 Lernaea species, commonly known as “anchorworms,” are crustacean, copepod parasites that can infect and cause disease and mortality in many types of freshwater fishes, especially wild-caught and pond-raised species. Infestations with Lernaea are most prevalent in the summer months and occur more commonly in stagnant or slow-moving water bodies. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Natalie Steckler and Roy P. E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, December 2012.
Lernaea species, commonly known as “anchorworms,” are crustacean, copepod parasites that can infect and cause disease and mortality in many types of freshwater fishes, especially wild-caught and pond-raised species. Infestations with Lernaea are most prevalent in the summer months and occur more commonly in stagnant or slow-moving water bodies. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Natalie Steckler and Roy P. E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, December 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa185
Category: Aquaculture
Argulus (Fish Louse) Infections in Fish (FA184)
 Argulus species (Family: Argulidae), more commonly known as fish lice, are members of a large group of branchiuran parasites that infest and cause disease in fish. The argulids are crustaceans and are related to crabs, lobsters, and shrimp. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Natalie Steckler and Roy P. E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, November 2013.
Argulus species (Family: Argulidae), more commonly known as fish lice, are members of a large group of branchiuran parasites that infest and cause disease in fish. The argulids are crustaceans and are related to crabs, lobsters, and shrimp. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Natalie Steckler and Roy P. E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, November 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa184
Sturgeon Aquaculture: Specialized Techniques: Determining the Sex of Sturgeon by Direct Examination of the Gonad Using a Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedure (FA183)
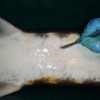 Because male sturgeon are harvested for meat at 2-4 years of age and females are retained for caviar production, being able to determine the sex of individual sturgeon has specific economical advantages. But it is difficult to tell females from males, especially when the fish are young (from hatch to 3 years old). This 5-page fact sheet describes the standard method and tools for determining the sex of sturgeon by direct examination of the gonad using a minimally invasive surgical procedure. Written by Frank A. Chapman and Joel P. Van Eenennaam, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, November 2012.
Because male sturgeon are harvested for meat at 2-4 years of age and females are retained for caviar production, being able to determine the sex of individual sturgeon has specific economical advantages. But it is difficult to tell females from males, especially when the fish are young (from hatch to 3 years old). This 5-page fact sheet describes the standard method and tools for determining the sex of sturgeon by direct examination of the gonad using a minimally invasive surgical procedure. Written by Frank A. Chapman and Joel P. Van Eenennaam, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa183
Spring Viremia of Carp (VM142/VM106)
 Spring viremia of carp is a viral disease that can cause significant mortality in several carp species including the common carp. It was reported in koi and feral carp in the United States for the first time in 2002. Diagnosis in farm raised fish in the U.S. may result in quarantine of the infected fish and depopulation. This 5-page fact sheet is intended to inform veterinarians, biologists, culturists, and hobbyists about Spring viremia of carp. Written by Barbara D. Petty, Ruth Francis-Floyd, and Roy P.E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, August 2012.
Spring viremia of carp is a viral disease that can cause significant mortality in several carp species including the common carp. It was reported in koi and feral carp in the United States for the first time in 2002. Diagnosis in farm raised fish in the U.S. may result in quarantine of the infected fish and depopulation. This 5-page fact sheet is intended to inform veterinarians, biologists, culturists, and hobbyists about Spring viremia of carp. Written by Barbara D. Petty, Ruth Francis-Floyd, and Roy P.E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, August 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm106
Aquatic Weeds: Crested Floating Heart (Nymphoides cristata) (SSAGR344/AG354)
Crested floating heart is a native of Asia, but was introduced to North America through the aquatic plant nursery trade and marketed as ‘snowflake.’ In the United States, crested floating heart escaped from cultivation and became established in Florida water bodies. Learn how to identify and manage this aquatic weed in this 5-page fact sheet written by Leif N. Willey and Kenneth A. Langeland and published by the UF Department of Agronomy, April 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ag354
Megalocytivirus Infections in Fish, with Emphasis on Ornamental Species (FA182)
Megalocytiviruses cause systemic infections that can result in moderate to heavy losses in many different species of freshwater and marine fishes in both cultured and wild stocks. This 8-page fact sheet was written by Roy P. E. Yanong and Thomas B. Waltzek, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, December 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa182
Lymphocystis Disease in Fish (FA181/FA181)
Lymphocystis is a chronic disease of freshwater and marine fishes caused by infection with an iridovirus known as Lymphocystivirus or Lymphocystis disease virus (LCDV). Infection results in the development of pebble or wart-like nodules most commonly seen on the fins, skin, or gills, although other tissues may be affected. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Roy P. E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, December 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa181
Viral Nervous Necrosis (Betanodavirus) Infections in Fish (FA180/FA180)
The betanodaviruses are an important, emerging group of viruses known to infect over 40 marine fish species worldwide. This 7-page fact sheet was written by Roy P. E. Yanong, and published by the UF Department of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, December 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa180
Sharks for the Aquarium and Considerations for Their Selection (FA179)
Sharks are magnificent animals and an exciting group of fishes. And they are becoming increasingly popular as pet animals. The proper care and display of sharks requires great attention to details. This 8-page fact sheet provides critical points aquarists must consider in deciding whether or not to include sharks in their aquaria. A table of the most popular sharks kept in public and home aquariums is provided to facilitate species selection. Written by Alexis L. Morris, Elisa J. Livengood, and Frank A. Chapman, and published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, December 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa179
FA178/FA178 Perkinsus Infections of Bivalve Molluscs
FA178, a 7-page fact sheet by Denise Petty, describes the infections caused by this group of protistan parasites that can infect shellfish — signs of infection in molluscs, life cycle, transmission, diagnosis, regulatory concerns, treatment and disinfection of facilities, and food safety. Includes references and glossary. Published by the UF Department of School of Forest Resources and Conservation, August 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa178
FA174 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: Spawning and Rearing Bivalve Molluscs–Spawning
FA174, a 9-page activity by R. Leroy Creswell, Cortney L. Ohs, Craig S. Kasper, Elisa J. Livengood, Amber L. Garr, Brian E. Myers, Carlos V. Martinez, and Frank A. Chapman, is activity 12 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 9-12, students will learn methods for spawning bivalve molluscs like clams or oysters using temperature manipulation. Students will use an ocular micrometer to measure the diameter of bivalve eggs and the length of bivalve larvae. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, May 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa174
FA172 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: What Makes a Good Fish Food?
FA172, a 5-page activity by Craig S. Kasper, Cortney L. Ohs, Brian E. Myers, Frank A. Chapman, Amber L. Garr, R. Leroy Creswell, Carlos V. Martinez, and Elisa J. Livengood, is activity 22 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 9-12, students will learn the common ingredients in fish food, design their own fish food, and discover how water stability relates to fish nutrition, production and the environment. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, July 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa172
FA173 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: Anatomy of a Fish
FA173, a 5-page activity by Amber L. Garr, Cortney L. Ohs, Craig S. Kasper, R. Leroy Creswell, Frank A. Chapman, Brian E. Myers, Elisa J. Livengood, and Carlos V. Martinez, is activity 1 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 5-12, students categorize types of fish, describe the basic biology of fish species, and identify the primary functions of anatomical features common to aquaculture. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, July 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa173
FA175 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: Spawning and Rearing Bivalve Molluscs — Larval Culture
FA175, a 4-page activity by R. Leroy Creswell, Cortney L. Ohs, Craig S. Kasper, Carlos V. Martinez, Elisa J. Livengood, Amber L. Garr, Frank A. Chapman, and Brian E. Myers, is activity 13 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 9-12, students learn to describe the reproductive biology and spawning of bivalve molluscs, leading to an understanding of the conditions used in hatcheries for commercial production of bivalve molluscs. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, July 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa175
FA176 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: Dancing with Brine Shrimp
FA176, a 7-page activity by Elisa J. Livengood, Cortney L. Ohs, Amber L. Garr, R. Leroy Creswell, Carlos V. Martinez, Craig S. Kasper, Brian E. Myers, and Frank A. Chapman, is activity 14 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 5-12, students will hatch and culture brine shrimp to observe the behavior and the different development stages of the organisms. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, July 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa176
FA177 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: Introduction
FA177, a 2-page fact sheet by Cortney L. Ohs, R. Leroy Creswell, Amber L. Garr, Carlos V. Martinez, Brian E. Myers, Elisa J. Livengood, Craig S. Kasper, and Frank A. Chapman, introduces the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. The curriculum is designed to engage students in aquaculture and the aquatic sciences through a series of hands-on activities involving all the sciences, mathematics, reading, and writing. Each activity in the series includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, July 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa177
FA169 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: Fish-Eating Contest
FA169, a 4-page activity by Amber L. Garr, Cortney L. Ohs, Brian E. Myers, Craig S. Kasper, R. Leroy Creswell, Frank A. Chapman, Carlos V. Martinez, and Elisa J. Livengood, is activity 2 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 5-12, students observe the external anatomy of fish to determine feeding behaviors and recommend an aquaculture diet based on their observations. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, May 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa169
FA170 Teach Aquaculture Curriculum: How Big Is That Pond?
FA170, a 5-page activity by Cortney L. Ohs, Amber L. Garr, R. Leroy Creswell, Elisa J. Livengood, Brian E. Myers, Carlos V. Martinez, Frank A. Chapman, and Craig S. Kasper, is activity 5 of the Teach Aquaculture Curriculum. In this activity for grades 5-12, students will learn to calculate the volume, surface area, stocking densities of fish, and chemical application amounts for various sizes of ponds. Includes student performance standards. Published by the UF School of Forest Resources and Conservation, Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, May 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa170
FE835 Economic Impacts of Alternative Regulatory Scenarios on the Florida Fresh Half-Shell Oyster Industry: A Study of Potential Outcomes
FE835, a 3-page executive summary of a report by K.L. Morgan, T.J. Stevens, R.L. Degner, S.L. Larkin, and C.M Adams, summarizes the results of a study to examine the economic impacts of possible closures of the fresh half-shell oyster market for varying time periods with the intention of protecting consumers from Vibrio vulnificus infections. Published by the UF Department of Food and Resource Economics, June 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fe835
FA168 Candidate Species for Florida Aquaculture: Pinfish, Lagodon rhomboides
FA168, a 6-page illustrated fact sheet by Cortney L. Ohs, Scott W. Grabe, Matthew A. DiMaggio, describes this marine baitfish of the Sparidae (porgy/sea bream) family which has potential for culture in the southeastern United States — general description, geographic distribution and habitat, nautral history, culture techniques, broodstock nutrition, broodstock reproduction, hatchery, nursery, growout, disease, and market. Includes references. Published by the UF Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, School of Forest Resources and Conservation, May 2010.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa168