Antibiotic-resistant microorganisms cause millions of illnesses and cost billions of dollars in the United States each year. This 5-page fact sheet written by Chad Carr, Matt Hersom, K. C. Jeong, Nicolas DiLorenzo, Jason Scheffler, Victoria Roberts, Gina Faniola, Stephanie Miller, Haley Denney, Nahilia Williams, and Bianca McCracken and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences discusses the use of antibiotics in cattle production operations and answers some common questions about antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant microorganisms.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an351
Tag: Matthew J. Hersom
Methods of Trace Mineral Supplementation
The forage cattle consume as the bulk of their diet is often deficient in trace mineral concentrations. Cattle producers can choose from a number of different methods to provide supplemental trace minerals to cattle. This 3-page document discusses several common ways to provide trace mineral supplements as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences, October 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an348
How to Measure Body Condition Score in Florida Beef Cattle
Body condition score (BCS) is both a good indicator of the past nutritional status of a cow and a way to determine future nutritional needs. The BCS technique is easy to learn and can help with management decisions. This new 5-page fact sheet discusses reasons to measure BCS, ways to evaluate BCS, and important assessment times. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences, August 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an347
How Much Does Bad Hay Cost a Beef Cattle Producer?
Everyone likes a good bargain, but when it comes to hay, low price often equates to low nutritional value. Because hay is often sold on a large round-bale basis, savings from the good bargain can decrease substantially if there is a negative impact on the cow herd nutritional program. This 4-page fact sheet discusses intake limitations, energy limitations, protein limitations, examples of hay quality, and bad hay’s impact on cow body condition. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF/IFAS Department of Animal Sciences, February 2018.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an339
Implications of Round Bale Dimensions on Hay Use
The dimensions of large round bales make a difference in many cases. Bale size determines the amount of hay in a purchased bale, the amount of nutrients in pounds, and the extent of spoilage during storage and feeding. Large round bales, the predominant form of hay made and fed to cattle, are under discussion. This 3-page fact sheet is a new document that examines the significance of bale dimensions, volume, density, and weight as well as the relationship of these factors to hay prices. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, June 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an326
How the Veterinary Feed Directive Affects Cattle Owners
The Veterinary Feed Directive is a federal regulation from the Food and Drug Administration that will change the additives that can be included in animal feed, the ways in which cattle producers manage their animals and veterinarians interact with cattle owners, and the products available for use on the ranch. This 3-page fact sheet provides an overview of the new regulation’s nature, functions, requirements, and implications for cattle owners. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, July 2016.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an327
Culling and Replacement Rate in the Beef Cow Herd
 Culling decisions are important to maintain the productivity and profitability of the beef cow herd. Culling of cows from the herd eliminates poorly performing cows, inferior genetics, and cows with quality defects that would limit short- and long-term productivity. This 4-page fact sheet discusses reasons to cull as well as replacement of culled cows. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2015.
Culling decisions are important to maintain the productivity and profitability of the beef cow herd. Culling of cows from the herd eliminates poorly performing cows, inferior genetics, and cows with quality defects that would limit short- and long-term productivity. This 4-page fact sheet discusses reasons to cull as well as replacement of culled cows. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an323
Shrink in Beef Cattle: A Marketing Consideration
 Shrink in beef cattle is weight loss that occurs between an animal’s departure from one location and weigh-in at another. Shrink in beef calves constitutes a potential economic loss to both the seller and the buyer if it is not fully considered. This 3-page fact sheet discusses factors that affect shrink and the effects of shrink on calf price. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2015.
Shrink in beef cattle is weight loss that occurs between an animal’s departure from one location and weigh-in at another. Shrink in beef calves constitutes a potential economic loss to both the seller and the buyer if it is not fully considered. This 3-page fact sheet discusses factors that affect shrink and the effects of shrink on calf price. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an322
Implications of Cow Body Condition Score on Productivity
Body condition score (BCS) indicates how much fat a cow has on its body, which is an important factor in cow health and reproductive capacity. Growers can use BCS to understand and manage the health of a herd and maintain a profitable operation. This 6-page fact sheet explains how BCS is measured, what different scores mean, the economic impact of various scores, and how changing cow nutrition can move BCS in a desired direction. Written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, September 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an319
Implants for Cow-Calf and Stocker Beef Cattle

Getting cattle to put on a lot of muscle quickly is a crucial part of a beef cattle operation’s profitability. Growth promoting implants are one of the most cost-effective ways of increasing lean tissue in cattle and work by releasing hormones into the cow’s body that encourage muscle growth. This 4-page fact sheet explains implants’ mechanisms of action, how implants are administered and used, and concerns associated with implants. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, August 2015.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an318
Cull Cow Beef Quality Issues series
 Cull cattle are those that are sold from a herd for lack of performance, lack of resources, or genetic improvement The non-fed beef cattle market (cattle that are not managed through traditional feedlot finishing systems) is comprised primarily of cull cows and bulls. To address liability and food safety concerns, this series of articles discusses some quality defects identified in the non-fed beef market, how to prevent them, and how to address them when they appear in cattle.
