 This 5-page fact sheet gives an overview of two methods for evaluating energy transformations in biofuels production. The Life Cycle Assessment approach involves measurements affecting greenhouse gases, which can be linked to the energy considerations used in the Emergy Assessment. Although these two methods have their basis in energy or greenhouse gas emission evaluations, their approaches can lead to a reliable judgment regarding a biofuel process. We can use them to evaluate the economic environmental component of a biofuel process, and decide which biofuel processes favor sustainability. The intended audiences of this publication are growers, researchers, students, and any other readers interested in agriculture and ecology. Written by J. Van Treese II, E. A. Hanlon, N. Y. Amponsah, J. L. Izursa, and J. C. Capece, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2013.
This 5-page fact sheet gives an overview of two methods for evaluating energy transformations in biofuels production. The Life Cycle Assessment approach involves measurements affecting greenhouse gases, which can be linked to the energy considerations used in the Emergy Assessment. Although these two methods have their basis in energy or greenhouse gas emission evaluations, their approaches can lead to a reliable judgment regarding a biofuel process. We can use them to evaluate the economic environmental component of a biofuel process, and decide which biofuel processes favor sustainability. The intended audiences of this publication are growers, researchers, students, and any other readers interested in agriculture and ecology. Written by J. Van Treese II, E. A. Hanlon, N. Y. Amponsah, J. L. Izursa, and J. C. Capece, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss579
Tag: Department of Soil and Water Sciences
Nutrient Cycling in Grazed Pastures (SL376/SS578)
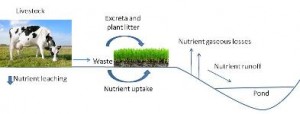 Many forage-based livestock production systems in Florida are characterized by extensive grazing with minimal inputs of commercial fertilizer and supplemental feed. In these systems, adequate soil fertility conditions are essential to sustain forage production. If nutrients become deficient, pasture and animal performance is reduced, and the economic returns of livestock operations may decline. This 3-page fact sheet discusses the different nutrient pathways in grazing pastures to help producers better understand how to promote nutrient cycling and pasture sustainability. Written by Maria L. Silveira, Joao M. B. Vendramini, Hiran M. da Silva, and Mariana Azenha, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, January 2013.
Many forage-based livestock production systems in Florida are characterized by extensive grazing with minimal inputs of commercial fertilizer and supplemental feed. In these systems, adequate soil fertility conditions are essential to sustain forage production. If nutrients become deficient, pasture and animal performance is reduced, and the economic returns of livestock operations may decline. This 3-page fact sheet discusses the different nutrient pathways in grazing pastures to help producers better understand how to promote nutrient cycling and pasture sustainability. Written by Maria L. Silveira, Joao M. B. Vendramini, Hiran M. da Silva, and Mariana Azenha, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss578
Salmonella y Escherichia coli enteropatogena en el ambiente de produccion de cultivos: fuentes potenciales, supervivencia y gestion (SL375Span/SS577)
 El objetivo de esta publicación EDIS es poner en evidencia los descubrimientos recientes que se enfocan en la ecología de los patógenos humanos en el área de producción de cultivo. Una mejor comprensión de cómo los patógenos persisten fuera de los huéspedes animales en el agua para la agricultura, en el suelo y en las plantas, tendrá grandes impactos en el manejo y procesamiento de los productos mismos, empezando desde el productor y hasta el consumidor. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Massimiliano Marvasi, Max Teplitski, Andrée George, and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2012.
El objetivo de esta publicación EDIS es poner en evidencia los descubrimientos recientes que se enfocan en la ecología de los patógenos humanos en el área de producción de cultivo. Una mejor comprensión de cómo los patógenos persisten fuera de los huéspedes animales en el agua para la agricultura, en el suelo y en las plantas, tendrá grandes impactos en el manejo y procesamiento de los productos mismos, empezando desde el productor y hasta el consumidor. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Massimiliano Marvasi, Max Teplitski, Andrée George, and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss577
Aquatic Toxicology Notes: Endothall (SL369/SS570)
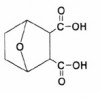 Endothall is the herbicidal active ingredient found in commercial formulations labeled for weed control in aquatic systems and on ditch banks. It is also used as a defoliant and desiccant in some terrestrial situations (e.g., in potato, hops, cotton, clover, and alfalfa production). This 7-page fact sheet introduces users of endothall to the physical, chemical, environmental, and ecological properties of this herbicidal active ingredient relative to the aquatic environment. Written by P. Chris Wilson and Jun Wu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
Endothall is the herbicidal active ingredient found in commercial formulations labeled for weed control in aquatic systems and on ditch banks. It is also used as a defoliant and desiccant in some terrestrial situations (e.g., in potato, hops, cotton, clover, and alfalfa production). This 7-page fact sheet introduces users of endothall to the physical, chemical, environmental, and ecological properties of this herbicidal active ingredient relative to the aquatic environment. Written by P. Chris Wilson and Jun Wu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss570
Aquatic Toxicology Notes: Diquat (SL368/SS569)
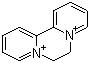 Diquat is applied directly to plants along ditch banks and within aquatic systems. It may also be applied to ponds, lakes, and drainage ditches to control algae and submersed aquatic weeds. This 7-page fact sheet introduces users of diquat to the physical, chemical, environmental, and ecological properties of this herbicidal active ingredient relative to the aquatic environment. Written by P. Chris Wilson and Jun Wu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
Diquat is applied directly to plants along ditch banks and within aquatic systems. It may also be applied to ponds, lakes, and drainage ditches to control algae and submersed aquatic weeds. This 7-page fact sheet introduces users of diquat to the physical, chemical, environmental, and ecological properties of this herbicidal active ingredient relative to the aquatic environment. Written by P. Chris Wilson and Jun Wu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss569
Florida Reclaimed Phosphate Mine Soils: Characteristics, Potential Uses, and Management Considerations (SL370/SS571)
 A critical nutrient for plant growth, phosphate helps sustain the world’s growing population. In 2010, seven mines in Florida produced approximately 10% of the world’s phosphate supply and more than 65% of the phosphate for the United States. But each year in Florida thousands of acres disturbed by strip-mining for phosphate rock must be reclaimed for other productive uses. This 11-page fact sheet provides a general characterization of the various soil types resulting from phosphate mine reclamation. Written by M. Wilson and E.A. Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
A critical nutrient for plant growth, phosphate helps sustain the world’s growing population. In 2010, seven mines in Florida produced approximately 10% of the world’s phosphate supply and more than 65% of the phosphate for the United States. But each year in Florida thousands of acres disturbed by strip-mining for phosphate rock must be reclaimed for other productive uses. This 11-page fact sheet provides a general characterization of the various soil types resulting from phosphate mine reclamation. Written by M. Wilson and E.A. Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss571
Salmonella and Pathogenic E. coli in the Crop Production Environment: Potential Sources, Survival, and Management (SL375/SS576)
 Over the last two decades, at least a dozen major outbreaks of gastroenteritis caused by non-typhoidal Salmonella or enterovirulent E. coli have been linked to the consumption of sprouts, nuts, and fresh (or minimally processed) fruits and vegetables. These outbreaks caught scientists and the public off guard because these pathogens were not previously considered “plant-associated.” This 3-page fact sheet highlights recent discoveries that focus on the ecology of human pathogens in the crop production environment. A better understanding of how pathogens persist outside of animal hosts in agricultural water, soils, and plants will have major impacts on managing produce safety from “farm to fork.” Written by Max Teplitski, Andree George, and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
Over the last two decades, at least a dozen major outbreaks of gastroenteritis caused by non-typhoidal Salmonella or enterovirulent E. coli have been linked to the consumption of sprouts, nuts, and fresh (or minimally processed) fruits and vegetables. These outbreaks caught scientists and the public off guard because these pathogens were not previously considered “plant-associated.” This 3-page fact sheet highlights recent discoveries that focus on the ecology of human pathogens in the crop production environment. A better understanding of how pathogens persist outside of animal hosts in agricultural water, soils, and plants will have major impacts on managing produce safety from “farm to fork.” Written by Max Teplitski, Andree George, and George Hochmuth, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, October 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss576
Carbon Sequestration in Grazing Land Ecosystems (SL373/SS574)
 Native and improved pastures play an important role in sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. Because of the relatively high sequestration rates and extensive area, grazing land represents an important component of terrestrial carbon dioxide (CO2) offset and is a significant sink for long-term carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas mitigation. This 4-page fact sheet contains information for stakeholders, students, scientists, and environmental agencies interested in enhancing ecosystems services provided by grazing lands. Written by Maria Silveira, Ed Hanlon, Mariana Azenha, and Hiran M. da Silva, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, September 2012.
Native and improved pastures play an important role in sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. Because of the relatively high sequestration rates and extensive area, grazing land represents an important component of terrestrial carbon dioxide (CO2) offset and is a significant sink for long-term carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas mitigation. This 4-page fact sheet contains information for stakeholders, students, scientists, and environmental agencies interested in enhancing ecosystems services provided by grazing lands. Written by Maria Silveira, Ed Hanlon, Mariana Azenha, and Hiran M. da Silva, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, September 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss574
Solutions for Managing Tomato Culls in Florida Tomato Packinghouses (SL371/SS572)
 Florida is the single largest producer of fresh-market tomatoes in the United States. Driven by urbanization and generation of large amounts of tomato culls, tomato packers in Florida often struggle to find ways to dispose of culls generated during the cleaning and sanitizing of tomatoes. This 5-page fact sheet provides guidelines for appropriate management practices to increase the use of culls produced in tomato packinghouses in Florida. Written by Gurpal Toor, Maninder Chahal, and Bielinski Santos, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, September 2012.
Florida is the single largest producer of fresh-market tomatoes in the United States. Driven by urbanization and generation of large amounts of tomato culls, tomato packers in Florida often struggle to find ways to dispose of culls generated during the cleaning and sanitizing of tomatoes. This 5-page fact sheet provides guidelines for appropriate management practices to increase the use of culls produced in tomato packinghouses in Florida. Written by Gurpal Toor, Maninder Chahal, and Bielinski Santos, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, September 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss572
Solutions for Managing Wastewater in Florida Tomato Packinghouses (SL372/SS573)
 A large amount of wastewater is produced in Florida's packinghouses during the cleaning and sanitizing of tomatoes. High transportation costs for off-site disposal and strict surface water discharge regulations are critical issues associated with the management of this wastewater. This 4-page fact sheet provides solutions for increasing the reuse of wastewater in tomato packinghouses in Florida. Written by Gurpal Toor, Maninder Chahal, and Bielinski Santos, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, August 2012.
A large amount of wastewater is produced in Florida's packinghouses during the cleaning and sanitizing of tomatoes. High transportation costs for off-site disposal and strict surface water discharge regulations are critical issues associated with the management of this wastewater. This 4-page fact sheet provides solutions for increasing the reuse of wastewater in tomato packinghouses in Florida. Written by Gurpal Toor, Maninder Chahal, and Bielinski Santos, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, August 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss573
Watersheds of Florida: Understanding a Watershed Approach to Water Management (SL367/SS568)
 Water is of primary importance to all life on earth. Freshwater is a finite resource, and managing freshwater requires an understanding of watersheds and a watershed approach. Both quantity and quality of water are important for balanced beneficial and efficient agricultural, industrial, rural, and urban uses. This 7-page fact sheet provides information on watersheds and introduces the watershed approach and management concept as practiced in the U.S., with a focus on Florida watersheds in particular. This document also provides information on the basins, basin groups, and hydrologic units of Florida used by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP) to implement watershed assessment, monitoring, and restoration programs. Written by Rao Mylavarapu, Kelley Hines, Thomas Obreza, and Greg Means, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, July 2012.
Water is of primary importance to all life on earth. Freshwater is a finite resource, and managing freshwater requires an understanding of watersheds and a watershed approach. Both quantity and quality of water are important for balanced beneficial and efficient agricultural, industrial, rural, and urban uses. This 7-page fact sheet provides information on watersheds and introduces the watershed approach and management concept as practiced in the U.S., with a focus on Florida watersheds in particular. This document also provides information on the basins, basin groups, and hydrologic units of Florida used by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP) to implement watershed assessment, monitoring, and restoration programs. Written by Rao Mylavarapu, Kelley Hines, Thomas Obreza, and Greg Means, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, July 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss568
Field Symptoms of Boron Toxicity and Deficiency in Florida Peanuts (SL366/SS567)
 Boron is an essential micronutrient needed by peanut to prevent “hollow heart” and to provide for sufficient plant growth, but it can be a challenge to manage for peanut production on sandy soils. There may be times when peanut growers, extension agents, and consultants find field symptoms when either boron toxicity or boron deficiency is the cause of peanut yield loss and low kernel quality. This 4-page fact sheet reviews the boron management strategy in Florida, presents information on boron sufficiency and toxicity levels from the literature, and provides photographs of field symptoms that can be used by growers and Extension agents. was written by J. W. Breman, W. D. Thomas, H. E. Jowers, and R. S. Mylavarapu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, May 2012.
Boron is an essential micronutrient needed by peanut to prevent “hollow heart” and to provide for sufficient plant growth, but it can be a challenge to manage for peanut production on sandy soils. There may be times when peanut growers, extension agents, and consultants find field symptoms when either boron toxicity or boron deficiency is the cause of peanut yield loss and low kernel quality. This 4-page fact sheet reviews the boron management strategy in Florida, presents information on boron sufficiency and toxicity levels from the literature, and provides photographs of field symptoms that can be used by growers and Extension agents. was written by J. W. Breman, W. D. Thomas, H. E. Jowers, and R. S. Mylavarapu, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, May 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss567
Landscape Diversity: Florida Phosphate Mine Pit Lakes (SL364/SS565)
 This 8-page fact sheet contains a synopsis of findings obtained through research, contrasted with limnological studies of natural lakes in central Florida. Written by M. Wilson and E.A. Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, May 2012.
This 8-page fact sheet contains a synopsis of findings obtained through research, contrasted with limnological studies of natural lakes in central Florida. Written by M. Wilson and E.A. Hanlon, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, May 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss565
Small-Scale Natural Wastewater Treatment Systems: Principles and Regulatory Framework (SL365/SS566)
 Natural systems use the natural processes of wetland ecosystems to both transform and hold on to many of the common pollutants that occur in household wastewater. This 8-page fact sheet briefly describes the principles and added benefits of natural systems. It then focuses on their use for treating small municipal wastewater flows from commercial and residential sites (i.e., septic systems or decentralized wastewater systems). Written by Kiara Winans, Shanin Speas-Frost, Mike Jerauld, Mark Clark, and Gurpal Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, May 2012.
Natural systems use the natural processes of wetland ecosystems to both transform and hold on to many of the common pollutants that occur in household wastewater. This 8-page fact sheet briefly describes the principles and added benefits of natural systems. It then focuses on their use for treating small municipal wastewater flows from commercial and residential sites (i.e., septic systems or decentralized wastewater systems). Written by Kiara Winans, Shanin Speas-Frost, Mike Jerauld, Mark Clark, and Gurpal Toor, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, May 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss566
Secuestro y Distribución de Carbono Orgánico del Suelo Bajo Diferentes Sistemas de Manejo de Pasturas (SL363/SS564)
 El secuestro de carbono en el suelo es el proceso de transformación del carbono del aire al carbono orgánico, almacenado en el suelo. A través del secuestro de carbono, los niveles de CO2 atmosférico pueden reducirse en la medida que los niveles de carbono orgánico del suelo aumentan. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Alejandra María Jimenez Madrid, José Trinidad Reyes Sandoval, and Maria L. Silveira, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, January 2012.
El secuestro de carbono en el suelo es el proceso de transformación del carbono del aire al carbono orgánico, almacenado en el suelo. A través del secuestro de carbono, los niveles de CO2 atmosférico pueden reducirse en la medida que los niveles de carbono orgánico del suelo aumentan. This 3-page fact sheet was written by Alejandra María Jimenez Madrid, José Trinidad Reyes Sandoval, and Maria L. Silveira, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, January 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss564
Engaging Youth in the Environment through the Florida Land Judging Program (SL362/SS563)
 The Florida 4-H/FFA Land Judging Contest is steeped in a tradition of enthusiastic participation, challenging science, and dynamic field conditions. Learn more in this 3-page fact sheet written by Amy L. Shober, L. Rex Ellis, Edward A. Hanlon, and Christine Wiese, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011.
