson, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep503
A Beginner's Guide to Water Management: Aquatic Plants in Florida Lakes
 This circular represents a summary of current knowledge on aquatic plants and aquatic plant management strategies, highlighting the Florida situation. The major focus of this circular is the management of aquatic plants as opposed to dealing with nutrients, algae, or water clarity. Included are sections on aquatic plant biology, aquatic plant management problems, and aquatic plant management techniques. This 43-page guide was written by Florida LAKEWATCH; reviewed by Mark Hoyer, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, June 2014.
This circular represents a summary of current knowledge on aquatic plants and aquatic plant management strategies, highlighting the Florida situation. The major focus of this circular is the management of aquatic plants as opposed to dealing with nutrients, algae, or water clarity. Included are sections on aquatic plant biology, aquatic plant management problems, and aquatic plant management techniques. This 43-page guide was written by Florida LAKEWATCH; reviewed by Mark Hoyer, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, June 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa163
Interpreting Dye Test Results for Improved Drip Irrigation Management for the Mulched Vegetable-Production Systems in South Florida
 With Florida’s water withdrawals expected to increase by 30% from 2000 to 2030, South Florida vegetable producers are conserving water by converting traditional seepage irrigation systems to drip irrigation, which can have up to 90% efficiency when used effectively. Dye tests can provide important information for implementing a proper drip irrigation management program. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Sanjay Shukla, Nathan Holt, and Gregory Hendricks, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, July 2014.
With Florida’s water withdrawals expected to increase by 30% from 2000 to 2030, South Florida vegetable producers are conserving water by converting traditional seepage irrigation systems to drip irrigation, which can have up to 90% efficiency when used effectively. Dye tests can provide important information for implementing a proper drip irrigation management program. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Sanjay Shukla, Nathan Holt, and Gregory Hendricks, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, July 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae506
Communicating with Extension Clients about Water
 As the U.S. and Florida populations continue to increase and the demand for fresh, clean water rises, water quality and quantity issues will become increasingly important. Extension faculty should understand public opinion surrounding water issues and identify the information that needs to be communicated to the public about water issues, as well as the best mode for this communication. This EDIS publication will provide an overview of how to communicate with Florida residents about water, including information about their preferred communication method and what topics surrounding water Florida residents find of interest. This publication will better equip Extension faculty to discuss water quantity and quality issues with Florida residents. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Caroline G. Roper and Alexa J. Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, June 2014.
As the U.S. and Florida populations continue to increase and the demand for fresh, clean water rises, water quality and quantity issues will become increasingly important. Extension faculty should understand public opinion surrounding water issues and identify the information that needs to be communicated to the public about water issues, as well as the best mode for this communication. This EDIS publication will provide an overview of how to communicate with Florida residents about water, including information about their preferred communication method and what topics surrounding water Florida residents find of interest. This publication will better equip Extension faculty to discuss water quantity and quality issues with Florida residents. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Caroline G. Roper and Alexa J. Lamm, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, June 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc165
Water and Nitrogen BMPs for Tomato and Watermelon: Water Quality and Economics
 Results of a two-year, four-crop-cycles experiment indicated that the recommended Best Management Practice (BMP) water and fertilizer nitrogen (N) rates for seepage-irrigated tomato in south Florida can reduce water use and N leaching to groundwater without adversely impacting yield. The same is true for watermelon for average rainfall conditions. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Sanjay Shukla, Gregory S. Hendricks, Fritz M. Roka, and Thomas A. Obreza, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, May 2014.
Results of a two-year, four-crop-cycles experiment indicated that the recommended Best Management Practice (BMP) water and fertilizer nitrogen (N) rates for seepage-irrigated tomato in south Florida can reduce water use and N leaching to groundwater without adversely impacting yield. The same is true for watermelon for average rainfall conditions. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Sanjay Shukla, Gregory S. Hendricks, Fritz M. Roka, and Thomas A. Obreza, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae503
Water Withdrawals and Their Use in Florida in 2010
 This publication is based on Florida water use information collected by the United States Geological Service. It expands on EDIS document FE797 that examined Florida water withdrawals data for 2005. In addition, in EDIS document FE757 (Florida’s Water Resources), the authors describe Florida’s abundant water resources—the state receives about 54 inches of rainfall per annum, compared to 30 inches nationwide, and it overlies prolific aquifers. Whether water is scarce or abundant, however, depends not only upon available supplies, but also upon patterns of water use. To gather this information, the United States Geological Survey employs several water-use categories to develop estimates of water withdrawals and water use. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Tatiana Borisova and Jenna Rogers, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2014.
