Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) and Good Handling Practices (GHPs) encompass the general procedures that growers, packers and processors of fresh fruits and vegetables should follow to ensure the food safety of their product. GAPs usually deal with preharvest practices (i.e., in the field), while GHPs cover postharvest practices, including packing and shipping. We will use the term GAPs in this fact sheet to generally cover pre- and postharvest practices associated with the safe handling of produce, both fresh and minimally processed. This five-page introduction to the Food Safety on the Farm series provides an overview of GAPs and GHPs, summarizing major principles and recommendations of later documents in the series. Written by Jaysankar De, Christopher R. Pabst, Jessica Lepper, Renée Goodrich Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs135
Tag: Keith R. Schneider
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Cyclosporiasis
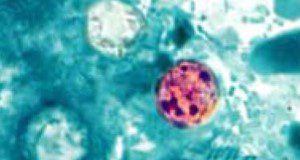
Cyclosporiasis is an intestinal illness caused by the microscopic parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis. People can become infected with Cyclospora by consuming food or water contaminated with the parasite. People living or traveling in countries where cyclosporiasis is endemic may be at increased risk for infection. This 6-page publication is part of the Preventing Foodborne Illness series and describes symptoms and strategies for cyclosporiasis prevention for farmers, restaurants and retailers, and consumers. This major revision was written by Christopher R. Pabst, Jaysankar De, Renée Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs130
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices: Transportation

Good agricultural practices (GAPs) and good handling practices (GHPs) encompass the general procedures growers, packers, and processors of fresh fruits and vegetables should follow to ensure the safety of their product. GAPs usually address preharvest practices (i.e., in the field), while GHPs cover postharvest practices, including packing and shipping. This 3-page fact sheet covers the GAPs of transporting crops. This major revision is a part of the Food Safety on the Farm series and was written by Christopher R. Pabst, Jaysankar De, Alina Balaguero, Jessica Lepper, Renée Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs151
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices: Water
Good agricultural practices (GAPs) and good handling practices (GHPs) encompass the general procedures growers, packers, and processors of fresh fruits and vegetables should follow to ensure the safety of their product. GAPs usually address preharvest practices (i.e., in the field), while GHPs cover postharvest practices, including packing and shipping. This 7-page fact sheet covers GAPs and GHPs relating to water use. This major revision is a part of the Food Safety on the Farm series and was written by Jaysankar De, Christopher R. Pabst, Jessica Lepper, Renée Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs136
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices: Field Sanitation
Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) and Good Handling Practices (GHPs) encompass the general procedures that growers, packers, and processors of fresh fruits and vegetables should follow to ensure the safety of their product. GAPs usually deal with preharvest practices (i.e., in the field), while GHPs cover postharvest practices, including packing and shipping. This 5-page fact sheet covers harvest practices associated with sanitation in the field, including basic principles for microbial food safety and control of potential hazards. This major revision is a part of the Food Safety on the Farm series and was written by Jessica Lepper, Jaysankar De, Christopher Pabst, Renée Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs160
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices: Traceback
Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) and Good Handling Practices (GHP) are voluntary audits that verify fruits and vegetables are produced, packed, handled, and stored as safely as possible to keep the risks of microbial food safety hazards at the minimal level. Good Agricultural Practices usually deal with preharvest practices (i.e., in the field), while GHPs cover postharvest practices, including packing and shipping. This 3-page fact sheet in the Food Safety on the Farm series covers GAPs and GHPs relating to traceback, or the ability to track food items, such as fresh produce, back to their source. This major revision was written by Jaysankar De, Christopher R. Pabst, Alexandra S. Chang, Renée M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs152
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices: Manure and Municipal Biosolids
Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) and Good Handling Practices (GHPs) encompass the general procedures growers, packers, and processors of fresh fruits and vegetables should follow to ensure the safety of their product. GAPs usually deal with pre-harvest practices (i.e., in the field), while GHPs tend to cover post-harvest practices, including packing and shipping. This 5-page entry in the Food Safety on the Farm series focuses on Good Agricultural Practices, including pathogen reduction and handling and application, to control potential hazards when working with manure and biosolids. This major revision was written by Jaysankar De, Christopher R. Pabst, Jessica Lepper, Renée M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs150
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Yersiniosis
 Yersiniosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia and is typically associated with the consumption of contaminated food or liquids. Yersiniosis is characterized by common symptoms of gastroenteritis such as abdominal pain and mild fever. The bacterium is prevalent in the environment, enabling it to contaminate water and food systems. Outbreaks of yersiniosis have been associated with improperly pasteurized milk, ready-to-eat salad mix, oysters, and more commonly with consumption of undercooked meals containing pork. Yersiniosis incidents have been reported frequently in Northern Europe, Scandinavia, and Japan, and rarely in the United States. However, the reported low incidence of Yersinia in the US food supply may be underestimated due to the long incubation time and misdiagnosis of patients with Y. enterocolitica infections, along with the inability to identify the source of infection and the fact that only serious cases are reported. This 4-page major revision, written by Christopher Pabst, Jaysankar De, Aswathy Sreedharan, Correy Jones, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, also describes long-term effects and complications of yersiniosis, members of the population most at risk, and prevention methods.
Yersiniosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia and is typically associated with the consumption of contaminated food or liquids. Yersiniosis is characterized by common symptoms of gastroenteritis such as abdominal pain and mild fever. The bacterium is prevalent in the environment, enabling it to contaminate water and food systems. Outbreaks of yersiniosis have been associated with improperly pasteurized milk, ready-to-eat salad mix, oysters, and more commonly with consumption of undercooked meals containing pork. Yersiniosis incidents have been reported frequently in Northern Europe, Scandinavia, and Japan, and rarely in the United States. However, the reported low incidence of Yersinia in the US food supply may be underestimated due to the long incubation time and misdiagnosis of patients with Y. enterocolitica infections, along with the inability to identify the source of infection and the fact that only serious cases are reported. This 4-page major revision, written by Christopher Pabst, Jaysankar De, Aswathy Sreedharan, Correy Jones, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, also describes long-term effects and complications of yersiniosis, members of the population most at risk, and prevention methods.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs193
The Food Recall Manual (Version 2)
Any business involved in the manufacture, processing, packing, holding, or delivery of food to humans needs to understand and address food recalls. When safety concerns arise with food you are manufacturing, you have a legal and ethical responsibility to mitigate any damage to the health and wellbeing of consumers. This manual details what you need to know to effectively understand and handle a food recall. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renee Goodrich-Schneider, Douglas A. Archer, Michelle D. Danyluk, George L. Baker, and Chris Thomas and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs108
HACCP: An Overview
HACCP is a food safety management system that is used in various segments of the food industry. The objectives of this 4-page fact sheet are to introduce the topic and to summarize the key components of a HACCP program. Written by J. A. Lepper, R. M. Goodrich-Schneider, K. R. Schneider, M. D. Danyluk and A. Sreedharan and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs122
The Food Safety Modernization Act of 2011-Final Rule for Preventive Controls for Human Food

This 7-page fact sheet is one in a series covering the different rules promulgated under the new Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), which was signed into law on January 4, 2011. It is intended to provide an overview of the final Preventive Controls for Human Food (PCHF) rule. Written by Jessica A. Lepper, Soohyoun Ahn, Keith R. Schneider, Michelle D. Danyluk, and Renee Goodrich-Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs301
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices-Sanitary Facilities
The Food Safety on the Farm series is a collection that reviews the generally recognized principles of GAPs (good agricultural practices) as they relate to produce, primarily at the farm level and with a particular focus on fresh Florida crops and practices. This publication focuses on GAPs and GHPs (good handling practices) relating specifically to sanitary facilities. Written by Jessica A. Lepper, Aswathy Sreedharan, Renee M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, January 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs159
Preventing Foodborne Illness: E coli "The Big Six"
This 7-page fact sheet is one in a series of fact sheets discussing common foodborne pathogens of interest to food handlers, processors, and retailers. It covers the characteristics of, and symptoms caused by, the bacterium E. coli (particularly the “big six” strains), and also details how to minimize the risk of spreading or contracting an E. coli infection. Written by Bruna Bertoldi, Susanna Richardson, Renee Goodrich-Schneider, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs233
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices-Packing Operation Sanitation
The ‘Food Safety on the Farm’ series is a collection that reviews the generally recognized principles of GAPs (good agricultural practices) as they relate to produce, primarily at the farm level and with a particular focus on fresh Florida crops and practices. This publication focuses on GAPs and GHPs (good handling practices) relating specifically to packing operation sanitation. Written by Jessica A. Lepper, Aswathy Sreedharan, Renee M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, December 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs189
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices-Worker Health and Hygiene

The ‘Food Safety on the Farm’ series is a collection that reviews the generally recognized principles of GAPs (good agricultural practices) as they relate to produce, primarily at the farm level and with particular focus on fresh Florida crops and practices. This 4-page publication focuses on GAPs and GHPs (good handling practices) relating specifically to worker health and hygiene. Written by Jessica A. Lepper, Keith R. Schneider, Renee M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Aswathy Sreedharan and published by the UF/IFAS Food Science and Human Nutrition Department, December 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs158
Food Safety on the Farm: Good Agricultural Practices and Good Handling Practices-Field Sanitation
The ‘Food Safety on the Farm’ series is a collection that reviews the generally recognized principles of GAPs (good agricultural practices) as they relate to produce, primarily at the farm level and with particular focus on fresh Florida crops and practices. This 4-page publication focuses on GAPs and GHPs (good handling practices) relating specifically to field sanitation. Written by Jessica A. Lepper, Aswathy Sreedharan, Renee M. Goodrich-Schneider, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs160
Food Allergies
A food allergy is a specific immune system reaction that happens after a person consumes what is normally considered a safe food. Reactions can range in severity from minor to fatal. This 4-page document discusses the cause, symptoms, and management of food allergies in children and adults. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renee Goodrich-Schneider, Soohyoun Ahn, Susie Richardson, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Bruna Bertoldi and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs123
Food Safety Tips for the Holiday Season
Food is always an important part of holiday festivities, but holiday meals can take a turn for the worse if food safety is not properly practiced when preparing and cooking the food. This 7-page factsheet provides information about safe food practices for the holidays. Written by Soohyoun Ahn, Jessica A. Lepper, and Keith R. Schneider and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs260
Preventing Foodborne Illness: Clostridium botulinum
Clostridium botulinum is the bacterium that causes botulism.This seven-page fact sheet describes the different types of botulism, the symptoms of botulism, the foods associated with botulism, and ways to prevent botulism. Written by Keith R. Schneider, Renée M. Goodrich Schneider, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Bruna Bertoldi and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs104
Preventing Foodborne Illness Associated with Clostridium perfringens
The bacterium Clostridium perfringens causes one of the most common types of foodborne gastroenteritis in the United States, often referred to as perfringens food poisoning. It is associated with consuming contaminated food that contains great numbers of vegetative cells and spores that will produce toxin inside the intestine. This six-page fact sheet describes the bacterium, outbreaks associated with it, and how to prevent illness from this bacterium. Written by Keith R. Schnedier, Renee Goodrich-Schneider, Ploy Kurdmongkoltham, and Bruna Bertoldi and published by the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs101