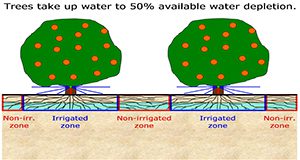
Water is a limiting factor in Florida citrus production due to non-uniform rainfall distribution and the low water-holding capacity of our sandy soils. Because periods of low rainfall coincide with critical stages of citrus production, additional irrigation is necessary to reduce the negative effects of water stress. This 6-page document covers recent findings on water use of trees affected by citrus greening and the impact this would have on irrigation management considerations. Written by Davie Kadyampakeni, Kelly Morgan, Mongi Zekri, Rhuanito Ferrarezi, Arnold Schumann, and Thomas A. Obreza and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Soil and Water Sciences, October 2017.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ss659
Tag: Irrigation and Soil-Water Relationship
Application of Surfactants in Commercial Crop Production for Water and Nutrient Management in Sandy Soil
 Water-repellent soils are unable to effectively adsorb or retain water. On these soils, water may simply pool on the surface or may move down preferred pathways, leaving large amounts of soil dry even when a large volume of water is applied. Thus, managing water and nutrients in sandy soils is often challenging. This 6-page fact sheet provides an overview of surfactants and how they may be used to better manage water and nutrients in sandy soils for vegetable and fruit production. Written by Guodong Liu, Monica Ozores-Hampton, Gene McAvoy, Ben Hogue, and Crystal A. Snodgrass, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2013.
Water-repellent soils are unable to effectively adsorb or retain water. On these soils, water may simply pool on the surface or may move down preferred pathways, leaving large amounts of soil dry even when a large volume of water is applied. Thus, managing water and nutrients in sandy soils is often challenging. This 6-page fact sheet provides an overview of surfactants and how they may be used to better manage water and nutrients in sandy soils for vegetable and fruit production. Written by Guodong Liu, Monica Ozores-Hampton, Gene McAvoy, Ben Hogue, and Crystal A. Snodgrass, and published by the UF Department of Horticultural Sciences, October 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/hs1230