This publication is based on Florida water use information collected by the United States Geological Service. It expands on EDIS document FE797 that examined Florida water withdrawals data for 2005. In addition, in EDIS document FE757 (Florida’s Water Resources), the authors describe Florida’s abundant water resources—the state receives about 54 inches of rainfall per annum, compared to 30 inches nationwide, and it overlies prolific aquifers. Whether water is scarce or abundant, however, depends not only upon available supplies, but also upon patterns of water use. To gather this information, the United States Geological Survey employs several water-use categories to develop estimates of water withdrawals and water use. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Tatiana Borisova and Jenna Rogers, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe943
Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Concerns about Water Quality Issues of Master Gardener Program Volunteers
 To respond to residents’ informational needs, the Cooperative Extension Service offers a variety of volunteer training and certification programs. Who participates in such programs? What types of audiences are being reached? Do such programs increase knowledge and change behavior of the volunteers? In this article, we attempt to answer these questions by summarizing existing studies and using responses to a regional public survey, and by focusing on the Master Gardener program and surface water quality issues as examples. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Tatiana Borisova, Michael Smolen, Maria Pilar Useche, Jon Calabria, Nickola Sochacka, Damian Adams, Diane Boellstorff, Jason Evans, and Robert Mahler, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2014.
To respond to residents’ informational needs, the Cooperative Extension Service offers a variety of volunteer training and certification programs. Who participates in such programs? What types of audiences are being reached? Do such programs increase knowledge and change behavior of the volunteers? In this article, we attempt to answer these questions by summarizing existing studies and using responses to a regional public survey, and by focusing on the Master Gardener program and surface water quality issues as examples. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Tatiana Borisova, Michael Smolen, Maria Pilar Useche, Jon Calabria, Nickola Sochacka, Damian Adams, Diane Boellstorff, Jason Evans, and Robert Mahler, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, May 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe942
The Potential of Sea-level Rise on Florida’s Coastal Ecosystems
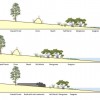 Sea-level rise may have significant effects on Florida’s coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems are the foundation upon which much of Florida’s natural beauty and economy are based. Understanding what changes may happen in the future can help us plan for those changes and, to the extent possible, lessen the impacts of those changes. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Whitney Gray, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, October 2013.
Sea-level rise may have significant effects on Florida’s coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems are the foundation upon which much of Florida’s natural beauty and economy are based. Understanding what changes may happen in the future can help us plan for those changes and, to the extent possible, lessen the impacts of those changes. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Whitney Gray, and published by the UF Department of Sea Grant, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/sg131
Water Issues in Florida: How Extension Can Facilitate Stakeholder Engagement and Involvement
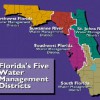 This 6-page fact sheet is a brief description of recent discussions and policies surrounding water management, use, and quality in Florida. The goal of this publication is to provide brief, but clear, information about the trends in policies that can be used by Extension agents to increase educated conversations about water issues. Water in Florida is a contested issue, and Extension agents may be called upon as a source of unbiased information by the public. Having an understanding of important agricultural and natural resources issues in Florida, including water, can help facilitate conversation, raise awareness, and lead to informed decision making. Written by Erica Odera, Alexa Lamm, Tracy Irani, Hannah Carter, and Sebastian Galindo-Gonzalez, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, December 2013.
This 6-page fact sheet is a brief description of recent discussions and policies surrounding water management, use, and quality in Florida. The goal of this publication is to provide brief, but clear, information about the trends in policies that can be used by Extension agents to increase educated conversations about water issues. Water in Florida is a contested issue, and Extension agents may be called upon as a source of unbiased information by the public. Having an understanding of important agricultural and natural resources issues in Florida, including water, can help facilitate conversation, raise awareness, and lead to informed decision making. Written by Erica Odera, Alexa Lamm, Tracy Irani, Hannah Carter, and Sebastian Galindo-Gonzalez, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural Education and Communication, December 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/wc151
The Role of Soil Management in Minimizing Water and Nutrient Losses from the Urban Landscape
 Soil is the most important building block of a healthy, attractive landscape, serving many important physical, chemical, and biological functions. Soil provides a physical substrate for plant support and holds nutrients and water for plant use. It also facilitates groundwater recharge (water moving from surface water to groundwater) and provides long-term storage for organic matter. Soil also provides a habitat for microorganisms that aid in the transformation and availability of nutrients. Soil is an integral part of any ecosystem, but urbanization often changes soils in ways that negatively affect plant development. Soils in urban areas may have reduced water infiltration, resulting in increased runoff and increased potential for nutrient losses. Homeowners in urban areas often overcompensate for poor planting conditions by applying inappropriate amounts of fertilizer and water. These practices eventually lead to nutrient losses through stormwater runoff or soil leaching, and these lost nutrients negatively impact groundwater and ecosystems in nearby springs, streams, and water bodies. This 6-page fact sheet was written by George Hochmuth, Laurie Trenholm, Esen Momol, Don Rainey, Claire Lewis, and Brian Niemann, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2013.