Cull cattle are those that are sold from a herd for lack of performance, lack of resources, or genetic improvement The non-fed beef cattle market (cattle that are not managed through traditional feedlot finishing systems) is comprised primarily of cull cows and bulls. To address liability and food safety concerns, this series of articles discusses some quality defects identified in the non-fed beef market, how to prevent them, and how to address them when they appear in cattle.
- Overview of Cull Cow Beef Quality Issues
- Injection Sites and Abscesses
- Horns, Ocular Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Lumpy Jaw
- Bruising, Condemnation, and Foreign Objects
- Cow Condition and Muscling
- Hide Defects, Contamination, and Non-Ambulatory Cattle
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/topic_series_cull_cow_beef_quality_issues
The Interaction of Nutrition and Health in Beef Cows
 In cattle, all physiological processes in the body, including the immune system, are influenced by the cattle’s nutritional status. Therefore, the past and present nutritional status serves as an immune function modulator in cattle that can influence the performance and reproduction of beef cattle. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Matt Hersom, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, June 2014.
In cattle, all physiological processes in the body, including the immune system, are influenced by the cattle’s nutritional status. Therefore, the past and present nutritional status serves as an immune function modulator in cattle that can influence the performance and reproduction of beef cattle. This 6-page fact sheet was written by Matt Hersom, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, June 2014.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an292
Does the Method of Castration Affect Calf Performance?
 This 4-page fact sheet discusses the purpose of castration in male calves as well as the different methods used to castrate. Most methods of castration cause a certain amount of pain and stress for calves, which can affect calf performance. UF/IFAS researchers recently tested different methods of castration in calves to determine the effects of each method on calf health and performance. This publication presents these results. Written by Trey Warnock, Matt Hersom, and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2013.
This 4-page fact sheet discusses the purpose of castration in male calves as well as the different methods used to castrate. Most methods of castration cause a certain amount of pain and stress for calves, which can affect calf performance. UF/IFAS researchers recently tested different methods of castration in calves to determine the effects of each method on calf health and performance. This publication presents these results. Written by Trey Warnock, Matt Hersom, and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an291
Effect of Age at Castration on Beef Calf Performance (AN289)
 A study in Florida was conducted to examine the issue of age at castration to determine if castration timing resulted in significant differences in growth rate and weaning weight in nursing calves. In addition, the study included a comparison between Angus and Brangus calves in the treatment groups to determine if there was a breed by castration effect. No differences in calf growth rates were observed in early compared to late castration. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Amie Imler, Todd Thrift, Matt Hersom, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, March 2013.
A study in Florida was conducted to examine the issue of age at castration to determine if castration timing resulted in significant differences in growth rate and weaning weight in nursing calves. In addition, the study included a comparison between Angus and Brangus calves in the treatment groups to determine if there was a breed by castration effect. No differences in calf growth rates were observed in early compared to late castration. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Amie Imler, Todd Thrift, Matt Hersom, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, March 2013.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an289
Food Processing: The Meat We Eat (AN283)
 Meat processing technology is used to produce many of the foods we enjoy, such as hot dogs, hamburgers, and chicken nuggets. Recently, the media has focused on certain meat products, giving them names such as “pink slime” and “meat glue.” The names of these products might have many people wondering what we are eating and how the meat we eat is produced. Part of being a good consumer is learning about what you eat, from how the food is made to whether the food is safe. This publication discusses the facts about meat processing so you can make knowledgeable decisions about the meat you eat. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Erica L. Bub, Keith Schneider, Chad Carr, and Matt Hersom, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2012.
Meat processing technology is used to produce many of the foods we enjoy, such as hot dogs, hamburgers, and chicken nuggets. Recently, the media has focused on certain meat products, giving them names such as “pink slime” and “meat glue.” The names of these products might have many people wondering what we are eating and how the meat we eat is produced. Part of being a good consumer is learning about what you eat, from how the food is made to whether the food is safe. This publication discusses the facts about meat processing so you can make knowledgeable decisions about the meat you eat. This 5-page fact sheet was written by Erica L. Bub, Keith Schneider, Chad Carr, and Matt Hersom, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an283
Application of Ionophores in Cattle Diets (AN285)
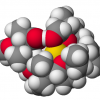 Beef cattle producers should consider using ionophores to increase calf gain and gain efficiency in a cost-effective manner. Ionophores are feed additives used in cattle diets to increase feed efficiency and body weight gain. They are compounds that alter rumen fermentation patterns. Ionophores can be fed to any class of cattle and can be used in any segment of the beef cattle industry. Similar to many other feed additives, ionophores are fed in very small amounts and supplied via another feedstuff as carrier for intake. Ionophores decrease incidence of coccidiosis, bloat, and acidosis in cattle. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2012.
Beef cattle producers should consider using ionophores to increase calf gain and gain efficiency in a cost-effective manner. Ionophores are feed additives used in cattle diets to increase feed efficiency and body weight gain. They are compounds that alter rumen fermentation patterns. Ionophores can be fed to any class of cattle and can be used in any segment of the beef cattle industry. Similar to many other feed additives, ionophores are fed in very small amounts and supplied via another feedstuff as carrier for intake. Ionophores decrease incidence of coccidiosis, bloat, and acidosis in cattle. This 4-page fact sheet was written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, December 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an285
Utilization of Cull Vegetables as Feedstuffs for Cattle (AN280)
 Cull vegetables can be an economical source of nutrients in beef cattle diets. They may be offered to beef cattle producers at a decreased cost or no cost. This 3-page fact sheet discusses the nutrient content and characteristics that need to be understood when utilizing cull vegetables. Written by Courtney Davis, Lindsey Wiggins, and Matt Hersom, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, August 2012.
Cull vegetables can be an economical source of nutrients in beef cattle diets. They may be offered to beef cattle producers at a decreased cost or no cost. This 3-page fact sheet discusses the nutrient content and characteristics that need to be understood when utilizing cull vegetables. Written by Courtney Davis, Lindsey Wiggins, and Matt Hersom, and published by the UF Department of Animal Sciences, August 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an280
Factors that Affect Calf Selling Price at Marketing (AN278)
 There are differences between the real and perceived reasons that cattle buyers discount calves; cattle producers can control some reasons for price differentials, but they cannot control all of them. This 4-page fact sheet will review some of the attributes that affect market calf price and overall value. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, May 2012.
There are differences between the real and perceived reasons that cattle buyers discount calves; cattle producers can control some reasons for price differentials, but they cannot control all of them. This 4-page fact sheet will review some of the attributes that affect market calf price and overall value. Written by Matt Hersom and Todd Thrift, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, May 2012.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an278
Strategies for Cost-Effective Supplementation of Beef Cattle (SSANS14/AN085)
 Forage should provide the majority of the nutrition for the beef herd. Seasonal forage growth and changes in forage quality challenge most cattle managers to provide adequate nutrition at reasonable costs. This 6-page fact sheet gives several alternatives to consider in your cow-calf production system. Written by Matt Hersom and W.E. Kunkle, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, October 2011.
Forage should provide the majority of the nutrition for the beef herd. Seasonal forage growth and changes in forage quality challenge most cattle managers to provide adequate nutrition at reasonable costs. This 6-page fact sheet gives several alternatives to consider in your cow-calf production system. Written by Matt Hersom and W.E. Kunkle, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, October 2011.
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an085
Comparison of Hay or Round Bale Silage as a Means to Conserve Forage (AN266)
 Florida’s climate makes conserving forages for later feeding challenging. Traditional hay harvest systems require optimal cutting, drying, and baling weather conditions. The use of round bale silage overcomes several of the challenges to hay production in Florida and offer an attractive compliment to traditional hay harvest systems. Learn more in this 6-page fact sheet written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, August 2011. (Photo: Thomas Wright, UF/IFAS)
Florida’s climate makes conserving forages for later feeding challenging. Traditional hay harvest systems require optimal cutting, drying, and baling weather conditions. The use of round bale silage overcomes several of the challenges to hay production in Florida and offer an attractive compliment to traditional hay harvest systems. Learn more in this 6-page fact sheet written by Matt Hersom, Todd Thrift, and Joel Yelich, and published by the UF Department of Animal Science, August 2011. (Photo: Thomas Wright, UF/IFAS)
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/an266





