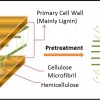
 This 4-page fact sheet discusses bioethanol as a renewable form of energy, explaining the importance of using ligno-cellulosic biomass to produce biofuels. It describes the pretreatment step in producing biofuels and the need for more research into this step so that ligno-cellulosic biofuels can be produced cheaply and efficiently at a commercial scale. Written by Zhaohui Tong, Nusheng Cheng, and Pratap Pullammanappallil, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, January 2013.
This 4-page fact sheet discusses bioethanol as a renewable form of energy, explaining the importance of using ligno-cellulosic biomass to produce biofuels. It describes the pretreatment step in producing biofuels and the need for more research into this step so that ligno-cellulosic biofuels can be produced cheaply and efficiently at a commercial scale. Written by Zhaohui Tong, Nusheng Cheng, and Pratap Pullammanappallil, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, January 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae495
Tag: Biomass
How Ethanol Is Made from Cellulosic Biomass (AE493)
 Ethanol can be derived from sugar-based, corn-based, and cellulose-based materials. Production of ethanol from sugar and corn is often viewed as competing with food production and increasing prices of food and fuel. But using non-edible cellulose-based biomass to produce ethanol minimizes competition with the food industry. This 4-page fact sheet provides a general overview of the production process for manufacturing ethanol from cellulosic biomass, including its constituents, conversion processes, and final products. Written by Zhaohui Tong, Pratap Pullammanappallil, and Arthur A. Teixeira, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, November 2012.
Ethanol can be derived from sugar-based, corn-based, and cellulose-based materials. Production of ethanol from sugar and corn is often viewed as competing with food production and increasing prices of food and fuel. But using non-edible cellulose-based biomass to produce ethanol minimizes competition with the food industry. This 4-page fact sheet provides a general overview of the production process for manufacturing ethanol from cellulosic biomass, including its constituents, conversion processes, and final products. Written by Zhaohui Tong, Pratap Pullammanappallil, and Arthur A. Teixeira, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, November 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae493
Bio-based Products from Biomass (AE483)
 Biomass is renewable biological materials, such as trees, plants, grasses, vegetables, algae, food wastes, animal manures, and other organic wastes. Like fossil fuels, biomass can produce a wide selection of bio-based by-products while producing renewable energy. Learn more in this 5-page fact sheet written by Zhaohui Tong, Letian Wang, and Clay B. Olson, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, September 2011.(AP photo/University of Florida/IFAS/Thomas Wright)
Biomass is renewable biological materials, such as trees, plants, grasses, vegetables, algae, food wastes, animal manures, and other organic wastes. Like fossil fuels, biomass can produce a wide selection of bio-based by-products while producing renewable energy. Learn more in this 5-page fact sheet written by Zhaohui Tong, Letian Wang, and Clay B. Olson, and published by the UF Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, September 2011.(AP photo/University of Florida/IFAS/Thomas Wright)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ae483