Soil is the most important building block of a healthy, attractive landscape, serving many important physical, chemical, and biological functions. Soil provides a physical substrate for plant support and holds nutrients and water for plant use. It also facilitates groundwater recharge (water moving from surface water to groundwater) and provides long-term storage for organic matter. Soil also provides a habitat for microorganisms that aid in the transformation and availability of nutrients. Soil is an integral part of any ecosystem, but urbanization often changes soils in ways that negatively affect plant development. Soils in urban areas may have reduced water infiltration, resulting in increased runoff and increased potential for nutrient losses. Homeowners in urban areas often overcompensate for poor planting conditions by applying inappropriate amounts of fertilizer and water. These practices eventually lead to nutrient losses through stormwater runoff or soil leaching, and these lost nutrients negatively impact groundwater and ecosystems in nearby springs, streams, and water bodies. This 6-page fact sheet was written by George Hochmuth, Laurie Trenholm, Esen Momol, Don Rainey, Claire Lewis, and Brian Niemann, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss593
Maximizing the Benefits of Reclaimed Water for Irrigating the Landscape and Protecting the Environment
 Reclaimed water is water that has been treated in municipal wastewater facilities and is safe to use for designated purposes, including residential landscape irrigation. “Water reuse” is the term used to describe the beneficial application of reclaimed water. Approximately 663 million gallons of reclaimed water are used daily in Florida. Florida is a national leader in using reclaimed water, and in 2006 Florida’s reuse program received the first U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Water Efficiency Leader Award. Using reclaimed water in Florida meets a state objective for conserving freshwater supplies, and preserves the water quality of rivers, streams, lakes, and aquifers. This publication discusses the benefits of using reclaimed water to irrigate the landscape and explains how using reclaimed water helps to protect the environment. This 4-page fact sheet was written by George Hochmuth, Laurie Trenholm, Don Rainey, Esen Momol, Claire Lewis, and Brian Niemann, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2013.
Reclaimed water is water that has been treated in municipal wastewater facilities and is safe to use for designated purposes, including residential landscape irrigation. “Water reuse” is the term used to describe the beneficial application of reclaimed water. Approximately 663 million gallons of reclaimed water are used daily in Florida. Florida is a national leader in using reclaimed water, and in 2006 Florida’s reuse program received the first U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Water Efficiency Leader Award. Using reclaimed water in Florida meets a state objective for conserving freshwater supplies, and preserves the water quality of rivers, streams, lakes, and aquifers. This publication discusses the benefits of using reclaimed water to irrigate the landscape and explains how using reclaimed water helps to protect the environment. This 4-page fact sheet was written by George Hochmuth, Laurie Trenholm, Don Rainey, Esen Momol, Claire Lewis, and Brian Niemann, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss587
Economic Consequences of Harmful Algal Blooms: Literature Summary
 This 10-page fact sheet summarizes the existing literature that attempts to measure some of the economic consequences associated with harmful algal blooms and describes the methodologies, types and sources of data used, types of HABS examined, research gaps in previous studies. Was written by Sherry L. Larkin and Charles M. Adams, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, August 2013.
This 10-page fact sheet summarizes the existing literature that attempts to measure some of the economic consequences associated with harmful algal blooms and describes the methodologies, types and sources of data used, types of HABS examined, research gaps in previous studies. Was written by Sherry L. Larkin and Charles M. Adams, and published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, August 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe936
Using Reclaimed Water to Irrigate Turfgrass: Lessons Learned from Research with Phosphorus
 Municipal wastes are treated at a wastewater treatment facility to produce biosolids and reclaimed water. Reclaimed water treated by filtration and chlorination is safe to use for designated purposes, such as residential landscape irrigation. Florida began using reclaimed water in 1966, and it is a leading state for using reclaimed water. Approximately 660 million gallons of reclaimed water are used every day in Florida, and the state encourages using reclaimed water as an alternative water source to reduce the pressure on potable water supplies. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of a recent research project and provides research-based information for improving nutrient and water management with reclaimed water irrigation of turfgrass. Written by George Hochmuth, Jinghua Fan, Jason Kruse, and Jerry Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2013.
Municipal wastes are treated at a wastewater treatment facility to produce biosolids and reclaimed water. Reclaimed water treated by filtration and chlorination is safe to use for designated purposes, such as residential landscape irrigation. Florida began using reclaimed water in 1966, and it is a leading state for using reclaimed water. Approximately 660 million gallons of reclaimed water are used every day in Florida, and the state encourages using reclaimed water as an alternative water source to reduce the pressure on potable water supplies. This 3-page fact sheet summarizes the results of a recent research project and provides research-based information for improving nutrient and water management with reclaimed water irrigation of turfgrass. Written by George Hochmuth, Jinghua Fan, Jason Kruse, and Jerry Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss592
Florida-Friendly Plants for Stormwater Pond Shorelines (ENH1215/EP476)
 Selecting aquatic and shoreline plants for stormwater ponds is more challenging than selecting plants for a typical landscape. Site conditions can vary greatly and are more difficult to control. For example, water depth sometimes fluctuates widely, creating wet and dry conditions. Water quality varies with rainfall and fertilizer inputs. Steep slopes can make plant establishment and retention difficult. The concept of using the right plant in the right place is particularly important in the shoreline environment because the planting area includes a dry slope and a littoral shelf with shallow and deep water areas. This 4-page fact sheet recommends plants that were selected based on these three questions: 1) What environmental conditions does the plant need to grow? 2) How do you want the plant to function? 3) What do you want the plant to look like? Written by Gail Hansen and Shangchun Hu, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, May 2013.
Selecting aquatic and shoreline plants for stormwater ponds is more challenging than selecting plants for a typical landscape. Site conditions can vary greatly and are more difficult to control. For example, water depth sometimes fluctuates widely, creating wet and dry conditions. Water quality varies with rainfall and fertilizer inputs. Steep slopes can make plant establishment and retention difficult. The concept of using the right plant in the right place is particularly important in the shoreline environment because the planting area includes a dry slope and a littoral shelf with shallow and deep water areas. This 4-page fact sheet recommends plants that were selected based on these three questions: 1) What environmental conditions does the plant need to grow? 2) How do you want the plant to function? 3) What do you want the plant to look like? Written by Gail Hansen and Shangchun Hu, and published by the UF Department of Environmental Horticulture, May 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ep476
Water Quality and the Effectiveness of Pesticides (PI245)
 Pesticide applicators do not usually blame the mix for a pest control failure. Rather, the applicator will check if the correct pesticide was chosen for the job, if the pest was misidentified, if application equipment was properly calibrated, or if there was pesticide resistance. However, pesticide applicators should be aware that water quality can play a role in the efficacy of a pesticide treatment. Some pesticides lose their effectiveness when mixed with water that contains suspended or dissolved solids. This publication discusses how water quality affects pesticide mixes. This 2-page fact sheet was written by F. M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, April 2013.
Pesticide applicators do not usually blame the mix for a pest control failure. Rather, the applicator will check if the correct pesticide was chosen for the job, if the pest was misidentified, if application equipment was properly calibrated, or if there was pesticide resistance. However, pesticide applicators should be aware that water quality can play a role in the efficacy of a pesticide treatment. Some pesticides lose their effectiveness when mixed with water that contains suspended or dissolved solids. This publication discusses how water quality affects pesticide mixes. This 2-page fact sheet was written by F. M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi245
Valuing the Ecosystem Services of Florida‹s Forest Conservation Programs: The Economic Benefits of Protecting Water Quality (FOR309/FR377)
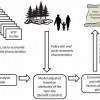 How much are Floridians willing to pay for water quality protection programs that include forest conservation? This 9-page fact sheet reports the results of a study to answer this question, using a benefit transfer approach. Written by Melissa M. Kreye, Francisco J. Escobedo, Damian C. Adams, Taylor Stein, and Tatiana Borisova, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, April 2013.
How much are Floridians willing to pay for water quality protection programs that include forest conservation? This 9-page fact sheet reports the results of a study to answer this question, using a benefit transfer approach. Written by Melissa M. Kreye, Francisco J. Escobedo, Damian C. Adams, Taylor Stein, and Tatiana Borisova, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fr377
How Are the Reservoirs in the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint River Basin Managed? (AE497)
 Many uses of the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint river basin depend on how the US Army Corp of Engineers operates dam releases from the reservoirs when managing lake levels and downstream river flows and water levels. However, no single set of protocols equally suited to all uses and demands governs the reservoir releases. The purpose of this publication is to describe how the USACE manages reservoirs and dams in the ACF and how the waters in the basin are used. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Christopher J. Martinez, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, March 2013.
Many uses of the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint river basin depend on how the US Army Corp of Engineers operates dam releases from the reservoirs when managing lake levels and downstream river flows and water levels. However, no single set of protocols equally suited to all uses and demands governs the reservoir releases. The purpose of this publication is to describe how the USACE manages reservoirs and dams in the ACF and how the waters in the basin are used. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Christopher J. Martinez, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae497