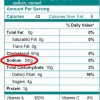
 El sodio es un mineral que se encuentra en la sal de mesa. Es necesario para mantener un balance de fluidos y el volumen de sangre. El consumo excesivo de sodio puede causar presión alta en la sangre e incrementar el riesgo de enfermedades del corazón y derrames cerebrales. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl y Lauren Foster, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
El sodio es un mineral que se encuentra en la sal de mesa. Es necesario para mantener un balance de fluidos y el volumen de sangre. El consumo excesivo de sodio puede causar presión alta en la sangre e incrementar el riesgo de enfermedades del corazón y derrames cerebrales. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl y Lauren Foster, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs211
Tag: Wendy Dahl
Preparation of Pureed Foods (FSHN1212/FS205)
 A puréed food is a food item that has been blended, mixed, or processed into a smooth and uniform texture. Examples of foods with a purée consistency include applesauce, pumpkin pie filling, and hummus. Puréed foods may be necessary for people with chewing and/or swallowing problems. For those requiring a puréed diet, it is important to provide a variety of foods. Almost any food can be puréed. However, some puréed foods may be much more acceptable than others. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Jamila R. Lepore, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
A puréed food is a food item that has been blended, mixed, or processed into a smooth and uniform texture. Examples of foods with a purée consistency include applesauce, pumpkin pie filling, and hummus. Puréed foods may be necessary for people with chewing and/or swallowing problems. For those requiring a puréed diet, it is important to provide a variety of foods. Almost any food can be puréed. However, some puréed foods may be much more acceptable than others. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Jamila R. Lepore, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs205
A Guide to Healthy Snacking for the Frail Older Adult (FSHN1219/FS214)
 Frail older adults face unique challenges that may lead to discouragement, decreased food consumption, and irregular eating patterns, which can further lead to various nutrient deficiencies. Simple, nutritious snacks that are easy to eat are a great way to add nutritious foods to their diet. This 3-page fact sheet provides several easy snack ideas. Written by Paula G. Harris-Swiatko and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Frail older adults face unique challenges that may lead to discouragement, decreased food consumption, and irregular eating patterns, which can further lead to various nutrient deficiencies. Simple, nutritious snacks that are easy to eat are a great way to add nutritious foods to their diet. This 3-page fact sheet provides several easy snack ideas. Written by Paula G. Harris-Swiatko and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs214
Pureed Foods, Thickened Beverages, and Water Needs (FSHN1301/FS218)
 Thickened liquids are often recommended for individuals who have problems swallowing thin liquids. Juice, milk, water, and even coffee can be thickened. Pre-thickened beverages are available commercially, or they can be prepared with various commercial thickeners. This 4-page fact sheet describes various consistencies of thickness, how much water various puréed foods contribute. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Thickened liquids are often recommended for individuals who have problems swallowing thin liquids. Juice, milk, water, and even coffee can be thickened. Pre-thickened beverages are available commercially, or they can be prepared with various commercial thickeners. This 4-page fact sheet describes various consistencies of thickness, how much water various puréed foods contribute. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs218
Shopping for Health: Fruit (FSHN1220/FS215)
 Fruits taste good, and they are good for you. Some fruits are very nutrient dense. This means they contain lots of the vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that your body needs to stay healthy. Whether you like fresh fruit or fruit juice, frozen fruit or fruit from a can, it’s important to choose a variety of different fruits every day. Here are some tips to help you before, during, and after your fruit shopping trip. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ashley R. Kendall and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Fruits taste good, and they are good for you. Some fruits are very nutrient dense. This means they contain lots of the vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that your body needs to stay healthy. Whether you like fresh fruit or fruit juice, frozen fruit or fruit from a can, it’s important to choose a variety of different fruits every day. Here are some tips to help you before, during, and after your fruit shopping trip. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ashley R. Kendall and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs215
Pureed Foods and Fiber (FSHN12-16/FS209)
 People with swallowing problems who require a puréed diet may not meet their recommended intake of fiber. But puréed diets can be planned to achieve fiber recommendations by choosing higher-fiber puréed foods often. And a variety of fiber ingredients are available that can be added to puréed foods. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2013.
People with swallowing problems who require a puréed diet may not meet their recommended intake of fiber. But puréed diets can be planned to achieve fiber recommendations by choosing higher-fiber puréed foods often. And a variety of fiber ingredients are available that can be added to puréed foods. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs209
Datos sobre las vitaminas (FCS8808S/FY1343)
 Las vitaminas son compuestos químicos que el cuerpo utiliza de muchas maneras. Nosotros necesitamos obtener las vitaminas en nuestra dieta porque nuestros cuerpos no las pueden crear. Existen 13 tipos de vitaminas que han sido identificadas como nutrientes importantes para los humanos. This 3-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
Las vitaminas son compuestos químicos que el cuerpo utiliza de muchas maneras. Nosotros necesitamos obtener las vitaminas en nuestra dieta porque nuestros cuerpos no las pueden crear. Existen 13 tipos de vitaminas que han sido identificadas como nutrientes importantes para los humanos. This 3-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1343
Datos sobre la niacina (FCS8669S/FY1340)
 La niacina es una de las vitaminas del grupo B (vitamina B3). Nuestro cuerpo necesita la niacina para usar los carbohidratos, las grasas y las proteínas. La niacina también se necesita para reparar el ADN y para el uso normal del calcio en el cuerpo. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
La niacina es una de las vitaminas del grupo B (vitamina B3). Nuestro cuerpo necesita la niacina para usar los carbohidratos, las grasas y las proteínas. La niacina también se necesita para reparar el ADN y para el uso normal del calcio en el cuerpo. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1340
Facts about Niacin (FCS8669/FY212)
 Niacin is one of the B vitamins (vitamin B3). Our bodies need niacin to use the energy in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Niacin also is needed for DNA repair and for the normal use of calcium in the body. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
Niacin is one of the B vitamins (vitamin B3). Our bodies need niacin to use the energy in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Niacin also is needed for DNA repair and for the normal use of calcium in the body. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy212
De compras para salud: Granos integrales (FSHN1013S/FS217)
 Los granos incluyen alimentos como el pan, la pasta, la avena, y las galletas. Cualquier alimento hecho con trigo, avena, arroz, maíz, cebada u otro cereal es considerado un grano. Sustituir los productos refinados por los de granos integrales puede ayudar con el manejo del peso y a disminuir el riesgo de enfermedades crónicas. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Food Science and Human Nutrition, and published by the UF Department of Wendy J. Dahl y Lauren Foster, January 2013.
Los granos incluyen alimentos como el pan, la pasta, la avena, y las galletas. Cualquier alimento hecho con trigo, avena, arroz, maíz, cebada u otro cereal es considerado un grano. Sustituir los productos refinados por los de granos integrales puede ayudar con el manejo del peso y a disminuir el riesgo de enfermedades crónicas. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Food Science and Human Nutrition, and published by the UF Department of Wendy J. Dahl y Lauren Foster, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs217
Datos sobre la riboflavina (FCS8668S/FY1344)
 La riboflavina es una de las vitaminas del grupo B. También es conocida como la vitamina B2. Nosotros necesitamos la riboflavina para utilizar los carbohidratos, grasas y proteínas en los alimentos que comemos. La riboflavina ayuda a utilizar estos nutrientes en energía para el cuerpo y para funciones como antioxidante. La riboflavina también se necesita para utilizar correctamente las vitaminas niacina, el ácido fólico y la vitamina B6. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
La riboflavina es una de las vitaminas del grupo B. También es conocida como la vitamina B2. Nosotros necesitamos la riboflavina para utilizar los carbohidratos, grasas y proteínas en los alimentos que comemos. La riboflavina ayuda a utilizar estos nutrientes en energía para el cuerpo y para funciones como antioxidante. La riboflavina también se necesita para utilizar correctamente las vitaminas niacina, el ácido fólico y la vitamina B6. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1344
Datos sobre los minerales (FCS8809S/FY1341)
 Los minerales son substancias como el calcio, el fósforo, el hierro y el zinc que se encuentran en las rocas y la tierra. También, se necesitan para tener una nutrición adecuada. Hay 16 minerales diferentes que sabemos que son necesarios en nuestra dieta. Varios otros minerales pueden ser necesarios en cantidades pequeñas. This 4-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
Los minerales son substancias como el calcio, el fósforo, el hierro y el zinc que se encuentran en las rocas y la tierra. También, se necesitan para tener una nutrición adecuada. Hay 16 minerales diferentes que sabemos que son necesarios en nuestra dieta. Varios otros minerales pueden ser necesarios en cantidades pequeñas. This 4-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1341
MyPlate for Dysphagia (FHSN1214/FS207)
 Resources and tools at ChooseMyPlate.gov that provide clear, actionable information about how to make better food choices can be easily adapted for persons with swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) that require texture-modified foods. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore, Nancy Gal, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2012.
Resources and tools at ChooseMyPlate.gov that provide clear, actionable information about how to make better food choices can be easily adapted for persons with swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) that require texture-modified foods. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore, Nancy Gal, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs207
Sensory Acceptability of Pureed Foods (FSHN1213/FS206)
 It is important that we enjoy the food we eat. This makes for a better quality of life. This is no different for those people needing to be on puréed diets due to swallowing problems. And just like you wouldn’t want to serve guests a recipe without trying it first, you don’t want to serve a puréed food without knowing that it is appealing. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
It is important that we enjoy the food we eat. This makes for a better quality of life. This is no different for those people needing to be on puréed diets due to swallowing problems. And just like you wouldn’t want to serve guests a recipe without trying it first, you don’t want to serve a puréed food without knowing that it is appealing. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs206
La aceptabilidad sensorial de los alimentos en pure (FSHN1213S/FS216)
 La evaluación sensorial es el proceso en el que utilizamos nuestros sentidos (gusto, olfato, tacto, vista) y su aplicación para la determinación de la aceptabilidad de los alimentos. ¡Simplemente, se están evaluando los alimentos para asegurarse que se ven, huelen y saben delicioso! This 6-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2012.
La evaluación sensorial es el proceso en el que utilizamos nuestros sentidos (gusto, olfato, tacto, vista) y su aplicación para la determinación de la aceptabilidad de los alimentos. ¡Simplemente, se están evaluando los alimentos para asegurarse que se ven, huelen y saben delicioso! This 6-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, December 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs216
Datos sobre la Tiamina (FCS8667S/FY1342)
 La tiamina es una de las vitaminas del grupo B. Es también llamada B1. Nosotros necesitamos tiamina para utilizar los carbohidratos que comemos. La tiamina ayuda a transformar los carbohidratos en energía para el cuerpo. El cuerpo también necesita tiamina para usar algunos de los aminoácidos que componen las proteínas. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
La tiamina es una de las vitaminas del grupo B. Es también llamada B1. Nosotros necesitamos tiamina para utilizar los carbohidratos que comemos. La tiamina ayuda a transformar los carbohidratos en energía para el cuerpo. El cuerpo también necesita tiamina para usar algunos de los aminoácidos que componen las proteínas. This 2-page fact sheet was written by R. Elaine Turner y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1342
Alimentos funcionales (FSHN1217S/FS213)
 Un alimento funcional es definido comúnmente como un alimento que proveen beneficios más allá de la nutrición básica proporcionada por dicho alimento. El beneficio adicional se debe a un componente en el alimento que ofrece beneficios físicos o biológicos, como por ejemplo, beneficios funcionales. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Amanda Ford y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
Un alimento funcional es definido comúnmente como un alimento que proveen beneficios más allá de la nutrición básica proporcionada por dicho alimento. El beneficio adicional se debe a un componente en el alimento que ofrece beneficios físicos o biológicos, como por ejemplo, beneficios funcionales. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Amanda Ford y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs213
Functional Foods (FSHN1217/FS210)
 A functional food is commonly defined as a food that provides benefits beyond the basic nutrition provided by that food. The additional benefit is due to a component in the food item that offers physical or biological benefits. As functional foods become increasingly popular in the U.S., it is important to be an informed shopper. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Amanda L. Ford and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
A functional food is commonly defined as a food that provides benefits beyond the basic nutrition provided by that food. The additional benefit is due to a component in the food item that offers physical or biological benefits. As functional foods become increasingly popular in the U.S., it is important to be an informed shopper. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Amanda L. Ford and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs210
Spoon Test for Pureed Food (FSHN1211/FS204)
 Puréed foods prepared for people with swallowing problems should meet the recommended textural guidelines. Proper texture is the priority when creating purées. A puréed food should have a uniform texture that is “spoon thick” and does not require chewing. It should not be too dry, sticky, lumpy, or thin. Adjustments in thickness may be made according to the individual’s specific needs. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Jamila R. Frazier, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
Puréed foods prepared for people with swallowing problems should meet the recommended textural guidelines. Proper texture is the priority when creating purées. A puréed food should have a uniform texture that is “spoon thick” and does not require chewing. It should not be too dry, sticky, lumpy, or thin. Adjustments in thickness may be made according to the individual’s specific needs. This 2-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Jamila R. Frazier, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs204
Ayude a su sistema digestivo: Entendiendo los probioticos (FSHN1111S/FS203)
 Los probióticos son conocidos como “bacterias buenas.” Frecuentemente cuando pensamos en las bacterias, pensamos en las que causan enfermedades. Aunque hay muchas bacterias que causan enfermedades, hay muchas otras que son benéficas para nuestra salud. Los probióticos son microorganismos vivos, los cuales cuando son administrados en cantidades adecuadas, proveen un beneficio para la salud. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Volker Mai, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs203
Los probióticos son conocidos como “bacterias buenas.” Frecuentemente cuando pensamos en las bacterias, pensamos en las que causan enfermedades. Aunque hay muchas bacterias que causan enfermedades, hay muchas otras que son benéficas para nuestra salud. Los probióticos son microorganismos vivos, los cuales cuando son administrados en cantidades adecuadas, proveen un beneficio para la salud. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Volker Mai, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, October 2012. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs203