 MiPlato es el ícono de los lineamientos alimentarios del Departamento de Agricultura de los Estados Unidos basado en las Guías Alimentarias del 2010 para los Estadounidenses. Es una imagen fácil de entender que se enfoca en la creación de un plato con alimentos saludables. Los recursos y herramientas en ChooseMyPlate.gov ofrece información clara y factible acerca de cómo escoger mejor alimentos que se pueden adaptar a personas con dificultades de deglución (disfagia) que requieren de alimentos con textura modificada. Aunque los alimentos magros y los alimentos bajos en grasa son recomendados, aquellos con dificultades de deglución pueden necesitar añadir la grasa a algunos alimentos para mejorar la aceptabilidad, la facilidad de deglución y también para ayudarlos a satisfacer sus necesidades de energía. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore, Nancy J. Gal, and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2013.
MiPlato es el ícono de los lineamientos alimentarios del Departamento de Agricultura de los Estados Unidos basado en las Guías Alimentarias del 2010 para los Estadounidenses. Es una imagen fácil de entender que se enfoca en la creación de un plato con alimentos saludables. Los recursos y herramientas en ChooseMyPlate.gov ofrece información clara y factible acerca de cómo escoger mejor alimentos que se pueden adaptar a personas con dificultades de deglución (disfagia) que requieren de alimentos con textura modificada. Aunque los alimentos magros y los alimentos bajos en grasa son recomendados, aquellos con dificultades de deglución pueden necesitar añadir la grasa a algunos alimentos para mejorar la aceptabilidad, la facilidad de deglución y también para ayudarlos a satisfacer sus necesidades de energía. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore, Nancy J. Gal, and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs223
Category: Health & Nutrition
Overweight and Weight Loss Maintenance (FSHN1304/FS226)
 For many people, weight loss is a chronic battle. Popular diets are often unsuccessful because they cannot be followed permanently. There is no magic diet to make you instantly shed pounds, but some good tips for steady, long-term weight loss are listed in this 2-page fact sheet written by Anne Mathews, Lauren Foster, and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2013.
For many people, weight loss is a chronic battle. Popular diets are often unsuccessful because they cannot be followed permanently. There is no magic diet to make you instantly shed pounds, but some good tips for steady, long-term weight loss are listed in this 2-page fact sheet written by Anne Mathews, Lauren Foster, and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs226
Shopping for Health: Herbs and Spices (FSHN1303/FS225)
 Herbs and spices have been used for hundreds of years in cooking and medicine. They add a wide range of flavors to food and may also provide health benefits. For some people, using herbs and spices in cooking may be a challenge, but it doesn’t have to be that way! The information below will get you on track to enjoying zesty, flavorful, healthy cooking.This 4-page fact sheet was written by Jenna A. Norris and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2013.
Herbs and spices have been used for hundreds of years in cooking and medicine. They add a wide range of flavors to food and may also provide health benefits. For some people, using herbs and spices in cooking may be a challenge, but it doesn’t have to be that way! The information below will get you on track to enjoying zesty, flavorful, healthy cooking.This 4-page fact sheet was written by Jenna A. Norris and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs225
Shopping for Health: A Menu for One (FSHN1302/FS224)
 In today’s busy world, many Americans find themselves cooking meals for one. Older adults and college students alike face the challenge of making meal preparation a priority when no one else is depending on them to create a balanced meal. Whether you pop a dish into the microwave after a busy day or spend time cooking a special meal for yourself, shopping for and preparing healthy, low-cost meals for one can be easy and enjoyable with just a little bit of planning. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Morgan Denhard and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2013.
In today’s busy world, many Americans find themselves cooking meals for one. Older adults and college students alike face the challenge of making meal preparation a priority when no one else is depending on them to create a balanced meal. Whether you pop a dish into the microwave after a busy day or spend time cooking a special meal for yourself, shopping for and preparing healthy, low-cost meals for one can be easy and enjoyable with just a little bit of planning. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Morgan Denhard and Wendy Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, February 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs224
Understanding Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease (FCS8028/FY1369)
 Several years ago, most people probably had never heard of gluten, but by 2011, gluten-free diets became more popular than low carbohydrate diets. One reason for this is the increased awareness and diagnosis of conditions in which gluten triggers an abnormal response in the body, such as gluten sensitivity and celiac disease. This 4-page fact sheet will help you learn about gluten sensitivity and celiac disease, as well as understand what they have in common and what is different about them. Written by Stephanie Meyer, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
Several years ago, most people probably had never heard of gluten, but by 2011, gluten-free diets became more popular than low carbohydrate diets. One reason for this is the increased awareness and diagnosis of conditions in which gluten triggers an abnormal response in the body, such as gluten sensitivity and celiac disease. This 4-page fact sheet will help you learn about gluten sensitivity and celiac disease, as well as understand what they have in common and what is different about them. Written by Stephanie Meyer, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1369
Choose MyPlate: Reduce Your Sodium (FCS80027/FY1360)
 Reducing sodium intake is one of the MyPlate recommendations for healthy eating. Most Americans eat more sodium than they need, which can have negative health effects. This publication provides facts about sodium and why reducing sodium intake is important. It also provides easy tips to reduce your sodium intake. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Ashley Hamm, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
Reducing sodium intake is one of the MyPlate recommendations for healthy eating. Most Americans eat more sodium than they need, which can have negative health effects. This publication provides facts about sodium and why reducing sodium intake is important. It also provides easy tips to reduce your sodium intake. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Ashley Hamm, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1360
Bottle-Feeding Your Baby (FCS80026/FY1359)
 Families choose to bottle-feed their babies for many reasons. While bottle-feeding is not difficult, you need to know several things to feed your baby safely and ensure that he or she receives the nutrition and bonding needed for proper growth and development. If you are considering bottle-feeding your baby or have decided that bottle-feeding is the best option for your situation, this publication will help you learn about bottle-feeding. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Sarah A. Schmidt, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
Families choose to bottle-feed their babies for many reasons. While bottle-feeding is not difficult, you need to know several things to feed your baby safely and ensure that he or she receives the nutrition and bonding needed for proper growth and development. If you are considering bottle-feeding your baby or have decided that bottle-feeding is the best option for your situation, this publication will help you learn about bottle-feeding. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Sarah A. Schmidt, Karla P. Shelnutt, and Gail P. A. Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1359
Choose MyPlate: Drink Water Instead of Sugary Drinks (FCS80025/FY1358)
 The regular consumption of sugary drinks has greatly increased over the past few decades. Most adults consume about 400 calories per day as beverages, and regular soda is the number one drink. The added sugars and calories in sugary drinks can really add up — so rethink what you drink! Use one or more of the tips provided to drink more water and get on the right track to living a healthier life. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jeanine Beatty, Karla Shelnutt, and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
The regular consumption of sugary drinks has greatly increased over the past few decades. Most adults consume about 400 calories per day as beverages, and regular soda is the number one drink. The added sugars and calories in sugary drinks can really add up — so rethink what you drink! Use one or more of the tips provided to drink more water and get on the right track to living a healthier life. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Jeanine Beatty, Karla Shelnutt, and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1358
Guia de merendar saludablemente para el adulto mayor fragil (FSHN1219S/FS222)
 El tomar decisiones inteligentes para la selección de las meriendas ayuda a asegurar que los adultos mayores frágiles satisfagan sus necesidades nutricionales. Estas son algunas meriendas sencillas y nutritivas que son apropiadas para los adultos mayores frágiles. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Paula G. Harris-Swiatko y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2013.
El tomar decisiones inteligentes para la selección de las meriendas ayuda a asegurar que los adultos mayores frágiles satisfagan sus necesidades nutricionales. Estas son algunas meriendas sencillas y nutritivas que son apropiadas para los adultos mayores frágiles. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Paula G. Harris-Swiatko y Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs222
Raising Healthy Children: Health Risks of Obesity (FCS80023/FY1356)
 Although babies need fat for warmth and normal growth, as children develop, too much fat can be unhealthy. Childhood obesity may result in health problems early in life and into adulthood. This 4-page fact sheet will help you understand the health risks of obesity and ways to help your child maintain a healthy weight. Written by Stephanie Meyer, Karla Shelnutt, and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
Although babies need fat for warmth and normal growth, as children develop, too much fat can be unhealthy. Childhood obesity may result in health problems early in life and into adulthood. This 4-page fact sheet will help you understand the health risks of obesity and ways to help your child maintain a healthy weight. Written by Stephanie Meyer, Karla Shelnutt, and Gail Kauwell, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, April 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy1356
Carbohydrate Counting: Meals for Diabetes (FSHN1218/FS212)
 “Carb” counting is a way to plan meals to help you maintain target blood glucose levels. Certain foods contain carbohydrate, and these are the foods that most influence your blood glucose. Your body needs carbohydrate in just the right amount. Not enough carbohydrate can lead to low blood glucose (hypoglycemia). Too much carbohydrate can lead to high blood glucose (hyperglycemia). This is why carb counting is a great tool to understand and practice because it can help you control your blood glucose and still give you the freedom to make varied food choices. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Cassie Rowe, Jamila R. Lepore, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
“Carb” counting is a way to plan meals to help you maintain target blood glucose levels. Certain foods contain carbohydrate, and these are the foods that most influence your blood glucose. Your body needs carbohydrate in just the right amount. Not enough carbohydrate can lead to low blood glucose (hypoglycemia). Too much carbohydrate can lead to high blood glucose (hyperglycemia). This is why carb counting is a great tool to understand and practice because it can help you control your blood glucose and still give you the freedom to make varied food choices. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Cassie Rowe, Jamila R. Lepore, and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs212
Pureed Foods: High Protein (FSHN1215/FS208)
 Protein is an important nutrient. Many older adults do not consume enough of this vital nutrient, crucial to overall health and well-being. For those with dysphagia and on a puréed diet, consuming sufficient protein is even more difficult. While a texture-modified diet may not be the diet of choice, the goal is to make it as appealing as possible so that the person consuming the purées can experience a better quality of life. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Protein is an important nutrient. Many older adults do not consume enough of this vital nutrient, crucial to overall health and well-being. For those with dysphagia and on a puréed diet, consuming sufficient protein is even more difficult. While a texture-modified diet may not be the diet of choice, the goal is to make it as appealing as possible so that the person consuming the purées can experience a better quality of life. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Jamila R. Lepore and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs208
De compras para la salud: Sodio (FSHN1006S/FS211)
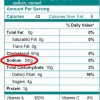 El sodio es un mineral que se encuentra en la sal de mesa. Es necesario para mantener un balance de fluidos y el volumen de sangre. El consumo excesivo de sodio puede causar presión alta en la sangre e incrementar el riesgo de enfermedades del corazón y derrames cerebrales. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl y Lauren Foster, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
El sodio es un mineral que se encuentra en la sal de mesa. Es necesario para mantener un balance de fluidos y el volumen de sangre. El consumo excesivo de sodio puede causar presión alta en la sangre e incrementar el riesgo de enfermedades del corazón y derrames cerebrales. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl y Lauren Foster, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs211
Preparation of Pureed Foods (FSHN1212/FS205)
 A puréed food is a food item that has been blended, mixed, or processed into a smooth and uniform texture. Examples of foods with a purée consistency include applesauce, pumpkin pie filling, and hummus. Puréed foods may be necessary for people with chewing and/or swallowing problems. For those requiring a puréed diet, it is important to provide a variety of foods. Almost any food can be puréed. However, some puréed foods may be much more acceptable than others. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Jamila R. Lepore, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
A puréed food is a food item that has been blended, mixed, or processed into a smooth and uniform texture. Examples of foods with a purée consistency include applesauce, pumpkin pie filling, and hummus. Puréed foods may be necessary for people with chewing and/or swallowing problems. For those requiring a puréed diet, it is important to provide a variety of foods. Almost any food can be puréed. However, some puréed foods may be much more acceptable than others. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Wendy J. Dahl and Jamila R. Lepore, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs205
Is Our Food Safe from Pesticides? (PI230)
 Growers of the food supply have adopted the use of integrated pest management (IPM) because it is no longer possible to rely solely on chemical pesticides to prevent unacceptable crop losses. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), IPM is the coordinated use of pest and environmental information and available pest control methods to prevent unacceptable levels of damage by the most economical means with the least possible hazard to people, property, and the environment. Scientific IPM strategies give the grower economic incentives for sustaining long-term crop protection with minimal disruption to the environment. The agricultural community typically will use pesticides sparingly as part of the IPM strategy whenever proven alternatives are not available for pest control. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Frederick M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2013.
Growers of the food supply have adopted the use of integrated pest management (IPM) because it is no longer possible to rely solely on chemical pesticides to prevent unacceptable crop losses. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), IPM is the coordinated use of pest and environmental information and available pest control methods to prevent unacceptable levels of damage by the most economical means with the least possible hazard to people, property, and the environment. Scientific IPM strategies give the grower economic incentives for sustaining long-term crop protection with minimal disruption to the environment. The agricultural community typically will use pesticides sparingly as part of the IPM strategy whenever proven alternatives are not available for pest control. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Frederick M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi230
A Guide to Healthy Snacking for the Frail Older Adult (FSHN1219/FS214)
 Frail older adults face unique challenges that may lead to discouragement, decreased food consumption, and irregular eating patterns, which can further lead to various nutrient deficiencies. Simple, nutritious snacks that are easy to eat are a great way to add nutritious foods to their diet. This 3-page fact sheet provides several easy snack ideas. Written by Paula G. Harris-Swiatko and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Frail older adults face unique challenges that may lead to discouragement, decreased food consumption, and irregular eating patterns, which can further lead to various nutrient deficiencies. Simple, nutritious snacks that are easy to eat are a great way to add nutritious foods to their diet. This 3-page fact sheet provides several easy snack ideas. Written by Paula G. Harris-Swiatko and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs214
EPA’s Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program (EDSP) (PI227)
 People have asked questions in recent years concerning the effects that certain chemicals may have on the endocrine system of humans and wildlife. Laboratory studies have produced evidence that show various chemicals disrupt the endocrine systems of animals. Other evidence has shown that the endocrine systems of certain fish and wildlife species have been affected by chemical contaminants. Do some of these same chemical contaminants also affect the human endocrine system? Do pesticides cause these effects? The relationship between human diseases of the endocrine system and exposure to environmental contaminants is poorly understood and controversial. This 2-page fact sheet discusses the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) screening program for potential effects to the endocrine system caused by pesticide exposure. Written by F.M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2013.
People have asked questions in recent years concerning the effects that certain chemicals may have on the endocrine system of humans and wildlife. Laboratory studies have produced evidence that show various chemicals disrupt the endocrine systems of animals. Other evidence has shown that the endocrine systems of certain fish and wildlife species have been affected by chemical contaminants. Do some of these same chemical contaminants also affect the human endocrine system? Do pesticides cause these effects? The relationship between human diseases of the endocrine system and exposure to environmental contaminants is poorly understood and controversial. This 2-page fact sheet discusses the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) screening program for potential effects to the endocrine system caused by pesticide exposure. Written by F.M. Fishel, and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pi227
Pureed Foods, Thickened Beverages, and Water Needs (FSHN1301/FS218)
 Thickened liquids are often recommended for individuals who have problems swallowing thin liquids. Juice, milk, water, and even coffee can be thickened. Pre-thickened beverages are available commercially, or they can be prepared with various commercial thickeners. This 4-page fact sheet describes various consistencies of thickness, how much water various puréed foods contribute. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Thickened liquids are often recommended for individuals who have problems swallowing thin liquids. Juice, milk, water, and even coffee can be thickened. Pre-thickened beverages are available commercially, or they can be prepared with various commercial thickeners. This 4-page fact sheet describes various consistencies of thickness, how much water various puréed foods contribute. Written by Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs218
Dealing with Picky Eaters (FAR8003/FM017)
 “There were motivations to eat that many baby boomers heard as they were growing up. Families across America were learning how to eat by the rules. But, according to current research, those rules may have done more harm than good…” This 2-page Family Album Radio transcript was written by Donna Davis, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2013.
“There were motivations to eat that many baby boomers heard as they were growing up. Families across America were learning how to eat by the rules. But, according to current research, those rules may have done more harm than good…” This 2-page Family Album Radio transcript was written by Donna Davis, and published by the UF Department of Family Youth and Community Sciences, February 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fm017
Shopping for Health: Fruit (FSHN1220/FS215)
 Fruits taste good, and they are good for you. Some fruits are very nutrient dense. This means they contain lots of the vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that your body needs to stay healthy. Whether you like fresh fruit or fruit juice, frozen fruit or fruit from a can, it’s important to choose a variety of different fruits every day. Here are some tips to help you before, during, and after your fruit shopping trip. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ashley R. Kendall and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
Fruits taste good, and they are good for you. Some fruits are very nutrient dense. This means they contain lots of the vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that your body needs to stay healthy. Whether you like fresh fruit or fruit juice, frozen fruit or fruit from a can, it’s important to choose a variety of different fruits every day. Here are some tips to help you before, during, and after your fruit shopping trip. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Ashley R. Kendall and Wendy J. Dahl, and published by the UF Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fs215