The Florida 4-H/FFA Land Judging Contest is steeped in a tradition of enthusiastic participation, challenging science, and dynamic field conditions. Learn more in this 3-page fact sheet written by Amy L. Shober, L. Rex Ellis, Edward A. Hanlon, and Christine Wiese, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss563
How to Characterize Soil Variability in Florida Citrus Groves as It Relates to Tree Growth and Yield (SL556/SS557)
 Non-uniform tree growth and fruit yield are very common throughout many Florida citrus groves, but variable groves are typically managed as if they were uniform. This 4-page fact sheet provides information about the relationship between soil variability and citrus production, proposes recommendations for soil sampling that account for spatial variability, and suggests site-specific management practices for variable Florida citrus groves. Written by Kirandeep K. Mann, Arnold W. Schumann, Thomas A. Obreza, Willie G. Harris, and Jerry B. Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, January 2011.
Non-uniform tree growth and fruit yield are very common throughout many Florida citrus groves, but variable groves are typically managed as if they were uniform. This 4-page fact sheet provides information about the relationship between soil variability and citrus production, proposes recommendations for soil sampling that account for spatial variability, and suggests site-specific management practices for variable Florida citrus groves. Written by Kirandeep K. Mann, Arnold W. Schumann, Thomas A. Obreza, Willie G. Harris, and Jerry B. Sartain, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, January 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss557
Rules and Scorecard Grading Policies for the Annual Florida 4-H/FFA Land Judging Contest (SL144/SS195)
 This 11-page fact sheet outlines the rules of the annual Florida 4-H/FFA Land Judging Contest and guides participants in correctly completing the Land Judging and Homesite Evaluation scorecards. Written by Amy L. Shober, L. Rex Ellis, Christine Wiese, Edward A. Hanlon, Randy B. Brown, and J.H. Herbert, Jr., and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011.
This 11-page fact sheet outlines the rules of the annual Florida 4-H/FFA Land Judging Contest and guides participants in correctly completing the Land Judging and Homesite Evaluation scorecards. Written by Amy L. Shober, L. Rex Ellis, Christine Wiese, Edward A. Hanlon, Randy B. Brown, and J.H. Herbert, Jr., and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss195
Onsite Sewage Treatment and Disposal Systems: Trace Organic Chemicals (SL352/SS554)
 Trace organic chemicals are potentially harmful to human and ecosystem health. They frequently occur in wastewater from septic systems and can be found in concentrations orders of magnitude higher than typical concentrations reported in centralized treatment plant wastewater. This 7-page fact sheet identifies common trace organic chemicals of concern in wastewater and their sources, and summarizes current research on the fate and transport of these chemicals in septic systems. Written by Gurpal S. Toor, Mary Lusk, and Tom Obreza, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011. (photo CC BY-SA 3.0 Mila)
Trace organic chemicals are potentially harmful to human and ecosystem health. They frequently occur in wastewater from septic systems and can be found in concentrations orders of magnitude higher than typical concentrations reported in centralized treatment plant wastewater. This 7-page fact sheet identifies common trace organic chemicals of concern in wastewater and their sources, and summarizes current research on the fate and transport of these chemicals in septic systems. Written by Gurpal S. Toor, Mary Lusk, and Tom Obreza, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011. (photo CC BY-SA 3.0 Mila)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss554
An Overview of Nutrient Budgets for Use in Nutrient Management Planning (SL361/SS562)
 For professionals responsible for ensuring water quality, this 4-page fact sheet describes the types and limitations of nutrient budgets. Written by Amy L. Shober, George Hochmuth, and Christine Wiese, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011.
For professionals responsible for ensuring water quality, this 4-page fact sheet describes the types and limitations of nutrient budgets. Written by Amy L. Shober, George Hochmuth, and Christine Wiese, and published by the UF Department of Soil and Water Science, November 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss562